Taxonomic Aids
Taxonomic studies of various plant, animal, and other organism species are useful in agriculture, forestry, and industry, and they aid in our understanding of biodiversity. These studies necessitate accurate organism taxonomy and identification. Identifying organisms necessitates extensive laboratory and field research. Taxonomic aids are collections of samples or preserved species that aid in the extended investigation for taxonomic hierarchy identification. The primary source of taxonomic studies is the collection of genuine specimens of plant and animal species. These are also necessary for systematics training and are crucial to studies. It's used to classify organisms, and the data acquired is saved alongside the specimens. In some situations, the specimen is saved for further research. Some popular taxonomic aids are discussed below
(I) Herbarium: A herbarium is a reference collection of properly selected and dried plants that are connected to standard-sized paper sheets and filed systematically so that they can be quickly found for study. It's a repository for plant specimens that have been collected, dried, pressed, and preserved on sheets. These sheets are organized according to a widely accepted classification scheme. These specimens, coupled with their descriptions on herbarium sheets, form a repository or storehouse for future use. A label on the herbarium sheets provides information such as the date and location of collection, English, local, and botanical names, family, and collector's name, among other things. In taxonomic investigations, herbaria also function as rapid referral systems.
The Museum of Natural History in Paris, The Royal Botanic Gardens in Kew, England, The New York Botanical Garden, and The Komarov Botanical Institute in St. Petersburg, Russia, have some of the world's largest herbaria, each having 7 to 9.5 million specimens.
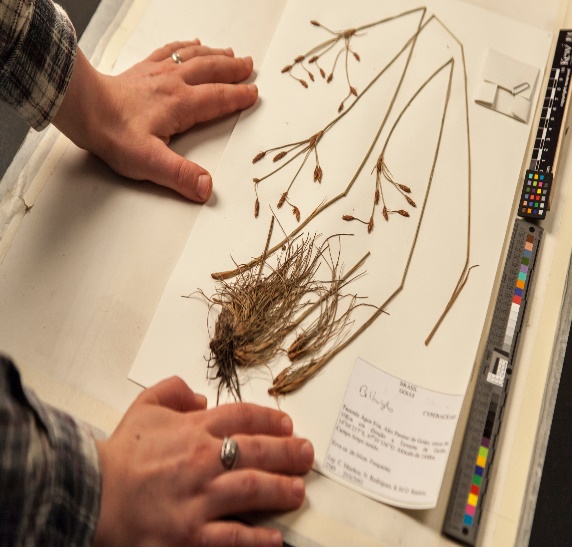
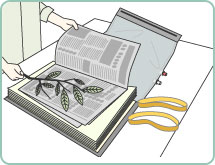
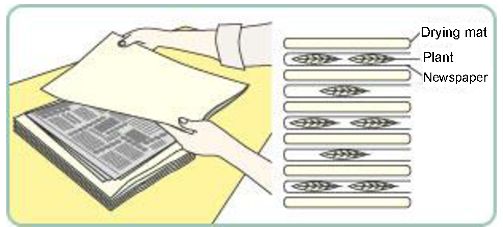
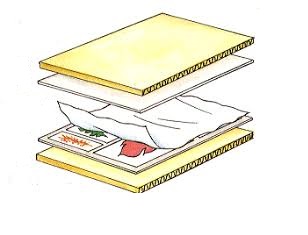

Figure 3: Different stages of herbarium preparation.
(II) Botanical Gardens:
For reference, these specialty gardens have collections of living plants. Plant species are planted in these gardens for identification, and each plant is labeled with its botanical/scientific name as well as its family. Botanical gardens commit their resources to plant research and conservation, as well as public awareness of the world's plant diversity. Royal Botanical Garden, Kew (England), Indian Botanical Garden, Howrah (India), and National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow are all well-known botanical gardens.
(III) Museum:
A museum is a building where historical, artistic, or scientific objects are displayed, maintained, or researched. Modern museums are designed to collect, preserve, interpret, and show objects of aesthetic, cultural, or scientific significance for public study and education. Biological museums are most commonly found at educational institutions like schools and colleges. For study and reference, museums have collections of preserved plant and animal specimens. Preservative solutions are used to preserve specimens in containers or jars. Dry specimens of plants and animals can also be preserved. After capturing, killing, and pinning insects, they are kept in insect boxes. Stuffed and preserved larger creatures, such as birds and mammals, are common. Animal skeletons are frequently shown in museums.With 19 museums and galleries, the National Zoological Park, and many examination stations, the Smithsonian is the world's largest exploration and museum complex. The company's headquarters are in Washington, D.C.

(IV) Zoological Parks:
Zoological parks are protected areas where animals are kept under human supervision and cared for. In zoological parks, many endangered species that are on the verge of extinction are rescued. These are facilities where wild animals are housed in safe conditions under human supervision so that we can learn about their eating habits, behavior, etc. Animals at zoos are kept in settings that are as close to their natural habitats as possible. These parks also contribute to the preservation of the natural balance by increasing the percentage of rainfall. They play a critical role in the conservation of animals. There are a total of 164 zoological parks in India. The Arignar Anna Zoological Park in Chennai is India's largest zoological park covering about 1300 acres with rare species of flora and fauna.

(V) Key:
Keys are used foridentifying and classifying various plants and animals based on their similarities and variances in characteristics. As a result, only one is accepted while the other is rejected. A lead is a name given to each assertion in the key. For identification purposes, separate taxonomic keys are necessary for each taxonomic group such as family, genus, and species. The majority of keys are analytical these are used to distinguish between classes, orders, families, genera, and species. It is split into pairs of characters that are either present or absent.
Other methods of recording descriptions include flora, manuals, monographs, and catalogs. They also assist with proper identification. Flora includes a detailed description of a certain area's habitat and plant distribution. These provide an index to the plant species that can be found in a certain area. A Catalogue is a comprehensive list, pamphlet, or register that contains a collection of traits and their variants found in diverse taxa.Manuals are important for identifying the names of species that can be found in a given area. Monographs are documents that focus on a single taxon.

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
