- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Biology Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Biology
ATP and NADPH used
DARK REACTION / PCR OR BLACKMAN REACTION
The light independent or dark reaction of photosynthesis reduces the carbon dioxide to glucose.
These reactions take place in the stroma of chloroplast where light independent enzymes are present.
Although this process does not require light, it depends upon the products of light reaction of photosynthesis.
The energy required for the reduction of carbon dioxide is derived from ATP and hydrogen from NADPH (formed in the light reaction of photosynthesis).
The dark reaction occurs through one of the following three methods under different conditions by various plants:
(1) Calvin cycle or C3 cycle
(2) Hatch and Slack cycle
(3) CAM cycle
(1)CALVIN CYCLE or C3 CYCLE
This process comprises a series of reactions controlled by enzymes.
The sequence of these reactions were determined in Chlorella and Scenedesmus by Calvin, Benson and Bassham using radioactive carbon 14C, and techniques like chromatography and autoradiography.
Therefore, it is also known as Calvin cycle or Calvin-Benson cycle.
First product of CO2 fixation is a 3C compound called 3-phosphoglyceric acid (PGA).
This cycle occurs in all photosynthetic plants; whether they have C3 or C4 or CAM pathways. The enzyme for CO2 fixation is RuBisCO.
It is a large enzyme found in stroma.
It is most abundant protein on earth and constitutes 16% of chloroplastic protein.
It shows bifunctional nature having both carboxylase and oxygenase activity.
The dark reaction is also known as Blackman's reaction.
The whole reaction can be studied in three parts:
(i) Carboxylation (Acceptance of CO2 by RuBP i.e., CO2 acceptor -it is a 5C compound),
(ii) Reduction, (iii) Regeneration of RuBP.
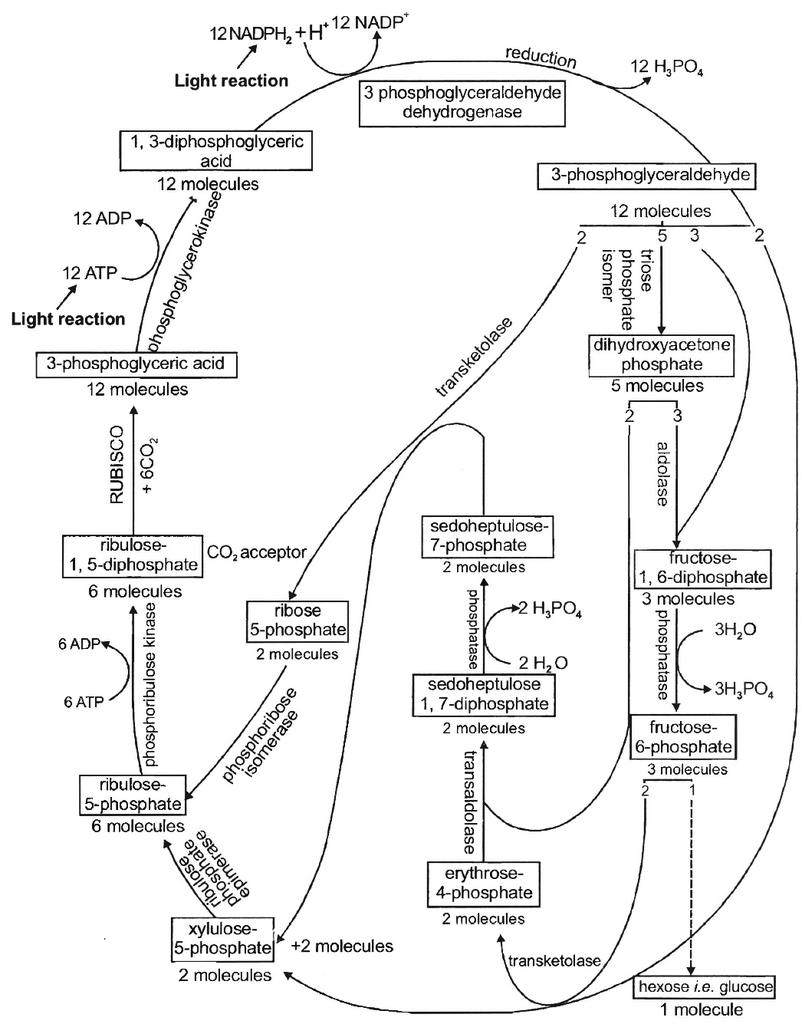
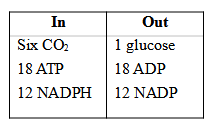
18 ATP and 12 NADPH + H+ are used for the formation of a molecule of glucose (or to reduce 6CO2).
During this process, 264 grams of CO2 and 216 grams of water are used for producing 108 grams of water and 192 grams of O2.
End product of photosynthesis. Hexose sugars are considered as the end products of photosynthesis. Generally, hexose sugar is stored in the form of starch, a long and branched chain of repeating units of simple sugars (usually glucose). Besides, under certain circumstances phosphoglyceraldehyde may also directly or indirectly give rise to fats and proteins in addition to hexose sugars.
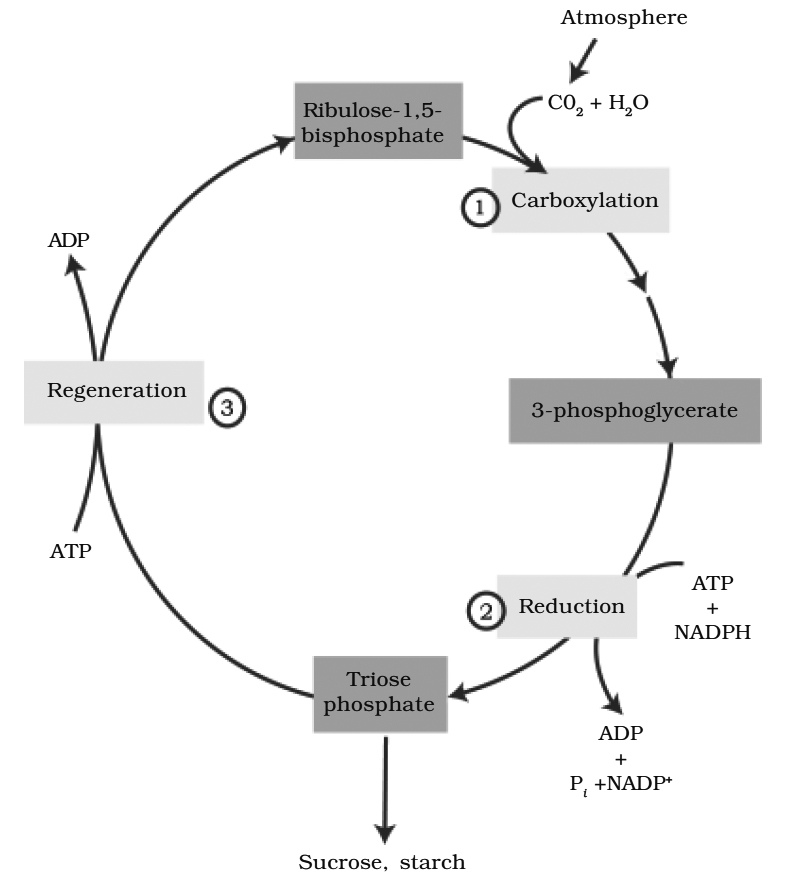
(1) carboxylation, during which CO2 combines with ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate;
(2) reduction, during which carbohydrate is formed at the expense of the
photochemically made ATP and NADPH; and
(3) regeneration during which the CO2 acceptor ribulose 1, 5-bisphosphate is formed again so that the cycle continues.

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
