- Books Name
- A TEXT OF BIOLOGY - CLASS XII
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Biology
BIOGEOGRAPHICAL EVIDENCES
The study of patterns of distribution of animals and plants in different parts of the earth is called Biogeography.
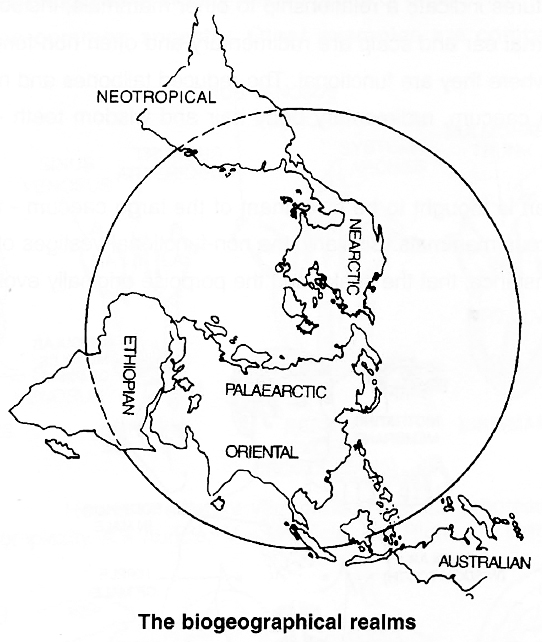
Alfred Russel Wallace (1823 -1913) divided the whole world into six major biogeographical regions or realms.
1. Palaearctic : Europe and Asia north of the tropics, north-western corner of Africa, including the Atlas Mountains.
2. Nearctic : North America exclusive of the tropics, Alaska, Canada, United States and Mexico.
3. Neotropical : Central America including low lands of Mexico, islands of the Caribbean and all of South America.
4. Ethiopian Africa (with exception of the Atlas Mountains), Madagascar and adjacent islands.
5. Oriental Tropical part of Asia (including India) south of the Himalaya Mountains and eastward through Sumatra, Java, Borneo and the Philippines.
6. Australian Australia, Tasmania, New Guinea and all islands of the Indonesian archipelago that lie east of Borneo, beginning with Celebes.
Biogeographic map of the world is that in which the six major biogeographic realms are present.
Geologists believe that millions of years ago, all the continents we demarcate today, were in the form of a single land mass.
On account of geological changes, especially movements of crustal plates below the surface of the earth, huge land masses broke off and drifted apart from one another.
As these land masses (continents) moved away, the seas separated them and acted as barriers to the free movement of organisms among the continents.
Because of variable environmental conditions prevailing on the different continents, over centuries, plants and animals evolved independently in each biogeographical region.
Concept Builder
India falls under Oriental realm. Two geographical regions separated by a high mountain ranges are Palaearctic and Oriental.
Consider, for example, two instances which show similarities in the pattern of distribution of plants and animals between two land masses which were once part of a larger land mass.
1. The flora and fauna on each of the Galapagos Island -a chain of 22 islands in the Pacific ocean on the west coast of South America resemble those of the South American mainland with which the Galapagos Islands were once connected.
2. Magnolias, Tulips and Sassafras are found naturally growing in the eastern USA and in China. Hence, these show disjunct distribution which means that these flora have different groups that are related but widely separated geographically.
The distribution pattern of the present-day animals and plants as well as the distribution of fossils are best explained on the basis of the theory of evolution.
The birds in Galapagos Islands show differences in bills and feeding habits.
The bills of several of these species resemble those of different, distinct families of birds on the mainland.
All these birds are thought to have evolved from a single common ancestor.

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
