- Books Name
- Ritan Sheth Chemistry Book
- Publication
- Ritan Sheth
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Chemistry
CHAPTER – 4
CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
KÖSSEL-LEWIS APPROACH TO CHEMICAL BONDING
• Chemical Bond
The force that holds different atoms in a molecule is called chemical bond.
• Octet Rule
Atoms of different elements take part in chemical combination in order to complete their octet or to attain the noble gas configuration.
• Valence Electrons
It is the outermost shell electron which takes part in chemical combination.
• Facts Stated by Kossel in Relation to Chemical Bonding
— In the periodic table, the highly electronegative halogens and the highly electro-positive alkali metals are separated by noble gases.
— Formation of an anion and cation by the halogens and alkali metals are formed by gain of electron and loss of electron respectively.
— Both the negative and positive ions acquire the noble gas configuration.
— The negative and positive ions are stabilized by electrostatic attraction Example,
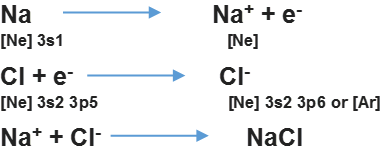
• Modes of Chemical Combination
— By the transfer of electrons: The chemical bond which formed by the complete transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another is termed as electrovalent bond or ionic bond.
— By sharing of electrons: The bond which is formed by the equal sharing of electrons between one or two atoms is called covalent bond. In these bonds electrons are contributed by both.
— Co-ordinate bond: When the electrons are contributed by one atom and shared by both, the bond is formed and it is known as dative bond or co-ordinate bond.

 Ritan Sheth
Ritan Sheth
