- Books Name
- Ritan Sheth Chemistry Book
- Publication
- Ritan Sheth
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Chemistry
ATMOSPHERIC POLLUTION
• Troposphere
The lowest region of atmosphere, in which the human beings along with other organisms live, is called troposphere.
It extends to the height of about 10 km from the sea level. It contains air, water vapours, clouds etc. The pollution in this region is caused by some poisonous gases, smoke fumes, smog etc.
• Stratosphere
It extends from height of 10 to 50 km above the sea level. Ozone and some other gaseous substances present in this region are responsible for the pollution.
• Tropospheric Pollution
Pollution in this region is caused by the presence of undesirable gaseous particles like oxides of sulphur, nitrogen and carbon, hydrocarbons along with solid particles like dust, mist, fumes, smoke etc.
• Oxides of Sulphur
These are produced when coal containing sulphur is burnt.
S + O2 → SO2
SO2 + ½ O2 → SO3
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
It is also produced during volcanic eruptions.
Harmful effects:
(i) It is poisonous to both animals and plants.
(ii) A very high concentration of S02 may cause respiratory diseases e.g., asthma,bronchitis, emphysema in human beings.
(iii) It causes irritation to the eyes, resulting in tears and redness.
(iv) Its high concentration leads to the stiffness of flower buds.
(v) Particulate matter present in the air can catalyse the formation of sulphur trioxide from sulphur dioxide.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2SO3
O3 and H2O2 also promote this reaction.
SO2(g) + O3(g) → SO3(g) + O2(g)
SO2(g) + H2O2(l) → H2SO4(aq)
• Oxides of Nitrogen
Main oxides of nitrogen are nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
Major Sources:
(i) Lightning discharge results in the combination of N2 and 02 to form NO.
(ii) Combustion of gasoline in automobilies, burning of hydrocarbons and coal etc.
Harmful effects:
Nitric oxide itself is not harmful to human beings, but it is very unstable and changes to nitrogen dioxide which is toxic in nature. These effects are as follows:
(i) It reacts with Ozone (03) present in the atmosphere and thus decrease the density of Ozone.
(ii) It affects the respiratory system and damages the lungs.
(iii) Higher concentrations of N02 damage the leaves of plants and retard the rate of photosynthesis.
(iv) It causes cracks in rubber.
(v) Nitrogen dioxide is also harmful to various textile fibres and metals.
• Hydrocarbons
Incomplete combustion of fossil fuel in industry and thermal power plants and the exhaust of automobiles release hydrocarbons into the atmosphere constantly causing pollution. Harmful Effects:
(i) They cause cancer.
(ii) Methane is one of the greenhouse gases.
(iii) They harm plants in various ways like breakdown of tissues, shedding of leaves etc.
• Oxides of Carbon
Carbon dioxide:
0.03% C02 is present in air by Volume.
Major Sources:
(i) By burning of fossil fuels.
(ii) By the decomposition of limestone during the manufacture of cement.
(iii) Emitted during volcanic eruptions.
(iv) C02 is released into the atmosphere by respiration.
Harmful effects:
Deforestation and burning of fossil fuel increases the C02 level which is mainly responsible for global warming.
Carbon Monoxide: Carbon Monoxide is a colourless and odourless gas.
Major Sources:
(i) Released by the automobile exhaust.
(ii) Incomplete combustion of coal, fire wood, petrol etc.
(iii) By the dissociation of C02 at high temperature.
Harmful effects:
(i) It binds to haemoglobin to form carboxyhaemoglobin which is more stable than oxygen-haemoglobin complex. Its concentration in blood when reaches to 3-4%, the oxygen carrying capacity of blood is greatly reduced.
The oxygen deficiency, results into headache, weak eyesight, nervousness etc.
(ii) It has harmful effects on plants when its concentration is (100 ppm or more).
