- Books Name
- A TEXT OF BIOLOGY - CLASS XII
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Biology
PARTURITION
The gestation period of the human is about 38 weeks/266 days followed by birth. The process of giving birth to a baby is called parturition.
It starts with rise in estrogen/progesterone ratio, increase in the level of oxytocin secretion by both, mother and foetus.
It includes 3 stages.
1. Dilation Stage:
The uterine contraction starts from top and occur at long intervals (once every thirty minutes). This forces the baby to push its head against cervix.
As a result, cervix gets dilated with vagina also showing similar dilation. Dilation of cervix increases the stimulus for oxytocin secretion, further increasing the strength and frequency of contractions (1-3 every minute).
With continued powerful contractions, the amnion ruptures and the amniotic fluid flows out through vagina.
2. Expulsion Stage:
With further increase in the intensity of uterine and abdominal contraction, the baby comes out through cervix and vagina with head coming out first.
It may take 20 -60 min. Umbilical cord is cut. The infant's lungs expand and it begins breathing. This requires a major switch over in the circulatory system.
Blood flow through the umbilical cord ductus arteriosus and foramen ovale ceases; the adult pattern of blood flow through the heart, aorta and pulmonary arteries begins.
In some infants, the switch over is incomplete, and blood flow through the pulmonary arteries is inadequate. Failure to synthesise enough nitric oxide (NO) is one cause.
3. After Birth:
Within 10-15 minutes after delivery, the placenta and the remains of the umbilical cord which is called 'after birth' is expelled out.
LACTATION
Although estrogen and progesterone are essential for the physical development of the breasts during pregnancy, a specific effect of both these hormones is to inhibit the actual secretion of milk. Conversely, the hormone prolactin has exactly the opposite effect on secretion: promotion of milk secretion.
This hormone is secreted by the mother's anterior pituitary gland and its concentration in her blood rises steadily from the fifth week of pregnancy until birth of the baby, at that time it has risen to 10 to 20 times the normal nonpregnant level.
In addition, the placenta secretes large quantities of human chorionic somatomammotropin, which probably also has lactogenic' properties, thus supporting the prolactin from the mother's pituitary during pregnancy.
The fluid that is secreted in the last few days before and first few days after parturition is called colostrum, it contains essentially the same concentrations of proteins and lactose as milk but almost no fat.
Ejection (or "Let-Down") Process in Milk Secretion
Milk is secreted continuously into the alveoli of the breasts, but milk does not flow easily from the alveoli into the duct system and, therefore, does not continually leak from the breast nipples.
Instead, the milk must be ejected from the alveoli into the ducts before the baby can obtain it. This is caused by a combined neurogenic and hormonal reflex that involves the posterior pituitary hormone oxytocin.
When the baby suckles, sensory impulses are transmitted through somatic nerves from the nipples to the mother's spinal cord and then to her hypothalamus, there causing nerve signals that promote oxytocin secretion at the same time they cause prolactin secretion.
The oxytocin is carried in the blood to the breasts, where it causes myoepithelial cells (that surround the outer walls of the alveoli) to contract, thereby expelling the milk from the alveoli into the ducts.
Summary of Human Pregnancy from Fertilization to Birth of the Baby

Concept Builder
Types of Placenta
(a) On the basis of structure, the placentae are of following types:
(i) Epitheliochorial - Placenta with all the six barriers between foetal and maternal blood; e.g. Horse, Ass.
(ii) Syndesmochorial - Uterine epithelium breaks down; only five barriers left; e.g. Cow, Buffalo, Sheep, Goat, Camel.
(iii) Endotheliochorial - Uterine epithelium and connective tissue eroded; only four barriers left; e.g. Tiger, Lion, Cat, Dog.
(iv) Haemochorial - Placenta with only three barriers, the maternal part of placenta eroded; e.g. Human, Ape, Lemurs.
(v) Haemo-endothelial-All barriers except endothelium of foetal part of placenta get eroded e.g. Rat, Rabbit.
