- Books Name
- Ritan Sheth Chemistry Book
- Publication
- Ritan Sheth
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Chemistry
REDOX REACTIONS AND ELECTRODE PROCESSES—ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS
A device in which the redox reaction is carried indirectly and the decrease in energy appears as the electrical energy are called electrochemical cell.
Electrolytic Cell. The cell in which electrical energy is converted into chemical energy. Example, when lead storage battery is recharged, it acts as electrolytic cell.
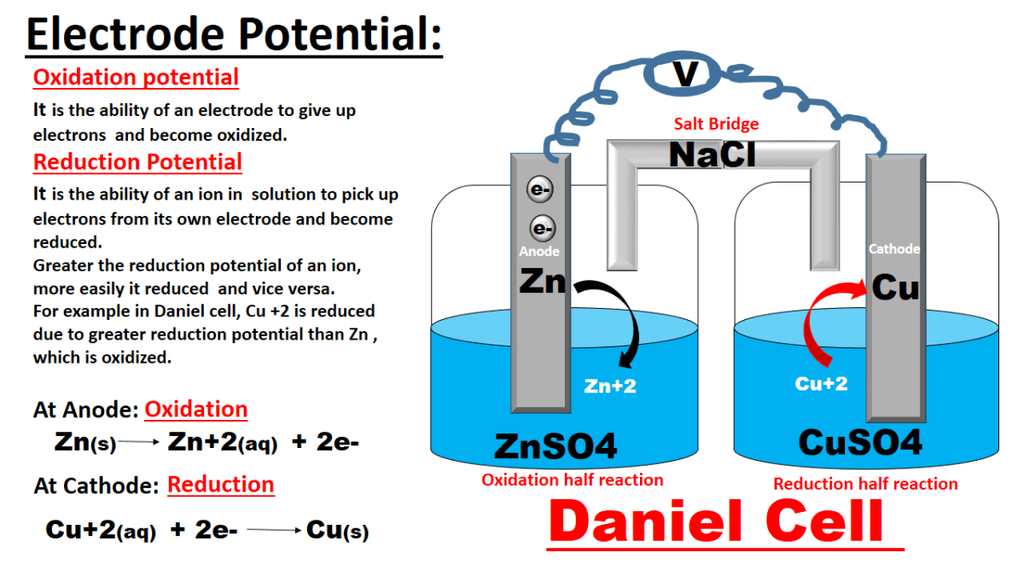
Redox Reactions and Electrode Processes. When zinc rod is dipped in copper sulphate solution redox reaction begins hence, zinc is oxidised to Zn2+ ions and Cu2+ ions are reduced to metal.
●Types of Electrochemical Cell
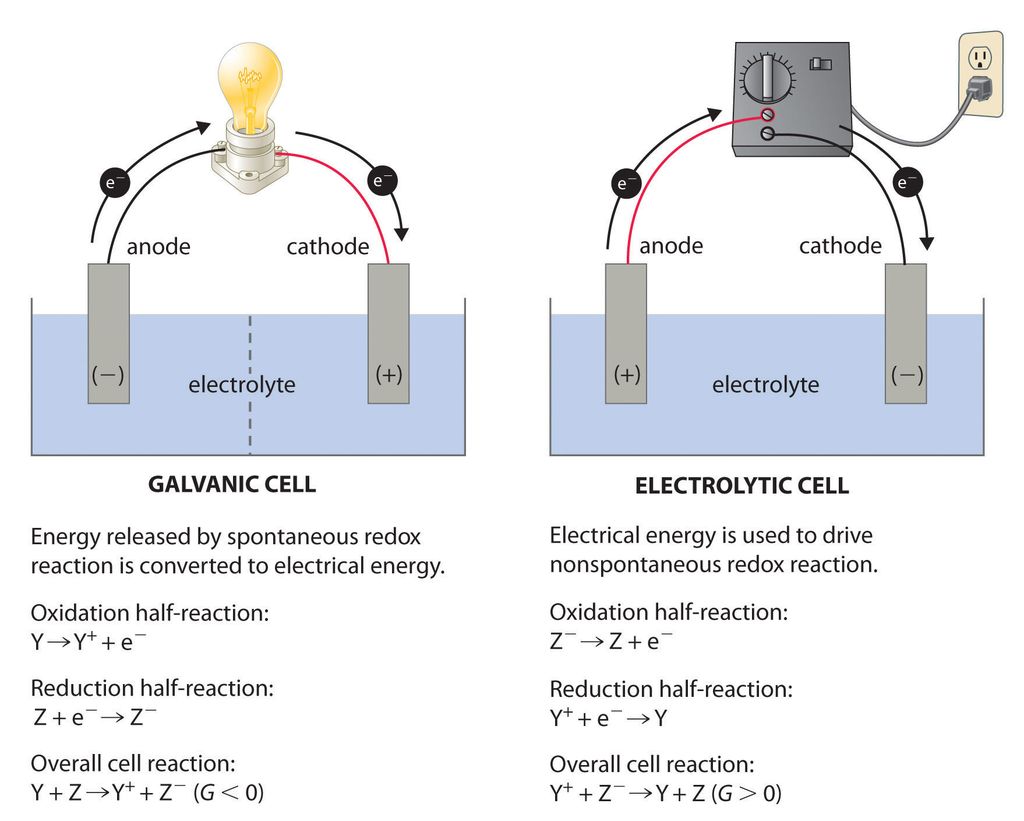
Electrochemical cells are primarily of two types:
1.Galvanic cell or voltaic cell
2.Electrolytic cell
Let us learn about both of their key features and differences in tabular form:
• Redox reaction. Reactions in which oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously are called redox reactions.
• Oxidation. Involves loss of one or more electrons.
• Reduction. Involves gain of one or more electrons.
• Oxidising agent. Accepting electrons.
• Reducing agent. Losing electrons.
• Electrochemical cell. It is a device in which redox reaction is carried indirectly and decrease in energy gives electrical energy.
• Electrode potential. It is the potential difference between the electrode and its ions in solution.
• Standard electrode potential. It is the potential of an electrode with respect to standard hydrogen electrode.
• Electrochemical series. It is activity series. It has been formed by arranging the metals in order of increasing standard reduction potential value.

 Ritan Sheth
Ritan Sheth
