- Books Name
- Ritan Sheth Chemistry Book
- Publication
- Ritan Sheth
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Chemistry
PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR MEASUREMENTS
Physical Properties: Those properties which can be measured or observed without changing the identity or the composition of the substance.
Some examples of physical properties are colour, odour, melting point, boiling point etc. Chemical Properties: It requires a chemical change to occur. The examples of chemical properties are characteristic reactions of different substances. These include acidity, basicity, combustibility etc.
• Units of Measurement
Fundamental Units: The quantities mass, length and time are called fundamental quantities and their units are known as fundamental units.
There are seven basic units of measurement for the quantities: length, mass, time, temperature, amount of substance, electric current and luminous intensity.
Si-System: This system of measurement is the most common system employed throughout the world.
It has given units of all the seven basic quantities listed above.
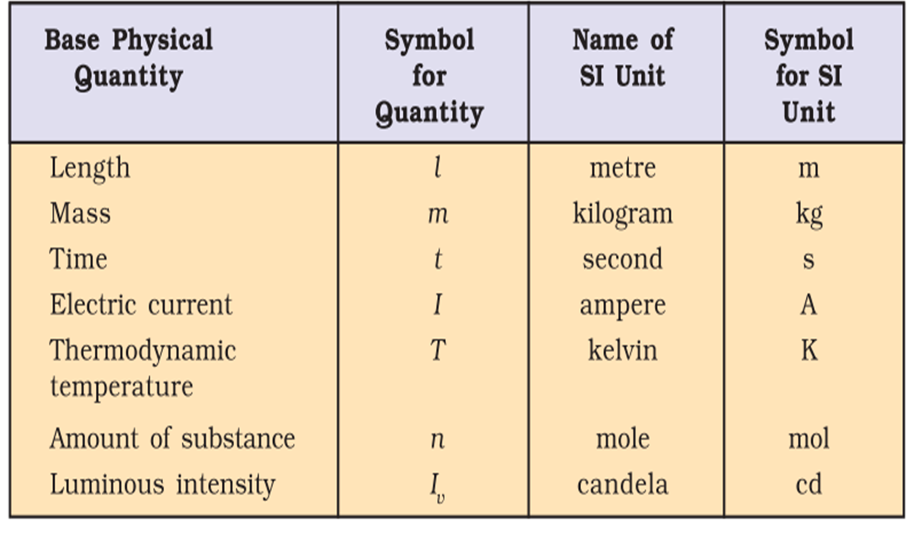
• Definitions of Basic SI Units
1. Metre: It is the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of 1/299792458 of a second.
2. Kilogram: It is the unit of mass. It is equal to the mass of the international prototype
of the kilogram. ,
3. Second: It is the duration of 9192631, 770 periods of radiation which correspond to the transition between the two hyper fine levels of the ground state of caesium- 133 atom.
4. Kelvin: It is the unit of thermodynamic temperature and is equal to 1/273.16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water.
5. Ampere: The ampere is that constant current which if maintained in two straight parallel conductors of infinite length, of negligible circular cross section and placed, 1 metre apart in vacuum, would produce between these conductors a force equal to 2 x 10-7 N per metre of length.
6. Candela: It may be defined as the luminous intensity in a given direction, from a source which emits monochromatic radiation of frequency 540 x 1012 Hz and that has a radiant intensity in that direction of 1/ 683 watt per steradian.
7. Mole: It is the amount of substance which contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 0.012 kilogram of carbon -12. Its symbol is ‘mol’.
• Mass and Weight
Mass: Mass of a substance is the amount of matter present in it.
The mass of a substance is constant.
The mass of a substance can be determined accurately in the laboratory by using an analytical
balance. SI unit of mass is kilogram.
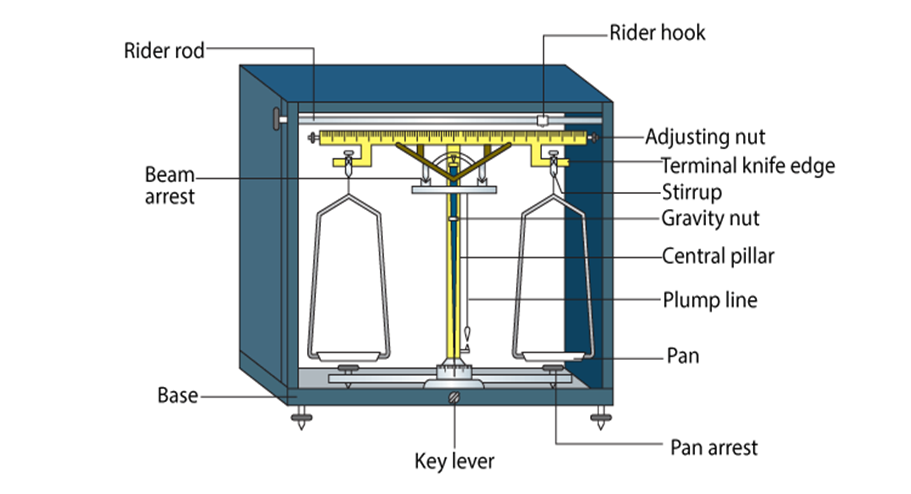
Weight: It is the force exerted by gravity on an object. Weight of substance may vary from one place to another due to change in gravity.
Volume: Volume means the space occupied by matter. It has the units of (length)3. In SI units, volume is expressed in metre3 (m3). However, a popular unit of measuring volume, particularly in liquids is litre (L) but it is not in SI units or an S.I. unit.
