- Books Name
- Ritan Sheth Chemistry Book
- Publication
- Ritan Sheth
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Chemistry
Chapter 2: STRUCTURE OF ATOM
DISCOVERY OF SUB -ATOMIC PARTICLES
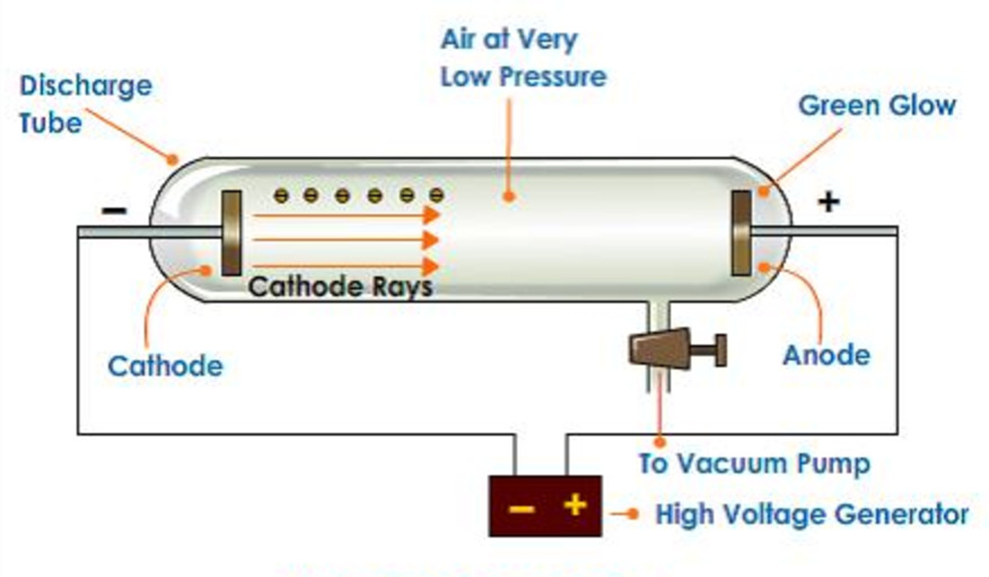
In 1879, William Crooks studied the conduction of electricity through gases at low pressure. He performed the experiment in a discharge tube which is a cylindrical hard glass tube about 60 cm in length. It is sealed at both the ends and fitted with two metal electrodes as shown in Fig. 2.1.
![]()
The electrical discharge through the gases could be observed only at very low pressures and at very high voltages.
The pressure of different gases could be adjusted by evacuation. When sufficiently high voltage is applied across the electrodes, current starts flowing through a stream of particles moving in the tube from the negative electrode (cathode) to the positive electrode (anode). These were called cathode rays or cathode ray particles.
• Properties of Cathode Rays
(i) Cathode rays travel in straight line.
(ii) Cathode rays start from cathode and move towards the anode.
(iii) These rays themselves are not visible but their behaviour can be observed with the help of certain kind of materials (fluorescent or phosphorescent) which glow when hit by them.
(iv) Cathode rays consist of negatively charged particles. When electric field is applied on the cathode rays with the help of a pair of metal plates, these are found to be deflected towards the positive plate indicating the presence of negative charge.
(v) The characteristics of cathode rays do not depend upon the material of electrodes and the nature of gas present in the cathode ray’tube.
• Determination of Charge/Mass (elm) Ratio for Electrons
J. J. Thomson for the first time experimentally determined charge/mass ratio called elm ratio for the electrons. For this, he subjected the beam of electrons released in the discharge tube as cathode rays to influence the electric and magnetic fields. These were acting perpendicular to one another as well as to the path followed by electrons.
According to Thomson, the amount of deviation of the particles from their path in presence of electrical and magnetic field depends upon following factors:
(i) Greater the magnitude of the charge on the particle, greater is the interaction with the electric or magnetic field and thus greater is the deflection.
(ii)The mass of the particle — lighter the particle, greater the deflection.
(iii) The deflection of electrons from their original path increases with the increase in the voltage across the electrodes or strength of the magnetic field.
By carrying out accurate measurements on the amount of deflections observed by the electrons on the electric field strength or magnetic field strength, Thomson was able to determine the value of
e/me = 1.758820 x 1011 C kg-1 where me = Mass of the electron in kg
e = magnitude of charge on the electron in coulomb (C).
• Charge on the Electron
R.A. Millikan devised a method known as oil drop experiment to determine the charge on the electrons.

• Discovery of Proton—Anode Rays
In 1886, Goldstein modified the discharge tube by using a perforated cathode. On reducing the pressure, he observed a new type of luminous rays passing through the holes or perforations of the cathode and moving in a direction opposite to the cathode rays. These rays were named as positive rays or anode rays or as canal rays. Anode rays are not emitted from the anode but from a space between anode and cathode.
• Properties of Anode Rays
(i) The value of positive charge (e) on the particles constituting anode rays depends upon the nature of the gas in the discharge tube.
(ii) The charge to mass ratio of the particles is found to depend on the gas from which these originate.
(iii) Some of the positively charged particles carry a multiple of the fundamental unit of electrical charge.
(iv) The behaviour of these particles in the magnetic or electric field is opposite to that observed for electron or cathode rays.
• Proton
The smallest and lightest positive ion was obtained from hydrogen and was called proton. Mass of proton = 1.676 x 10-27 kg
Charge on a proton = (+) 1.602 x 10-19 C
• Neutron
It is a neutral particle. It was discovered by Chadwick (1932).
By the bombardment of thin sheets of beryllium with fast moving a-particles he observed that highly penetrating rays consist of neutral particles which were named neutrons.

 Ritan Sheth
Ritan Sheth
