- Books Name
- Ritan Sheth Chemistry Book
- Publication
- Ritan Sheth
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Chemistry
IONIZATION OF ACIDS AND BASES
Strength of acid or base is determined with the help of extent of ionization in aqueous solution.
pH Scale: Hydrogen-ion concentration are measured as the number of gram ions of hydrogen ions present per litre of solution. Since these concentrations are usually small, the concentration is generally expressed as the pH of the solution. pH being the logarithm of the reciprocal of the hydrogen ion concentration.
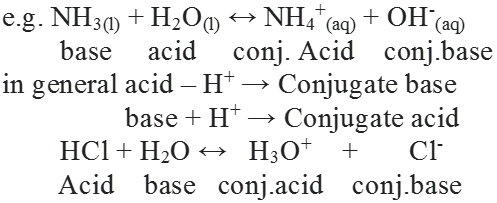
• Di and Polybasic Acids
Acids which contain more than one ionizable proton per molecule are called Dibasic acids or polybasic acids or polyprotic acids.
Common examples are oxalic acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid etc.
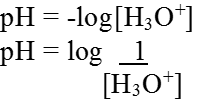
The pH range at 25º C is taken as 0 to 14.
pH = 7 Neutral
pH > 7 Basic
pH < 7 Acidic
The ionization reaction for a dibasic acid can be represented as:
H2X (aq) ↔ H+(aq) + HX-(aq)
HX-(aq) ↔ H+(aq) + X2-(aq)
Their equilibrium constant can be written as
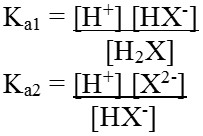
Ka1 and Ka2 are called first and second ionization constants respectively
For dibasic acid Ka1 > Ka2
Factors Affecting Acid Strength
When the strength of H-A bond decreases

The energy required to break the bond decreases, H-A becomes a stronger acid.
As the size of A increases down the group, H-A bond strength decreases and so the acid strength increases.
In a period, as the electronegativity of A increases, the strength of the acid increases.

• Common Ion Effect
If in a aqueous solution of a weak electrolyte, a strong electrolyte is added having an ion common with the weak electrolyte, then the dissociation of the weak electrolyte is decreased or suppressed. The effect by which the dissociation of weak electrolyte is suppresed is known as common ion effect.
CH3COOH(aq) ↔ CH3COO-(aq) + H+(aq)
• Hydrolysis of Salts and the pH of their Solutions
As per the hydrolysis formula,
For the salt of weak acid and weak base like CH3COONa
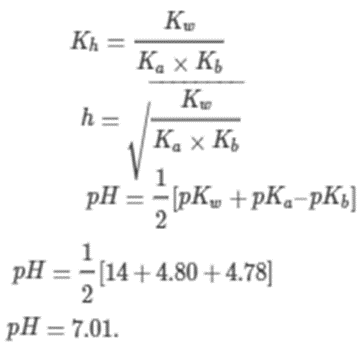
CH3COO- + Na+ H2O ↔ CH3COOH + Na+ + OH-
CH3COO- + H2O ↔ CH3COOH + OH-
Or,
After hydrolysis solution will be basic pH > 7
In this type of hydrolysis only anions of salt take part in the hydrolysis it is known as anionic hydrolysis.
Hydrolysis of weak acid and weak base
Salts belong to this type are CH3COONH4, (NH4)2CO3 etc.
CH3COONH4 + H2O ↔ CH3COOH + NH4OH
Or, CH3COO- + NH4+ + H2O ↔ CH3COOH + NH4OH
pH of the solution depends upon the relative strengths of acid and base.

 Ritan Sheth
Ritan Sheth