Mathematically,
1L = 1000 mL = 1000 cm3 = 1dm3.
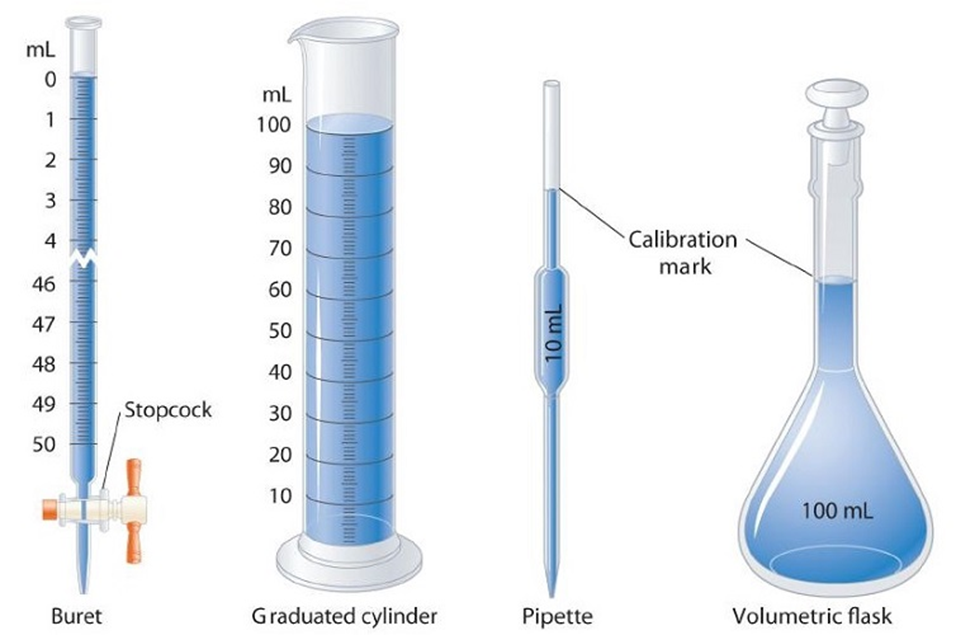
Volume of liquids can be measured by different devices like burette, pipette, cylinder, measuring flask etc. All of them have been calibrated.
Temperature: There are three scales in which temperature can be measured. These are known as Celsius scale (°C), Fahrenheit scale (°F) and Kelvin scale (K).
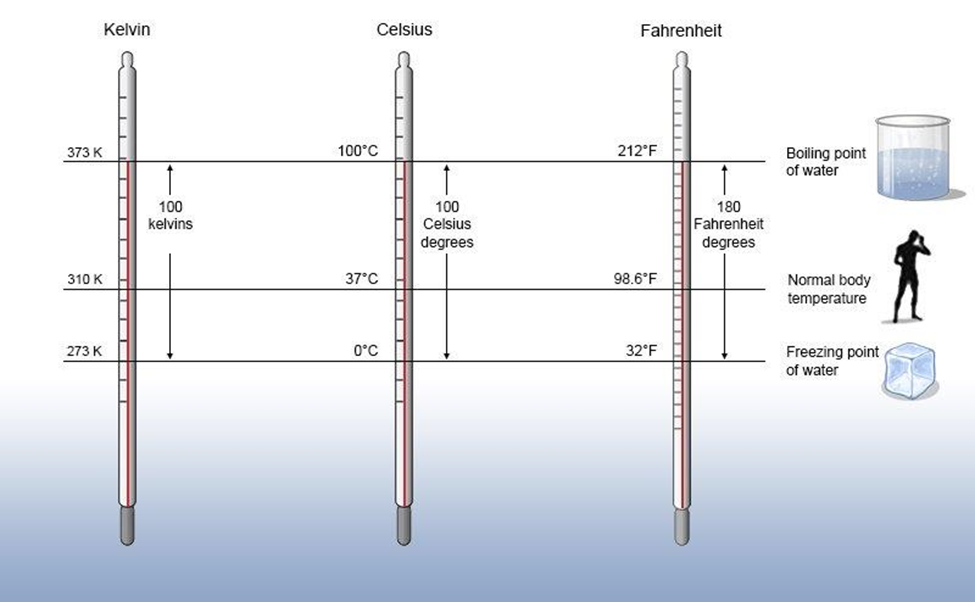
-> Thermometers with Celsius scale are calibrated from 0°C to 100°C.
-> Thermometers with Fahrenheit scale are calibrated from 32°F to 212°F.
-> Kelvin ‘scale of temperature is S.I. scale and is very common these days. Temperature on this scale is shown by the sign K.
The temperature on two scales are related to each other by the relationship

Density: Density of a substance is its amount of mass per unit volume. So, SI unit of density can be obtained as follows:
Matter is defined as something which has mass and occupies a certain volume. Mass of a body may or may not be uniformly distributed throughout the volume of the body. In order to understand the distribution of mass in a body we define a quantity called density.
Density is defined as the mass per unit volume of the substance.
The symbol for density is ρ and the formula to calculate density from mass and volume is
ρ=M/V
This formula implies that greater the mass of a body, greater is its density while greater the volume occupied by a body, smaller is the density of that body.
The S.I. unit of density is kg/m3. Its dimensional formula is [M1 L-3 T0].

 Ritan Sheth
Ritan Sheth