• Global Wanning and Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse Effect:
Some gases like carbondioxide, methane, ozone, water vapours, CFCs have the capacity to trap some of the heat radiations that are released from the earth or from sun. These gases are known as greenhouse gases and the effect is called greenhouse effect. This leads to global warming
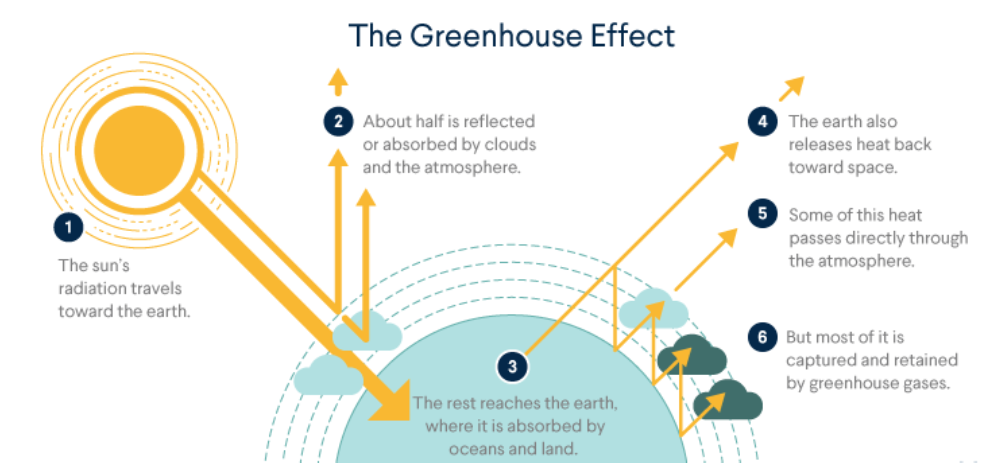
Consequences of global warming:
(i) It leads to melting of polar ice caps and flooding of low lying areas all over the earth.
(ii) Global rise in temperature increases the incidence of infectious diseases like dengue, malaria, yellow fever, sleeping sickness etc.
• Acid Rain
When the pH of the rain water drops below 5.6, it is known as acid rain.
Normal rain is slightly acidic due to dissolution of atmospheric carbon dioxide in water.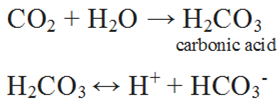
Oxides of nitrogen and sulphur released as a result of combustion of fossil fuels dissolve in water to form nitric acid and sulphuric acid.
4NO2 + O2 + 2H2O → 4HNO3
SO2 + ½ O2 → H2SO4
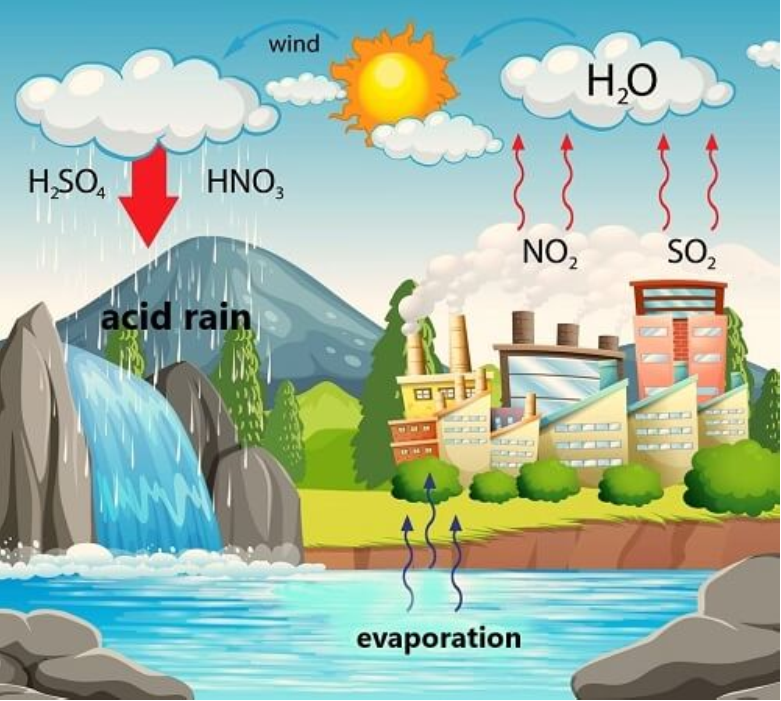
Harmful Effects of Acid Rain:
(i) It has harmful effects on trees and plants as it dissolves and washes away nutrients needed for their growth.
(ii) It has very bad effect on aquatic ecosystem.
(iii) Acid rain damages buildings and other structures made of stone or metal. Taj Mahal in India has beenaffected by acid rain.
CaCO3 (marble) + H2SO4 → CaSO3 + H2O + CO2
• Particulate Pollutants
Viable Particulates: They are minute living organisms that are dispersed in the atmosphere. e.g., bacteria, fungi) moulds, algae etc.
Non Viable Particulates:
(i) Smoke: It is the mixture of solid and liquid particles formed during combustion of organic matter,
Example: Cigarette smoke, smoke from burning of fossil fuel.
(ii) Dust: Composed of fine solid particles (over 2gm in diameter).
It is produced during crushing, grinding and attribution of solid particles.
(iii) Mist: These are produced due to the spray of liquids like herbicides and pesticides over the plants. They travel through air and form mist.
(iv) Fumes: They are generally released to the atmosphere by the metallurgical operations and also by several chemical reactions.
Harmful Effects of Particulate Pollutants:
(i) Fine particles less than 5 microns penetrate into the lungs. Inhalation of such particles can lead to serious lung diseases including lung cancer.
