- Books Name
- Ritan Sheth Chemistry Book
- Publication
- Ritan Sheth
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Chemistry
LAWS OF CHEMICAL COMBINATION
The combination of elements to form compounds is governed by the following five basic laws.
(i) Law of Conservation of Mass
(ii) Law of Definite Proportions
(iii) Law of Multiple Proportions
(iv) Law of Gaseous Volume (Gay Lussac’s Law)
(v) Avogadro’s Law
(i) Law of Conservation of Mass
The law was established by a French chemist, A. Lavoisier. The law states:
In all physical and chemical changes, the total mass of the reactants is equal to that of the products.
In other words, matter can neither be created nor destroyed.
The following experiments illustrate the truth of this law.
(a) When matter undergoes a physical change.
![]()
It is found that there is no change in weight though a physical change has taken place.
(b) When matter undergoes a chemical change.
For example, decomposition of mercuric oxide.
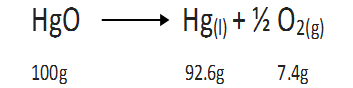
During the above decomposition reaction, matter is neither gained nor lost.
(ii) Law of Definite Proportions
According to this law:
A pure chemical compound always consists of the same elements combined together in a fixed proportion by weight.
For example, Carbon dioxide may be formed in a number of ways i.e.,
(a) By burning coke in air

(b)By the decomposition of ;limestone(CaCO3) on heating

(c)By the action of dil HCL on washing soda (Na2CO3)
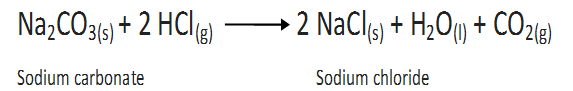
In all the three samples of CO2 carbon and oxygen are in the ratio 3:8 by weight
(iii) Law of Multiple Proportions
If two elements combine to form two or more compounds, the weight of one of the elements which combines with a fixed weight of the other in these compounds, bears simple whole number ratio by weight.
For example,
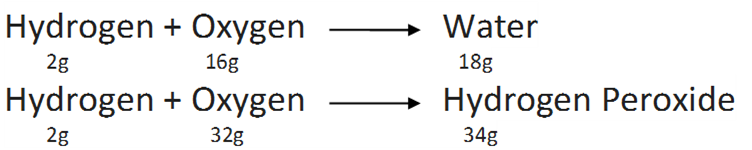
Hear, the masses of oxygen (16g and 32g ) which combine with a fixed mass of hydrogen (2g) bear a simple ratio 16:32 or 1:2 .
(iv) Gay Lussac’s Law of Gaseous Volumes
The law states that, under similar conditions of temperature and pressure, whenever gases combine, they do so in volumes which bear simple whole number ratio with each other and also with the gaseous products. The law may be illustrated by the following examples.
(a) Combination between hydrogen and chlorine:
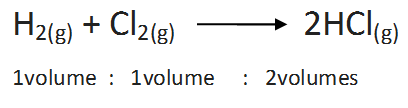
(b)Combination between nitrogen and hydrogen: The two gases lead to the formation of ammonia gas under suitable conditions. The chemical equation is
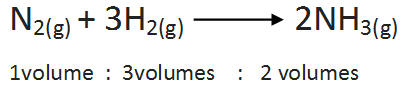
(v) Avogadro’s Law: Avogadro proposed that, equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure should contain equal number of molecules.
For example,
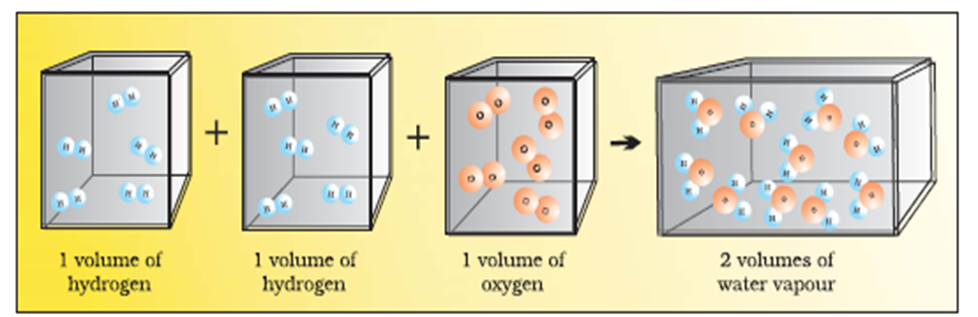
If we consider the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen to produce water, we see that two volumes of hydrogen combine with one volume of oxygen to give two volumes of water without leaving any unreacted oxygen.
Two volumes of hydrogen react with one volume of oxygen to give two volumes of water vapour.

 Ritan Sheth
Ritan Sheth
