- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Biology Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Biology
PHYLUM MOLLUSCA
Phylum mollusca is the second largest phylum in animal kingdom which includes over 60,000 species. General characters are :
- Molluscs are terrestrial, aquatic (fresh water or marine) triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical, schizocoelic and unsegmented animals.
- Most molluscs secrete a shell of calcium carbonate that protects and supports their soft tissues.
- The body is organised into three general regions: head, foot and visceral hump.
- The visceral hump contains the digestive tract and other visceral organs.
- The body is covered by a soft and spongy skin fold called mantle which secretes the shell.
- The space between the hump and the mantle is called mantle cavity in which feather like gills are present.
- Molluscs typically employ a feeding organ called radula which is armed with rows of chitinous teeth. The radula is protruded from the mouth and worked back and forth to rasp the food into fine particles.
- Circulatory system is mainly of open type but some reduced sinuses are present. Respiratory pigment is haemocyanin.
- Respiration occurs by feather like gills, pulmonary sac or both, or through general body surface.
- Excretion occurs by paired Organ of Bojanus. Another excretory organ called Keber's organ (Pericardial gland) is also present in Unioalongwith paired organ of Bojanus. It pours the waste into pericardium from where the waste is carried to the organ of Bojanus that opens out through mantle cavity.
- Sense organs include eyes, statocysts and osphradia (chemoreceptor to test chemical nature of water).
- Reproduction sexual, adults can be dioecious (unisexual) or monoecious (bisexual or hermaphrodite) Fertilization is generally external, development is direct or through free larval forms like trochophore, veliger (in Pila), glochidium (in Unio) -an ectoparasite on fishes.
Pila produces 2 types of sperms :
(i) Eupyrene -Motile and functional sperms, 25 µm long, thread like with a single cilium.
(ii) Oligopyrene -Non-motile and non-functional sperms, 32.5 µm long, spindle shaped with 4-5 cilia.
CLASSIFICATION
Molluscs' classification is mainly on the basis of shell and foot.
Concept Builder
(i) Architeuthis (Giant AtJantic squid) is the largest and heaviest among invertebrates, 55 feet length.
(ii) Nautilus is the only cephalopod with external shell, so ink glands are absent.
(iii) The colour change in cephalopods occurs due to chromatophores.
Phylum Mollusca
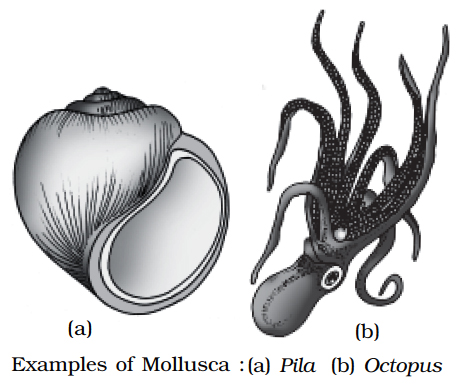
Molluscs are a diverse group of organisms that play a vital role in the global ecology. A calciferous shell is found on many creatures in this phylum. The bodies are usually soft and protected by a hard exoskeleton. They can be found both on land and in the deepest parts of the ocean. This is the second-largest phylum of animals. Molluscs are organ-system-organized terrestrial or aquatic (marine or freshwater) animals. They are animals that are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, and coelomate. A calcareous shell covers the body, which is unsegmented with a distinct head, muscular foot, and visceral hump. Over the visceral hump, a soft and spongy layer of skin forms a mantle.The mantle cavity is the region between the hump and the mantle, and it contains feather-like gills. They have breathing and excretory systems. Sensory tentacles can be found in the anterior head region. The radula, a file-like rasping organ in the mouth, is used for feeding. They are both a food and a jewellery source. The firm shells are used to create stunning jewellery. Even though it sounds strange, these are also raised as pets in some parts of the world. Bivalve and gastropod pearls are particularly valuable because they are lined with nacre. Natural pearls are generated when a small foreign object becomes lodged between the mollusc's mantle and shell.Bivalve molluscs are useful as freshwater and marine bioindicators. However, not all molluscs are beneficial to humans. Snails and slugs, for example, are considered pests.They are usually dioecious and oviparous with indirect development. Examples: Pila (Apple snail), Pinctada (Pearl oyster), Sepia (Cuttlefish), Loligo (Squid), Octopus (Devilfish), Aplysia (Seahare), Dentalium (Tusk shell), and Chaetopleura (Chiton).

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
