- Books Name
- AMARENDRA PATTANAYAK Mathmatics Book
- Publication
- KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Chapter 3
Trigonometric Functions
Angles, Measurement of Anges (Degree, Radian, Gradian) and Notational Convention:
Tri = three , gono= sides ,metric from metron(greek word) = study
The study of three sides is called trigonometry.
In other words , the trigonometry is that branch of mathematics which deals with measurement of sides and angles of a triangle.
Angles: a figure traced by rotating a given ray about its end points.
Otherwise An angle is formed when two straight lines or rays meet at a common endpoint. The common point of contact is called the vertex of an angle. The word angle comes from a Latin word named 'angulus,' meaning “corner.”
For measurement of sides, we need
- Units (cm,m,mm,hm,km,etc..)
- Devices ( Scale, tape, thread, gauge ,etc.,)
For measurement of angles , we need
- Units (degree, radian , gradian , staradian,etc..)
- Devices ( Protactor ,setsquare , angualar , trigonometric functions ,etc.,)
Three systems for measurement of angles.
- Sexagesimal system(FPS) or English System:
- Centesimal System(CGS) or French System
- Circular System
Sexagesimal system(FPS) or English System:
The sexagesimal system was an ancient system of counting, calculation, and numerical notation that used powers of 60 much as the decimal system uses powers of 10. Rudiments of the ancient system survive in vestigial form in our division of the hour into 60 minutes and the minute into 60 seconds.
In Sexagesimal System, an angle is measured in degrees, minutes and seconds.
A complete rotation describes 360°. In this system, a right angle is divided into 90 equal parts and each such part is called a Degree (1°); a degree is divided into 60 equal parts and each such part is called a Sexagesimal Minute (1’) and a minute is further sub-divided into 60 equal parts, each of which is called a Sexagesimal Second (1’’). In short,

Centesimal System(CGS) or French System:
In Centesimal System, an angle is measured in grades, minutes and seconds. In this system, a right angle is divided into 100
equal parts and each such part is called a Grade (1g); again, a grade is divided into 100 equal parts and each such part is called a Centesimal Minute (1‵) ; and a minute is further sub-divided into 100 equal parts, each of which is called a Centesimal Second (1‶). In short,

Note: (i) Clearly, minute and second in sexagesimal and centesimal systems are different.
For example,
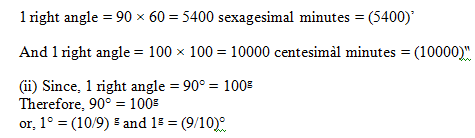
The first relation is used to reduce an angle of sexagesimal system to centesimal system and the second is used to reduce an angle of centesimal system to sexagesimal system.
Circular System:
In this System, an angle is measured in radians. In higher mathematics angles are usually measured in circular system. In this system a radian is considered as the unit for the measurement of angles.
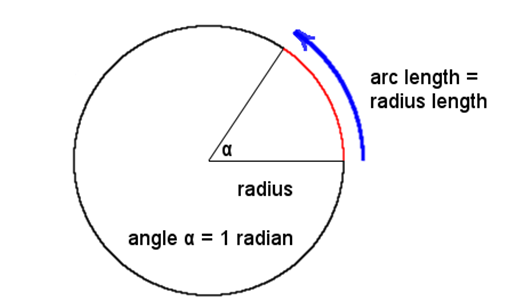
Definition of Radian: A radian is an angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc whose length is equal to the radius.
The circular measure of an angle is the number of radians it contains.
Thus the circular (radian) measure of a right angle is ![]()
If an angle is given without mentioning units, it is assumed to be in radians. The relation between degree measures and circular (radian) measures of some standard angles are given below:
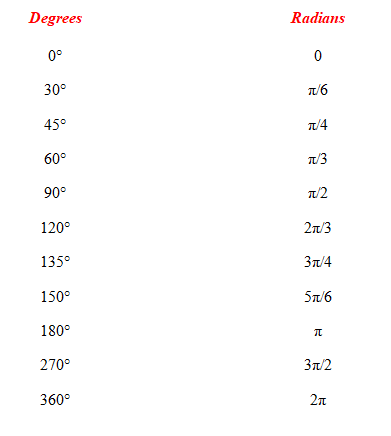
Radians = Degrees × π / 180
In terms of degrees, one complete counterclockwise revolution is 360° and whereas in radians, one complete counterclockwise revolution is 2π. These statements can be equated as:
One complete counterclockwise revolution in degrees = 360°
One complete counterclockwise revolution in radians = 2π
Radians = Degrees × (π/180°). We can follow the steps given below to calculate the measure of an angle given in degrees to radians.
- Note down the measure of the angle given in degrees.
- We know, 1°= (π)/180 radians. So, to convert the angle given in degrees to radians we multiply it with π/180°.
Angle in Radians = Angle in Degrees × π/180°. - Simplify the values and express the answer in radians.
Example: Convert 90 degrees to radians.
Solution: 90° = 90° × (π/180°) = π/2.
- Angles are measured in degrees, radians and gradian
- One full revolution is equal to 2π rad (or) 360°,100g.
- 1° = 0.017453 radians and 1 rad = 57.2958°.
- To convert an angle from degrees to radians, we multiply it by π/180°.
- To convert an angle from radians to degrees, we multiply it by 180°/π.
Example 1: In a circle with center O, points A and B are two points on the circle. ∠AOB = 60°. Convert ∠AOB's angle measure from degrees to radians.
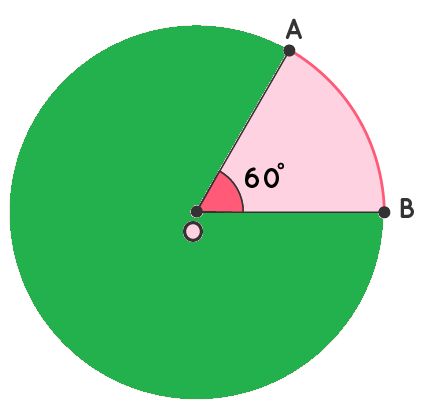
Solution:
We have, ∠AOB = 60°.
Degrees to radians conversion formula is given as (Degrees × π)/180°
Thus converting the given angle we get,
∠AOB in Radians = ∠AOB in degrees × (π/180°)
∠AOB in Radians = 60° × (π/180°)
∠AOB in Radians = π/3
Answer: ∠AOB = π/3 rad.
Convert the following degree measure to radian measure.
a) 20 degrees b) 28 degrees
Solution: To convert the following degree measure to radians we will use the following steps:
a) 20° × (π/180°) = π/9 Radians.
b) 28° × (π/180°) = 7π/45 Radians.

 KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
