






NON-PROFIT ORGANISATION
MEANING & CHARACTERISTICS
Organizations are of two types: - profit-making & non-profit making. Profit-making organizations operate with the main objective of earning profit. But there are organizations whose objective is not to earn profit but to render services. These organizations are called non-profit making organizations. The services are rendered to its own members or to the society at large. The main objective of such organizations may be social, educational, religious, or charitable. The surplus arising from rendering services is not distributed among its members by way of dividends or share of profit but utilized for the furtherance of the objective of the organization—examples of non-profit making organizations are clubs, societies, schools, colleges, hospitals, charitable trusts etc.
Features of non-profit making ORGANISATIONS:
The features of non-profit making organizations are as follows:
1. Service motive – Unlike profit-making organizations, the non-profit making organization operates with the motive to serve the people of the society.
2. Separate identity – The non-profit making organizations have separate legal entities.
3. Form of organization – Such organizations function in the form of schools, colleges, hospitals, clubs, societies, charitable trusts etc.
4. Utilisation of surplus – The excess revenue earned over the cost incurred in the process of rendering services is not distributed among its members. Rather it is utilized for achieving the objective of serving society.
5. Financing – Non-profit making organizations cannot financially operate only by receiving revenue from rendering services. Therefore, it receives donations either from members or outsiders to finance the cost of rendering services.
6. Budget – Each non-profit organization prepares an annual budget. The budget gives information about the anticipated receipt and expenditure for the ensuing year.
7. Management – Such organizations are managed by elected representatives of the members.
8. Accounting – Non-profit making organizations are required to prepare their annual accounts and these accounts are submitted to the members of the government departments. The accounts are prepared on an accrual basis.
- Books Name
- Vision classes Accountancy Book
- Publication
- Vision classes
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Accountancy
CHAPTER – 1
ACCOUNTING FOR NOT-FOR-PROFIT ORGANISATION
Meaning & characteristics of NPO
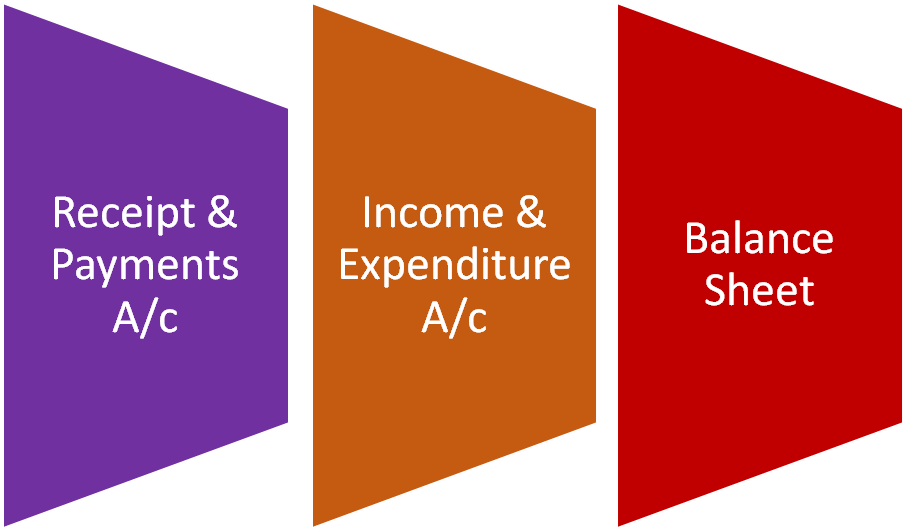
There are certain organisations which are set up for providing service to its members and the public in general. Such organisations include clubs, charitable institutions, schools, religious organisations, trade unions, welfare societies and societies for the promotion of art and culture. These organisations have service as the main objective and not the profit as is the case of organisations in business. Normally, these organisations do not undertake any business activity, and are managed by trustees who are fully accountable to their members and the society for the utilization of the funds raised for meeting the objectives of the organisation. Hence, they also have to maintain proper accounts and prepare the financial statement which take the form of Receipt and Payment Account; Income and Expenditure Account; and Balance Sheet. at the end of for every accounting period (normally a financial year).
This is also a legal requirement and helps them to keep track of their income and expenditure, the nature of which is different from those of the business organisations. In this chapter we shall learn about the accounting aspects relating to not-for-profit organisation.
Meaning and Characteristics of Not-for- Profit Organisation
Not-for -Profit Organisations refer to the organisations that are for used for the welfare of the society and are set up as charitable institutions which function without any profit motive. Their main aim is to provide service to a specific group or the public at large. Normally, they do not manufacture, purchase or sell goods and may not have credit transactions. Hence they need not maintain many books of account (as the trading concerns do) and Trading and Profit and Loss Account. The funds raised by such organisations are credited to capital fund or general fund. The major sources of their income usually are subscriptions from their members donations, grants-in-aid, income from investments, etc. The main objective of keeping records in such organisations is to meet the statutory requirement and help them in exercising control over utilisation of their funds. They also have to prepare the financial statements at the end of each accounting period (usually a financial year) and ascertain their income and expenditure and the financial position, and submit them to the statutory authority called Registrar of Societies.
The main characteristics of such organisations are:
1. Such organisations are formed for providing service to a specific group or public at large such as education, health care, recreation, sports and so on without any consideration of caste, creed and colour. Its sole aim is to provide service either free of cost or at nominal cost, and not to earn profit.
2. These are organised as charitable trusts/societies and subscribers to such organisation are called members.
3. Their affairs are usually managed by a managing/executive committee elected by its members.
4. The main sources of income of such organisations are: (i) subscriptions from members, (ii) donations (general). (iii) legacies(general). (iv) grant- in-aid, (v) income from investments, etc.
5. The funds raised by such organisations through various sources are credited to capital fund or general fund.
6. The surplus generated in the form of excess of income over expenditure is not distributed amongst the members. It is simply added in the capital fund.
7. The Not-for-Profit Organisations earn their reputation on the basis of their contributions to the welfare of the society rather than on the customers’ or owners’ satisfaction.
8. The accounting information provided by such organisations is meant for the present and potential contributors and to meet the statutory requirement.

 SUDIP CHAKRABORTY
SUDIP CHAKRABORTY
