Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change in velocity. It is a scalar quantity. Acceleration can be positive, negative and zero. It basically tells us how fast the speed of the object is changing.
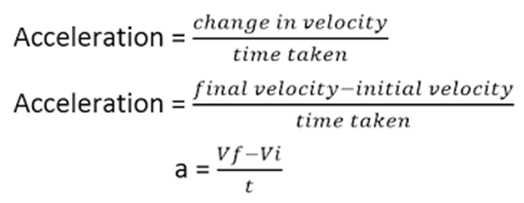
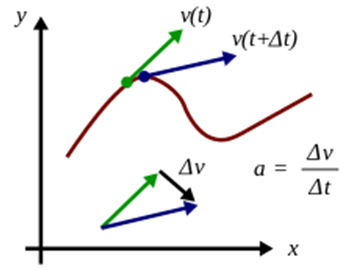
In the velocity-time graph, the slope of the velocity-time graph gives acceleration.
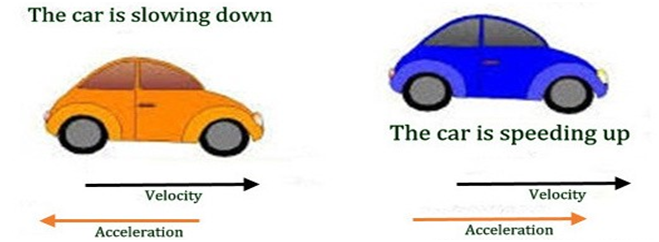
In the figure given below, In the first case, the direction of velocity and the acceleration is opposite and hence the car is slowing down. This is an example of negative acceleration. In the second case, the direction of velocity and acceleration is in the same direction and acceleration is said to be positive acceleration and the car is speeding up.
When the motion of the object is not uniform and the speed of the object changes with time. Then motion is said to be accelerated motion.
Example of negative acceleration
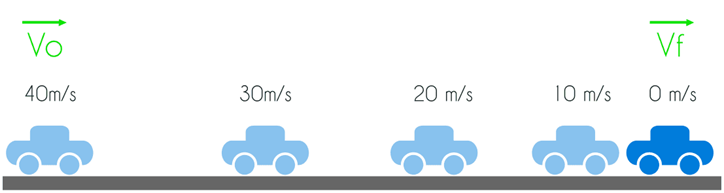
In the example given above the direction of motion is toward the right and its speed decreases continuously so the acceleration is opposite
to the motion and hence this is an example of negative acceleration.
Here ,
There are two kinds of accelerated motion.
- Uniform accelerated motion
- Non-uniform accelerated motion
Uniform accelerated motion -change of velocity is constant.
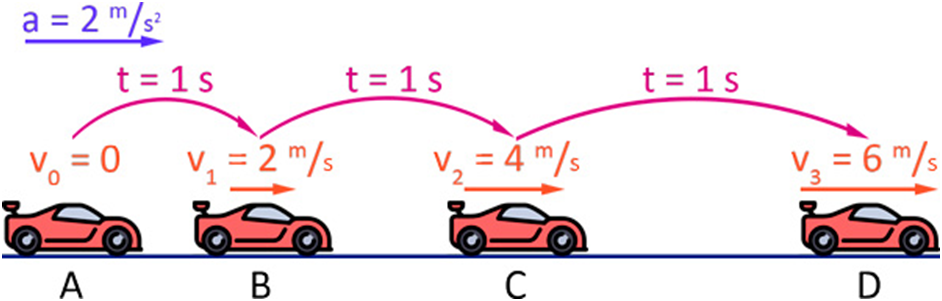
If a vehicle maintains a constant or a uniform change in its velocity in a given time interval along a straight line, then the vehicle is said to have a constant acceleration motion. Its motion is called uniform accelerated motion.
In the figure is given below a car is moving with acceleration
So it changes its velocity by 2m/s every second.
Velocity-time graph and displacement time graph for uniformly accelerated motion
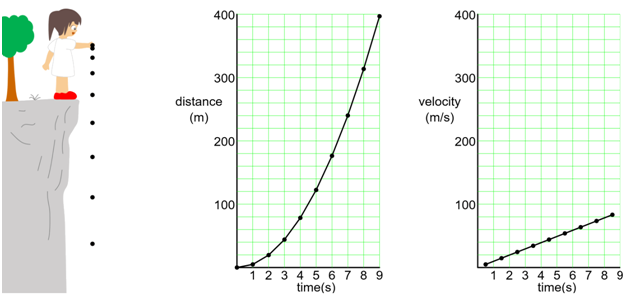
Freefall is an example of uniform accelerated motion
The V-t graph of uniform accelerated motion is a straight line, the slope of which gives the value of acceleration and the area under the curve gives the displacement.
