- Books Name
- Ritan Sheth Chemistry Book
- Publication
- Ritan Sheth
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Chemistry
ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATIONS AND TYPES OF ELEMENTS: s-, p-, d-, f- BLOCKS
Periods
Horizontal rows in a periodic table are known as periods.
There are in all seven periods in the long form of periodic table.
Characteristics of periods:
(i) In all the elements present in a period, the electrons are filled in the same valence shell.
(ii) The atomic sizes generally decrease from left to right.
s-Block Elements
General electronic configuration: ns1-2 Characteristics of s-block elements:
(i) All the elements are soft metals.
(ii) They have low melting and boiling points.
(iii) They are highly reactive.
(iv) Most of them impart colours to the flame.
(v) They generally form ionic compounds.
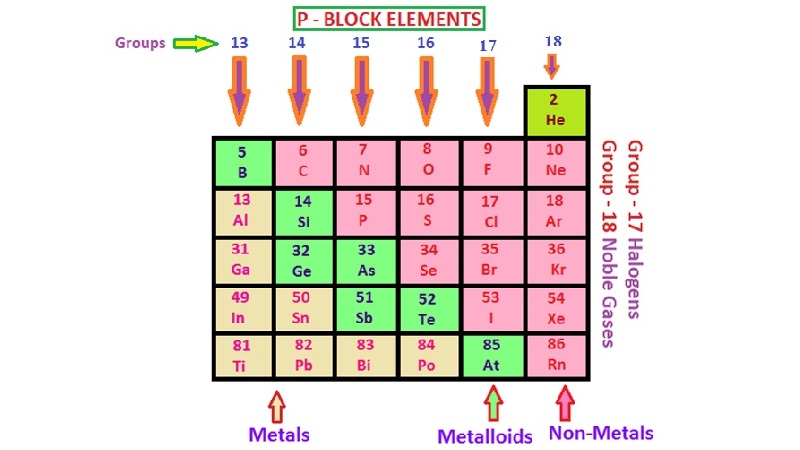
(vi) They are good conductors of heat and electricity. p-Block Elements
General electronic configuration: ns2np1-6
Characteristics of p-block elements:
(i) The compounds of these elements are mostly covalent in nature.
(ii) They show variable oxidation states.
(iii) In moving from left to right in a period, the non-metallic character of the elements increases.
(iv) The reactivity of elements in a group generally decreases downwards.
(v) At the end of each period is a noble gas element with a closed valence shell ns2 np6 configuration.
(vi) Metallic character increases as we go down the group.
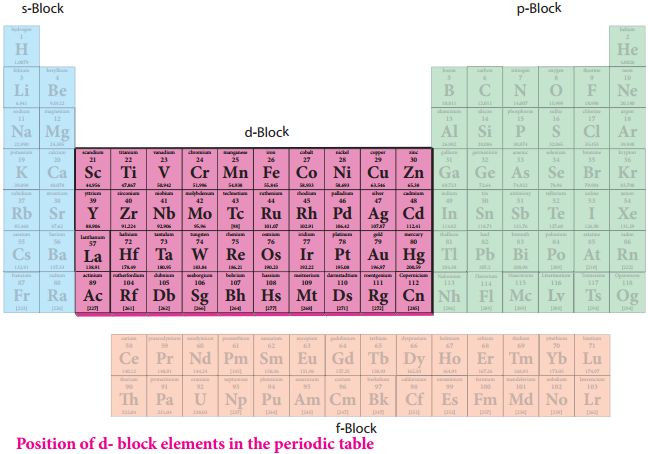
d-Block Elements:
General electronic configuration: (n -1) d1-10 ns0-2
The d-block elements are known as transition elements because they have incompletely filled d-orbitals in their ground state or in any of the oxidation states.
Characteristics of d-block elements:
(i) They are all metals with high melting and boiling points.
(ii) The compounds of the elements are generally paramagnetic in nature.
(iii) They mostly form coloured ions, exhibit variable valence (oxidation states).
(iv) They are of tenly used as catalysts.
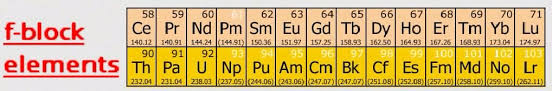
f-Block Elements
General electronic configuration: (n – 2) f1-14 (n -1) d0-1 ns2
They are known as inner transition elements because in the transition elements of d-block, the electrons are filled in (n – 1) d sub-shell while in the inner transition elements of f-block the filling of electrons takes place in (n – 2) f subshell, which happens to be one inner subshell.
Characteristics of f-Block elements:
(i) The two rows of elements at the bottom of the Periodic Table, called the Lanthanoids Ce (Z = 58) – Lu (Z = 71) and Actinoids Th (Z = 90) – Lr (Z = 103).
(ii) These two series of elements are called Inner Transition Elements (f-Block Elements).
(iii) They are all metals. Within each series, the properties of the elements are quite similar.
(iv) Most of the elements pf the actinoid series are radio-active in nature.
• Metals
(i) Metals comprise more than 78% of all known elements and appear on the left side of the Periodic Table.
(ii) Metals are solids at room temperature.
(iii) Metal usually have high melting and boiling points.
(iv) They are good conductors of heat and electricity.
(u) They are malleable and ductile.
• Non-metals
(i) Non-metals are located at the top right hand side of the Periodic Table.
(ii) Non-metals are usually solids or gases at low temperature with low melting and boiling points.
(iii) They are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
(iv) The non-metallic character increases as one goes from left to right across the Periodic
Table.
(v) Most non-metallic solids are brittle and are neither malleable nor ductile.
• Metalloids
The elements (e.g., silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony and tellurium) show the characteristic, of both metals and non-metals. These elements are also called semimetal.
• Noble Gases
– These are the elements present in group 18.
– Eash period ends with noble gas element.
– All the members are of gaseous nature and because of the presence of all the occupied filled orbitals, they have very little tendency to take part in chemical combination.
– These are also called inert gases.
• Representative Elements
The elements of group 1 (alkali metals), group 2 (alkaline earth metals) and group 13 to 17 constitute the representative elements. They are elements of s-block and p-block.
• Transition Elements
The transition elements include, all the d-block elements and they are present in the centre of the periodic table between s and p-block elements.
• Inner Transition Elements
Lanthanoids (the fourteen elements after Lanthanum) and actinides (the fourteen elements after actinium) are called inner transition elements. They are also called f-block elements.
The elements after uranium are also called transuranic elements.

 Ritan Sheth
Ritan Sheth