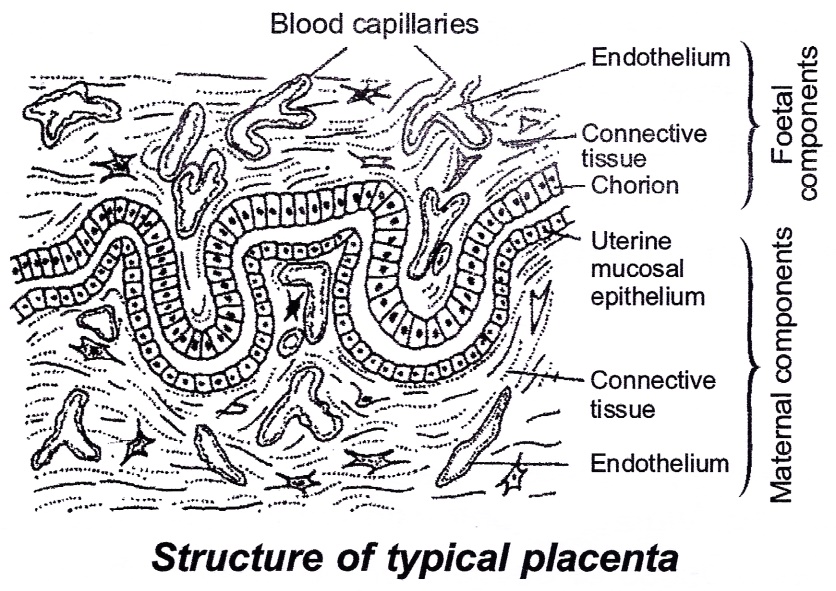
(b) On the basis of nature of uterine wall after parturition, the placenta may be :
(i) Non-deciduous-no part of uterine portion of placenta is broken off, e.g. Horse, Ass.
(ii) Deciduous-a portion of uterine tissue called decidua is detached and passed out at birth, e.g. most of the mammals.
(iii) Contra deciduous – even the foetal part of placenta is retained and gets absorbed to provide nourishment, e.g. Talpa, Parameles.
(c) On the basis of distribution of villi on the surface, the placentas are categorised into six types :
(i) Diffuse placenta-Villi distributed uniformly all over the surface. e.g. Horse, Pig .
(ii) Cotyledonary-the villi form tufts which fit into corresponding areas, the caruncles in uterine part of placenta, e.g.' Cow, Buffalo, Sheep.
(iii) Intermediate-villi occur singly as well as in tufts, e.g. Camel, Giraffe
(iv) Zonary-villi arranged in two transverse bands, e.g. Tiger, Lion, Cat, Dog, Elephant.
(v) Discoidal-When the villi are confined to a disc-like area, e.g. Rat, Rabbit, Bat.
(vi) Metadiscoidal-The placenta in which the villi are initially distributed uniformly all over the surface but later on get confined to a disc-like area fitting into a corresponding depression on the uterine wall. That is, the placenta is diffuse at first but later on becomes discoidal, e.g. Human beings and Apes.
Concept Builder
1. Amenorrhoea: Non occurrence of menses.
2. Inguinal hernia: Protrusion of intestinal loop into scrotum
3. Spontaneous ovulator : Ovulation with any external induction.
4. Orchidectomy: Removal of testes. It produces eunuchs.
5. Induced ovulator : Ovulation after copulation e.g., Rabbit.
6. Hysterectomy: Surgical removal of uterus.
7. Unejaculated sperms: Sperm production is a continuous process. unejaculated sperms are absorbed in vas deferens.
8. Corpus luteum : Persists for two weeks in case of non-pregnancy and four months when pregnancy has taken place.
9. Cryptorchidism: Failure of testes to descend in to scrotum.
10. Spermatogenesis takes about 74 days.
11. Androgenesis: Development in which the embryo has only paternal chromosomes, male parthenogenesis.
12. Gynogenesis : Development in which the embryo has only female chromosomes, female parthenogenesis.
13. Mictic females produce: haploid eggs which can be fertilized by males. Amictic females produce diploid eggs which develop parthenogenetically. A diploid egg may be produced by -autofertilization (polar body fuses with secondary oocyte) or Restitution: Chromosomes of both secondary oocyte and polar bodies arrange at equator during 1st cleavage e.g. hymenopterans (bees and wasps)
14. Paras: Fertile, can have pregnancy
15. Nulliparous: Women with no children
16. The most common method by which a baby comes out at parturition is left anterior oblique with head coming out first.
17. Fetal hemoglobin differs from adult hemoglobin because it has and chains. It has higher affinity for O2 and shifts HbO2 dissociation curve to left.
18. 1st Menses is called menarche while the onset of menses and development of secondary sexual characters is called puberty. Dysmenorrhoea - painful menses.
19. In the three trimesters of preganancy. (0-12 weeks 12-22 weeks and 22-28 weeks) if the baby dies from 0-22 weeks by natural or man-made causes it is called abortion because embryo is not called viable.