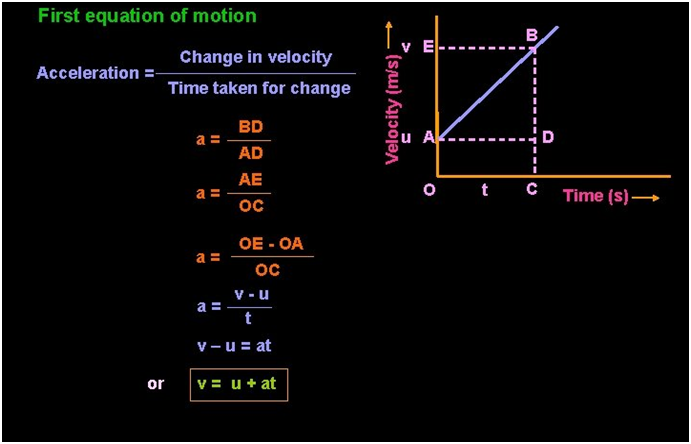
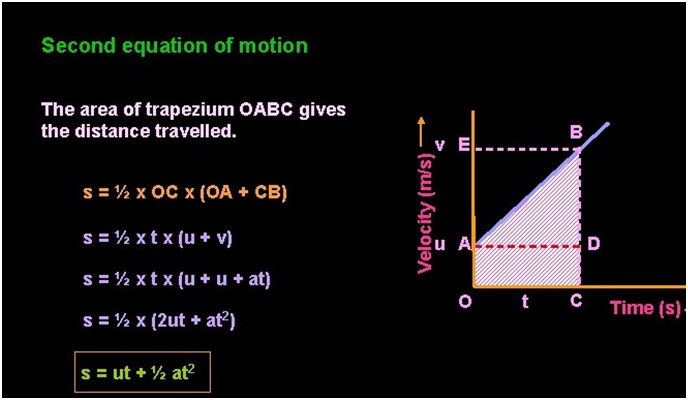
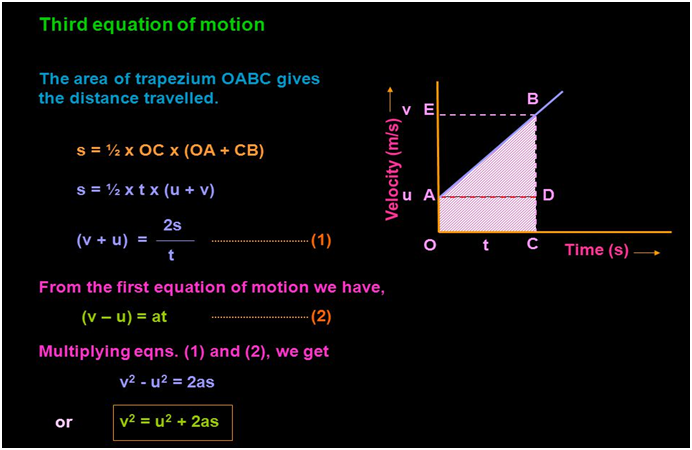
Equations of uniform accelerated motion
To solve the problems related to uniform accelerated motion, we have a set of equations.
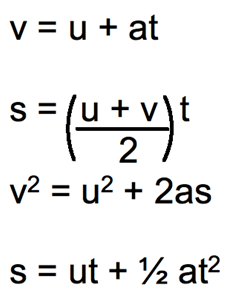
Here , v= final velocity ; u= initial velocity ; s= distance traveled
a= acceleration ; t= time taken.
