- Books Name
- AMARENDRA PATTANAYAK Mathmatics Book
- Publication
- KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Standard equations , Properties and Application of a circle
Circle:
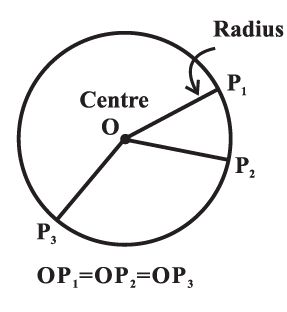
Definition: A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed
point in the plane.
The fixed point is called the centre of the circle and the distance from the centre
to a point on the circle is called the radius of the circle.
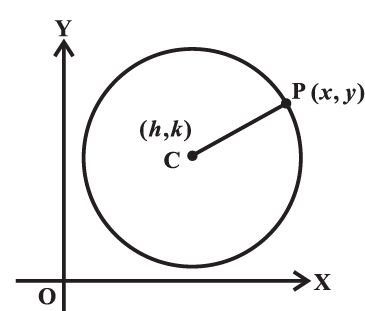
Given C (h, k) be the centre and r the radius of circle. Let P(x, y) be any point on
the circle . Then, by the definition, | CP | = r . By the distance formula,
we have
(x-h)2 + (y-k)2= r2
This is the required equation of the circle with centre at (h,k) and radius r .
General form of Equation of a Circle
The general equation of any type of circle is represented by:
x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0, for all values of g, f and c.
Adding g2 + f2 on both sides of the equation gives,
x2 + 2gx + g2+ y2 + 2fy + f2= g2 + f2 − c ………………(1)
Since, (x+g)2 = x2+ 2gx + g2 and (y+f)2 =y2 + 2fy + f2 substituting the values in equation (1), we have
(x+g)2+ (y+f)2 = g2 + f2−c …………….(2)
Comparing (2) with (x−h)2 + (y−k)2 = a2, where (h, k) is the center and ‘a’ is the radius of the circle.
h=−g, k=−f
a2 = g2+ f2−c
Therefore,
x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0, represents the circle with centre (−g,−f) and radius equal to a2 = g2 + f2− c.
- If g2 + f2 > c, then the radius of the circle is real.
- If g2 + f2 = c, then the radius of the circle is zero which tells us that the circle is a point that coincides with the center. Such a type of circle is called a point circle
- g2 + f2 <c, then the radius of the circle become imaginary. Therefore, it is a circle having a real center and imaginary radius.
N.B.: Standard Equation of Circle: ![]()
centre (0, 0) and Radius (r)
Equation of circle in centre radius form: ![]()
Centre (h, k), Radius = r
Equation of circle in General form: ![]()
Where (–g, –f ) centre
r2 = g2 + f2 – c .
![]()
Equation of circle with points P(x1, y1) and Q(x2, y2) as extremities of diameter is
(x – x1) (x – x2) + (y – y1) (y – y2) = 0
Equation of circle through three non-collinear points P(x1, y1), Q(x2, y2) and R(x3, y3) is
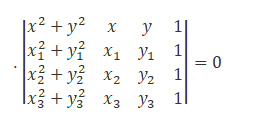
Area of circle = πr2
Perimeter = 2πr, where r is the radius.
Example: Find an equation of the circle with centre at (0,0) and radius r.
Solution :Here h = k = 0. Therefore, the equation of the circle is x2 + y2 = r2
Example: Find the equation of the circle with centre (–3, 2) and radius 4.
Solution: Here h = –3, k = 2 and r = 4. Therefore, the equation of the required circle is
(x + 3) 2 + (y –2)2 = 16
Example : Find the centre and the radius of the circle x2 + y2 + 8x + 10y – 8 = 0
Solution : The given equation is
(x2 + 8x) + (y22+ 10y) = 8
Now, completing the squares within the parenthesis, we get
(x2+ 8x + 16) + (y2 + 10y + 25) = 8 + 16 + 25
i.e. (x + 4)2 + (y + 5)2 = 49
i.e. {x – (– 4)} 2+ {y – (–5)} 2 = 72
Therefore, the given circle has centre at (– 4, –5) and radius 7.
Example : Find the equation of the circle which passes through the points (2, – 2), and (3, 4) and whose centre lies on the line x + y = 2.
Solution: Let the equation of the circle be (x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = r2.
Given that the circle passes through the points (2, –2) and (3, 4).
Thus,
(2 – h)2 + (–2 – k)2 = r2….(1)
and (3 – h)2 + (4 – k)2 = r2….(2)
Also, given that the centre lies on the line x + y = 2.
⇒ h + k = 2 ….(3)
Solving the equations (1), (2) and (3), we get
h = 0.7, k = 1.3 and r2 = 12.58
Hence, the equation of the required circle is
(x – 0.7)2 + (y – 1.3)2 = 12.58

 KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
