- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Biology Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Biology
Heart Beat: Regulation
Normal activities of the heart are regulated intrinsically, i.e., auto regulated by specialised muscles (nodal tissue), hence the heart is called myogenic.
A special neural centre in the medulla oblangata can moderate the cardiac function through autonomic nervous system (ANS).
Neural signals through the sympathetic nerves (part of ANS) can increase the rate of heart beat, the strength of ventricular contraction and thereby the cardiac output.
On the other hand, parasympathetic neural signals (another component of ANS) decrease the rate of heart beat, speed of conduction of action potential and thereby the cardiac output.
This happens because these nerves release chemicals (hormones) when stimulated. Adrenal medullary hormones can also increase the cardiac output.
(i) High levels of potassium and sodium ions decrease heart rate and strength of contraction.
(ii) An excess of calcium ions increases heart rate.
(iii) Increased body temperature during fever increases heart rate.
(iv) Strong emotions such as fear, anger and anxiety increase heart rate, resulting in increased blood pressure.
(v) Mental states such as depression and grief decrease heart rate.
(vi) The heart beat is somewhat faster in females.
(vii) The heart beat is fastest at birth, moderately fast in youth, average in adulthood and above average in old age.
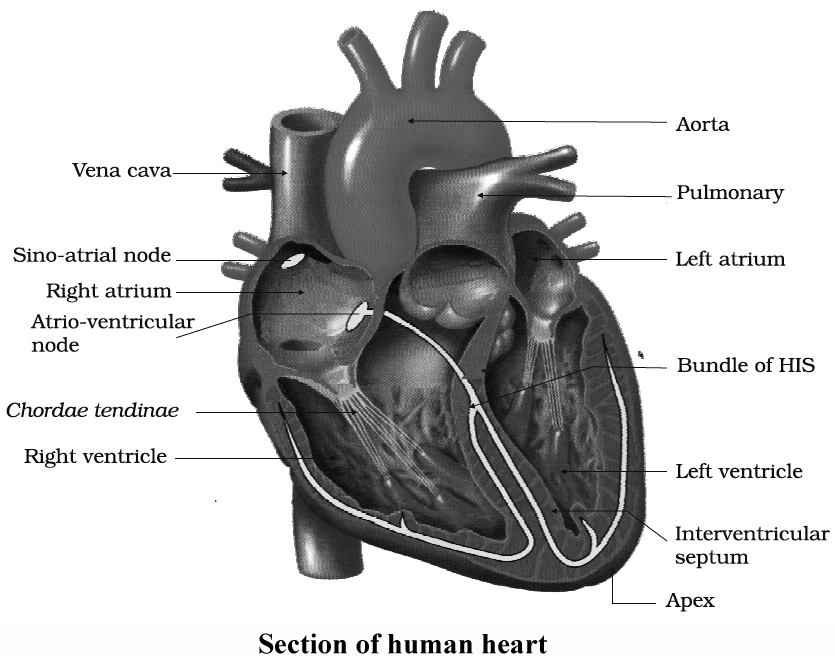
Heart Sounds
These are caused due to sudden closure of the valves of heart. There are mainly two sounds.
(i) First Sound : Occurs at the onset of ventricular systole and is caused due to the sudden closure of AV valves and the ejection of blood from the ventricles. It is dull and pronounced as L -U -B.
(ii) Second Sound : Occurs at the onset of ventricular diastole and is caused by sudden closure of the semilunar valves of the aorta and pulmonary artery.
It is short and sharp like the word D -U -P.
The sequence of both these sounds is like this : first sound ® second sound ® pause; first sound ® second sound ® pause; so on. Sometimes if damage occurs as in rheumatic fever, blood may leak out through the valrves and a characteristic sound mur-mur is produced.
Pulse Rate
The blood is pumped from the ventricles of the heart into the aorta to be distributed to all the parts of the body.
This happens during the ventricular systole and is repeated after every 0.8 seconds.
The blood from aorta then goes to other arteries of the body.
This causes a rhythmic contraction of the aorta and its main arteries and is felt as regular jerks or pulse in them.
It can be felt in the regions where arteries are present superficially like wrist, neck and temples.
The pulse rate is, therefore, same as that of heart beat rate.

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