20. After 20-22 weeks abortion is banned in India.
21. The number of eggs at the time of birth in a young female undergoes drastic reduction by a process called atresia.
22. Gynandromorphs: An individual possessing both male and female parts.
23. Menopause: Stopping of menses, average age 51 years. Post menopausal effects includes increased risk to heart attack due to decreased estrogens, hot flushes, irritability, fatigue, anxiety decreased strength of bones.
24. Implantation takes place in 7 days. Conceptus remains in fallopian tube for 3-4 days and then by 7-9 days implantation occurs.
25. Vasectomy : Cutting of vas deferens.
26. Gynaecomastia: Males developing breasts due to hormonal imbalances.
Gestation: The period of development of the young in the womb of the mother is called gestation. Maximum weight gain and maximum growth rate of foetus takes place between 7-9 months of pregnancy.
27. Human Egg 0.1 mm in diameter or 100 µm.
28. Human sperm 0.06 mm or 60 µm long
29. Largest sperm 5.8 cm (20 times longer than the body of fly) in Drosophila bifurca.
30. Ectopic Pregnancy : It is the growth of the foetus outside the uterus, commonly inside the fallopian tube. Hence also called as tubal pregnancy. By 6th week as growing foetus may cause rupturing of fallopian tube hence its immediate surgical removal.
31. Animal cloning: First performed by Willmut and Campbell (1997). The first cloned animal was sheep Dolly (Feb. 13, 1997). Egg cell was taken out when maturation promoting factors (MPF) were maximum. It was denucleated. A nucleus from udder cell arrested in non-dividing growth phase (GP) by serum starvation was inserted in the denucleated egg.
32. Spermatozoa of turbellarians and Ascaris (nematode) and sporozoans lack acrosome.
33. Non flagellate sperms are found in Ascaris, Procambarus (Crayfish) Callinectes (blue crab).
34. Biflagellate spermatozoa are found in Opsanus (toad fish)
35. Ascaris megalocephola univalens shows the process of chromosome dimunition. In these spiral clevage of egg takes place and each cell except the one giving rise to gametes looses a part of chromosome set. Other e.g. -Gall midges (Mayetiola) and fungus grats (Wachtiella)
36. Compact ovaries are found in -cyclostomes, elasmobranchs, osteichthyes fishes, reptiles, birds and mammals.
37. Saccular ovaries are found in amphibians.
38. Lampbrush chromosomes : Found in oocytes of amphibians. They resemble the brushes used to clean the chimneys in London. They store extra information for survival of egg. They consist of two homologous chromosomes held together at chiasmata present in (diplotene) prophase cell stage
39. Polytene chromosomes : Found in the interphase stage of cells of salivary glands of chromosomes of Drosophila larvae. They exhibit gene amplification.
40. Fecundity: Animals potential capability to produce off springs.
41. Fertility -Animal's actual capability to conceive or induce conception.
42. Precocial young ones: ungulates and jackrabits -hair and open eyes, ability to move around.
43. Altricial: young ones are naked blind and helpless.
44. Estrous cycle: When females are most receptive to male (not in man) -phases -Estrus -Metaestrus -Diestrus -Proestrus. It occurs in non-primates.
45. Rut cycle: Testicular activity in the majority of mammals, is a seasonal event as is the associated period of sexual excitement.
46. F.R. Lillie gave the fertilization theory. Fertilizin of egg of one species locks with antifertilizin of same species (1914).
47. Sperms are decapacitated in epididymis where they mature. They are recapacitated in vaginal fluid / uterus.
48. Spermetogensis : Is the process of formation of haploid sperm from the diploid primary spermatocyte in the testis.
49. Spermiogenesis : Is the process of transformation of haploid spermatid to the functional sperm.
50. Spermiation : Is the process of releasing the mature sperms from the semniferons tubuels.
51. Insemination : Is the process of introduction of sperms (or semen) in the female reproductive system.
52. Semination : Is the process of ejaculation of semen from the male reproductive system.
53. Menarche : Is the process of start of menstrual cycle in the life of a female human at puberty.
54. Follicular phase : Primary follicles in the ovary grow to become mature follicle (Graafian follicle).
55. Luteal phase : The process of transformation of ruptured Graafian follicle into corpus luteum.
56. Capacitation : Is the process of activation of sperms in the female reproductive system after their ejaculation into it.

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