(ii) Suspended particles of bigger size can hinder the sun rays from reaching the earth surface. This can lower the temperature of earth and make the weather foggy.
• Smog
This is the common form of air pollution which is combination of smoke and fog.
Smog exists in two types:
(i) Classical Smog: Occurs in cool humid climate. It contains smoke, fog and sulphur dioxide. It is also called as reducing smog.
(ii) Photochemical Smog: This type of smog result from the action of sunlight on unsaturated hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides released by the vehicles and industries. It has high concentration of oxidising agents and is therefore, called as oxidising smog.
Formation of Photochemical Smog
![]()
Oxygen atoms combine with air (O2) and form O3 .
O(g) + O2(g) ↔ O3(g)
NO(g) + O3(g) → NO2(g) + O2(g)
![]()
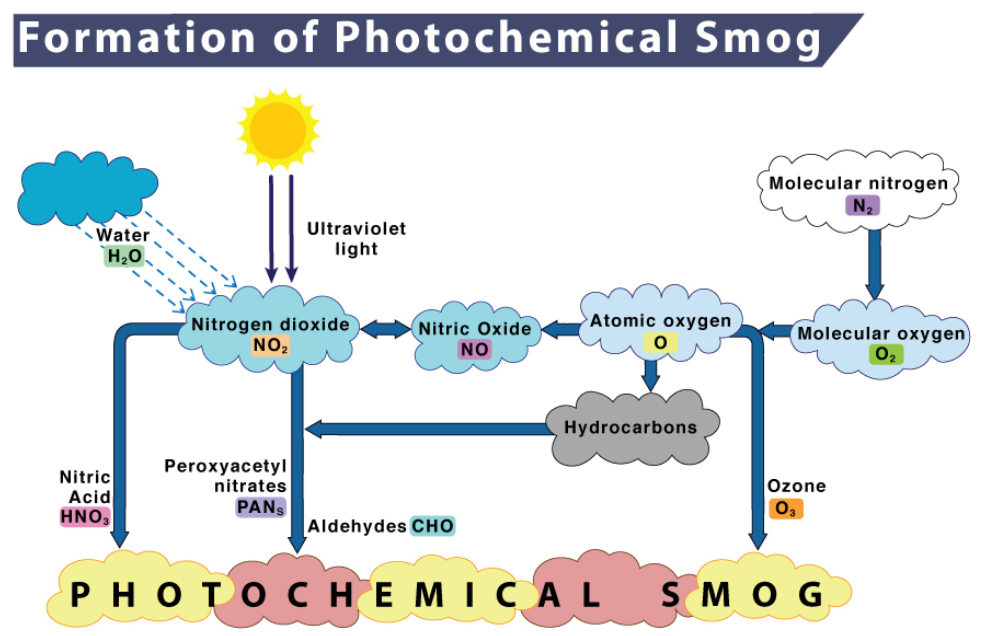
Harmful effects of photochemical smog:
(i) It can cause cough, bronchitis, irritation of respiratory system etc.
– To control this type of pollution the engines of the automobiles are fitted with catalytic converters to check the release of both oxides of nitrogen and hydrocarbons in the atmosphere.
– Some plants like Vitis, Pinus, Juniparus, Quercus, Pyrus can metabolise nitrogen
oxide and therefore, their plantation can be done.
• Stratospheric Pollution
Formation of Ozone: Ozone in the stratosphere is produced by UV radiations. When UV – radiations act on dioxygen (02) molecules, Ozone is produced.
![]()
![]()
Ozone is thermodynamically unstable and decomposes to molecular oxygen. Thus there exists an equilibrium between production and decomposition of Ozone molecules.
Depletion of Ozone layer:
Ozone blanket in the upper atmosphere prevent the harmful UV radiations from reaching earth.
But in recent years, there have been reports of depletion of this layer due to presence of ,certain chemicals in the stratosphere. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), nitrogen oxides, chloride, CCl4 etc. are the chemicals responsible for depletion.
Cl2CF2 → •Cl + •CClF2
•Cl + O3 → ClO• + O2
ClO• + O• → •Cl + O2
Chlorofluorocarbons dissociate in the presence of light gives chlorine free radicals which catalyse the conversion of ozone into oxygen.
Effects of the depletion of Ozone layer:
(i) This leads to many diseases like skin cancer, sunburn, ageing of skin, cataract etc.
(ii) UV radiations can kill many phytoplanktons, damage the fish productivity.
(iii) It can decrease moisture content of the soil by increasing the evaporation of surface water.
(iv) UV radiations can damage paints and fibres, causing them to fade faster.

 Ritan Sheth
Ritan Sheth
