- Books Name
- Ritan Sheth Chemistry Book
- Publication
- Ritan Sheth
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Chemistry
LIQUIFACTION OF GASES
Liquifaction of gases can be achieved either by lowering the temperature or increasing the pressure of the gas simultaneously.
Thomas Andrews plotted isotherms of C02 at various temperatures shown in figure.
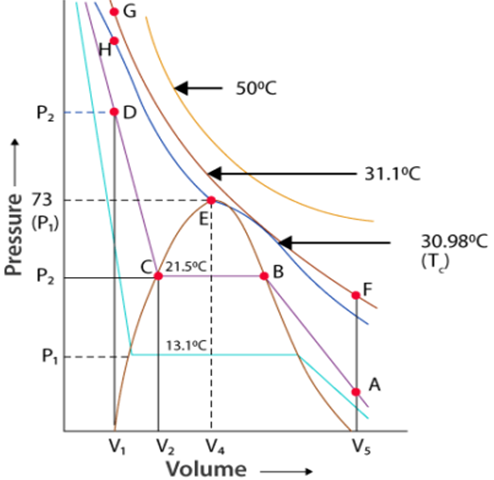
Critical Temperature (Tc): It is defined as that temperature above which a gas cannot be liquified however high pressure may be applied on the gas.
Tc = 8a/27bR
(Where a and b are van der Waals constants)
Critical Pressure (Pc): It is the pressure required to Liquify the gas at the critical temperature.
Pc = a/27b2
The volume occupied by one mole of the gas at the critical temperature and the critical pressure is called the critical volume (Vc).
For Example. For C02 to Liquify.
Tc = 30.98°C
Pc = 73,9 atm.
Vc = 95-6 cm3/mole
All the three are collectively called critical constants.

 Ritan Sheth
Ritan Sheth
