- Books Name
- Ritan Sheth Chemistry Book
- Publication
- Ritan Sheth
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Chemistry
SPONTANEITY
Spontaneous Process: A process which can take place by itself or has a tendency to take place is called spontaneous process.
Spontaneous process need not be instantaneous. Its actual speed can vary from very slow to quite fast.
A few examples of spontaneous process are:
(i) Common salt dissolves in water of its own.
(ii) Carbon monoxide is oxidised to carbon dioxide of its own.
• Entropy (S)
The entropy is a measure of degree of randomness or disorder of a system. Entropy of a substance is minimum in solid state while it is maximum in gaseous state.
The change in entropy in a spontaneous process is expressed as ΔS
ΔS = ΔSsystem + ΔSsurroundings
ΔS = Overall change in entropy
ΔSsystem = Change in entropy of the system
ΔSsurroundings =Change in entropy of the surroundings
ΔS > 0, + entropy change, reaction is spontaneous
ΔS < 0, - entropy change, reaction is nonspontaneous
Equation for the total change in entropy
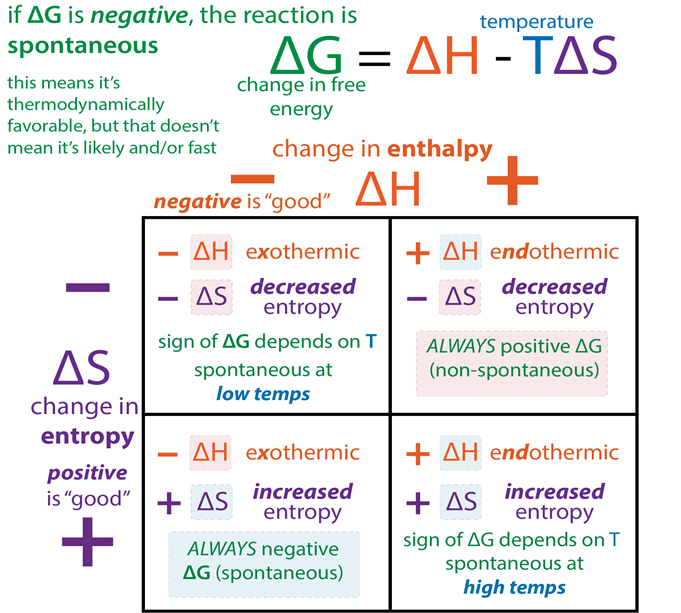
• Gibbs Energy and Spontaneity
A new thermodynamic function, the Gibbs energy or Gibbs function G, can be defined as G = H-TS
ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
Gibbs energy change = enthalpy change – temperature x entropy change ΔG gives a criteria for spontaneity at constant pressure and temperature, (i) If ΔG is negative (< 0) the process is spontaneous.
(ii) If ΔG is positive (> 0) the process is non-spontaneous.
• Free Energy Change in Reversible Reaction
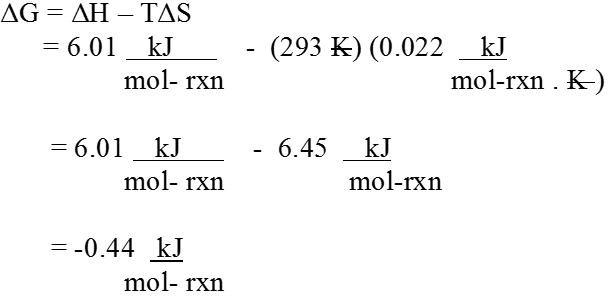
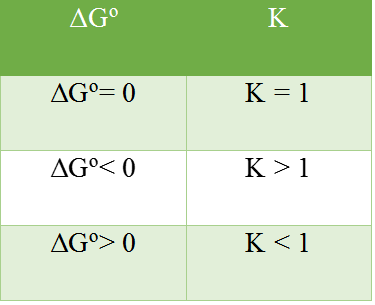
qualitative relationship between the change in standard free energy and the equilibrium constant for a given relation

 Ritan Sheth
Ritan Sheth