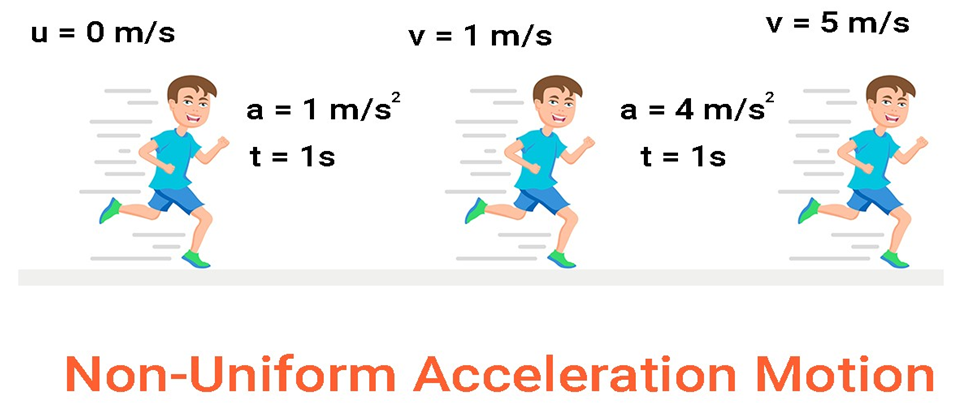
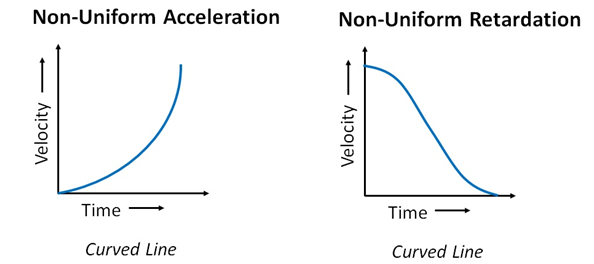
Non-uniform accelerated motion:
An object is said to be in non-uniform acceleration if the velocity of the object changes by unequal amounts in equal intervals of time.
Position -Time and velocity-Time graph
We have discussed the position-time graph and velocity-time graph with each topic. Let us now see all possible types of position-time graphs with different kinds of motions.
Slope of the position-time graph gives velocity. The greater the slope faster the body moves.
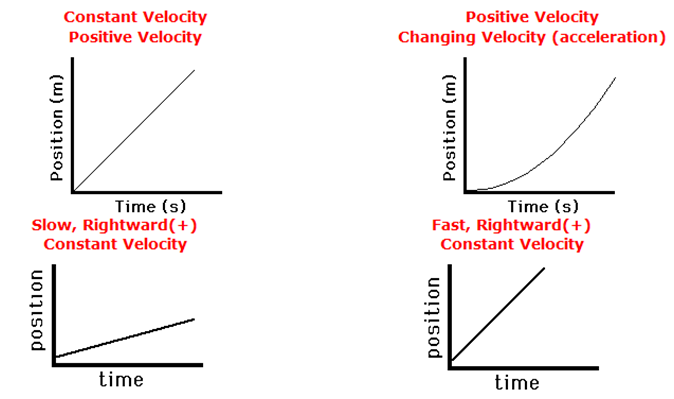
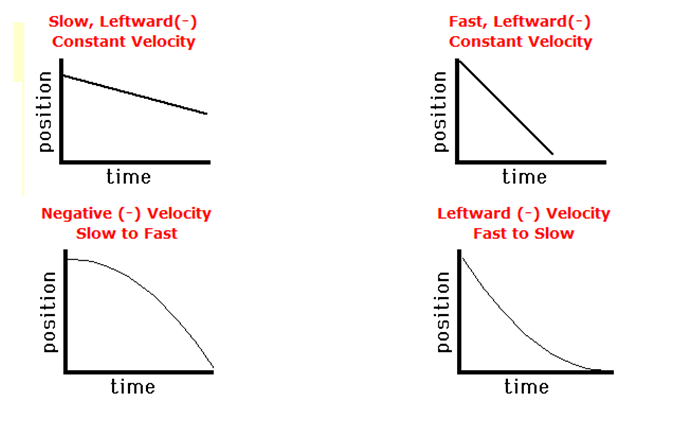
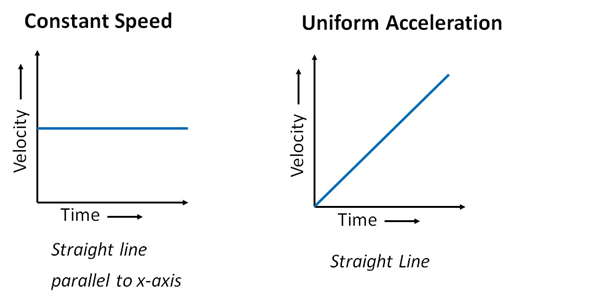
Now we will recap the velocity-time graph for different kinds of motions.
Slope of the velocity-time graph gives the value of acceleration.
The area under the curve of the v-t graph gives the value of the distance traveled.
Derivation of the equation using the graphical method
We can derive the equation of accelerated motion using a graphical method by using the property of the v-t graph.
- Slope of the v-t graph gives acceleration.
- Area under the v-t graph gives distance traveled.

 Madhava Publications
Madhava Publications
