- Books Name
- Ritan Sheth Chemistry Book
- Publication
- Ritan Sheth
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Chemistry
ATOMIC AND MOLECULAR MASSES
• Atomic MassThe atomic mass of an element is the number of times an atom of that element is heavier than an atom of carbon taken as 12. It may be noted that the atomic masses as obtained above are the relative atomic masses and not the actual masses of the atoms.
One atomic mass unit (amu) is equal to l/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon-12 isotope. It is also known as unified mass.
• Average Atomic Mass
Most of the elements exist as isotopes which are different atoms of the same element with different mass numbers and the same atomic number. Therefore, the atomic mass of an element must be its average atomic mass and it may be defined as the average relative mass of an atom of an element as compared to the mass of carbon atoms (C-12) taken as 12w.
• Molecular Mass
Molecular mass is the sum of atomic masses of the elements present in a molecule. It is obtained by multiplying the atomic mass of each element by number of its atoms and adding them together.
For example,
Molecular mass of methane (CH4)
= 12.011 u + 4 (1.008 u)
= 16.043 u
• Formula Mass
Ionic compounds such as NaCl, KNO3, Na2C03 etc. do not consist of molecules i.e., single entities but exist “as ions closely packed together in a three dimensional space as shown in -Fig. 1.5.
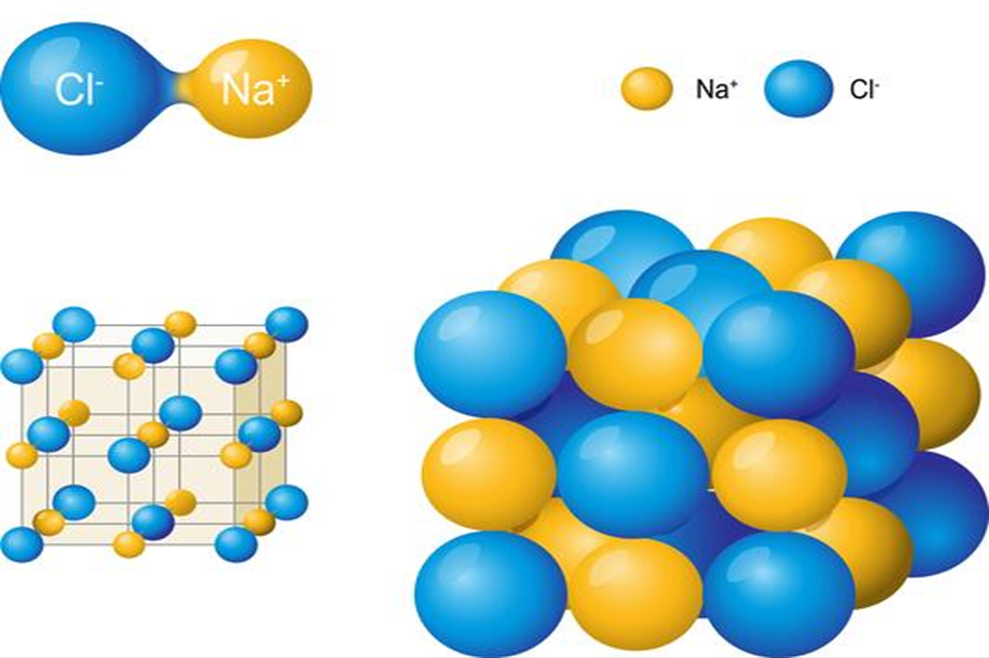
Packing of Na+ and Cl- ions in Sodium chloride molecule
In such cases, the formula is used to calculate the formula mass instead of molecular mass. Thus, formula mass of NaCl = Atomic mass of sodium + atomic mass of chlorine
= 23.0 u + 35.5 u = 58.5 u.

 Ritan Sheth
Ritan Sheth
