- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Biology Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Biology
URINE FORMATION
Nephric excretion involves the formation of urine. Urine formation occurs in three steps -glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion.
1. Glomerular Filtration (Ultrafiltration):
Blood present in the glomerular 'capillaries is separated from the capsular space of Bowman's capsule by
(i) Endothelial covering of blood vessels.
(ii) Basement membrane of blood vessel.
(iii) Basement membrane of visceral layer
(iv) Visceral layer or inner wall of Bowman's capsule.
Therefore, the actual barrier between blood and capsular space consists of two basement membranes which are, however, permeable to small sized molecules.
Development of Filtration Pressure:
Blood flows through glomerular capillaries under a pressure.
The pressure is due to two reasons:
(i) Wider diameter of afferent arteriole as compared to diameter of efferent arteriole.
(ii) Natural arterial pressure caused by pumping activity of heart. Blood pressure in glomerular blood is about 60 mm Hg, this is called glomerular hydrostatic pressure (GHP). Osmotic concentration of proteinaceous content of glomerular blood is equivalent to 30 mm Hg, this is called blood colloidal osmotic pressure (BCOP). Pressure of interstitial fluid and pressure of renal filtrate is collectively called capsular hydrostatic pressure (CHP =20 mmHg). The pressure being exerted on glomerular blood for undergoing filtration is called glomerular filtration pressure (GFP). It is about 10 mm Hg.
or, GFP = GHP -(BCOP + CHP)
= 60 – (30 + 20) = 10 mmHg
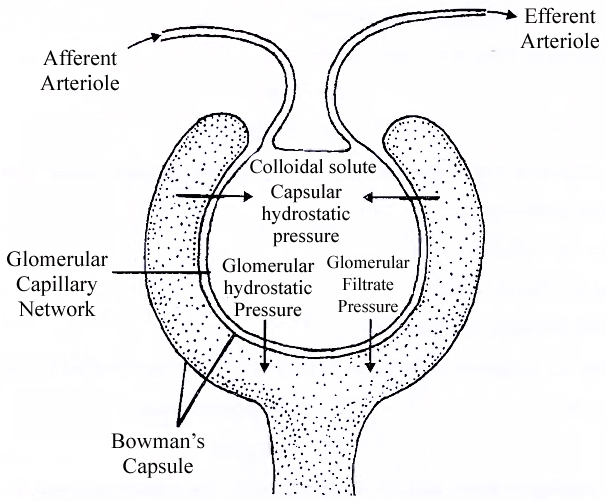
Ultrafiltration:
As there is net higher hydrostatic pressure of 10 mm Hg in the lumen of glomerular capillaries as compared to lumen of Bowman's Capsule, the filterable components of blood are passed out of the glomerular capillaries.
They pass through endothelial fenestrations, basement membranes and filtration slits of podocytes to enter the lumen of Bowman's capsule.
The phenomenon is called nephric or glomerular filtration.
About 1100-1200 ml of blood is put to filtration in the two kidneys every minute which constitutes roughly 1/5th of the blood pumped out by each ventricle of the heart in a minute.
It produces a glomerular or nephric filtrate of about 125 ml/min or 180 Uday.
The rate of filtration is called glomerular filtration rate or GFR.
Nephric filtrate consists of water, various electrolytes (Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, PO43–), glucose, amino acids, hormones, vitamins, urea, creatinine, uric acid etc.
It is alkaline like blood but excludes large sized particles and structures like fats, proteins, platelets, leucocytes and erythrocytes.
Separation of small volume solutes from large volume solutes and components due to filtration through small sized pores or slits by the application of pressure is called ultrafiltration.
Autoregulation of Glomerular Filtration:
There are three methods by which renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) are automatically regulated.
(a) Myogenic Autoregulation:
A rise in blood pressure should normally increase blood flow through glomeruli.
However, stretching of the vascular wall increases passage of Ca2+ ions from extracellular fluid into the cells resulting in their contraction.
Contraction checks overstretching of vascular walls and raises vascular resistance so that rate of blood flow and GFR are brought down to normal.
(b) Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA):
The apparatus becomes active when there is decrease in renal blood pressure or decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
It promotes release of renin from Juxta-glomerular cells.
Renin converts protein angiotensinogen into peptide angiotensin.
Angiotensin is a hormone that raises glomerular blood pressure through constricting efferent arterioles resulting in restoring GFR.
It also brings about release of aldosterone.
(c) Neural Control:
Blood vessels of the kidney are innervated by nerve fibres of the sympathetic nervous system.
When activated, the nerve fibres bring about constriction of renal arteries and cause decrease in renal blood flow as well as glomerular filtration rate.

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
