- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Biology Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Biology
Functions of the Tubules
Types of Nephron
A kidney has two types of nephrons-cortical and juxtamedullary. They are held together with the help of connective tissue
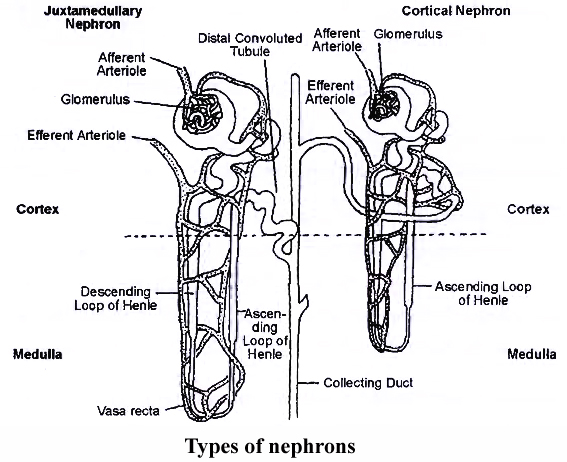
(a) Cortical Nephrons:
They constitute about 85%, of the total nephrons.
Cortical nephrons are smaller in size with major part lying in the cortex.
The tubule is much coiled.
Loop of Henle is short and extends into medulla to a short distance.
Vasa recta are absent or highly reduced.
Glomeruli lie in the outer cortex.
(b) Juxtamedullary Nephrons:
They are approximately 15% of the total and are present at the junction of cortex and medulla region of kidney.
They have large size, less coiling and a long loop of Henle.
Glomeruli occur in the inner cortex.
The long loops of Henle placed deep in the medulla.
Vasa recta occur over the loops of Henle.
Juxtamedullary nephrons become active during shortage of water.
They increase water reabsorption and, therefore, control the volume of plasma.
The system usually works under stress conditions.
Structure of Nephron (Renal Tubule, Uriniferous Tubule)
Nephron or uriniferous tubule is the structural and functional unit of kidney.
It is about 3 cm long and 20-60 mm in diameter. Each nephron consists of two parts -Glomerulus and renal tubule (Bowman's capsule, PCT, Henle's loop and DCT)
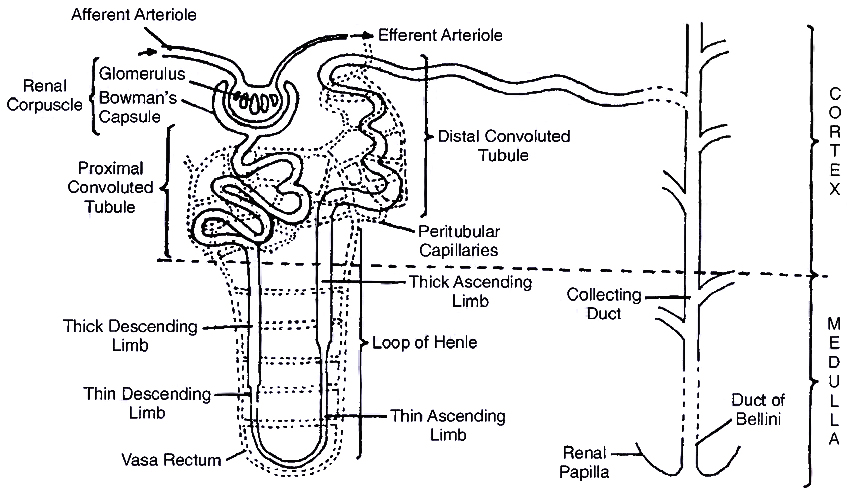
1. Bowman's Capsule:
It is blind double walled cup-shaped structure. The two walls of Bowman's capsule are inner visceral and outer parietal. Both are single layered and are supported over basement membrane.
(i) Visceral Layer (Inner Wall):
It consists of flat squamous epithelial cells on the periphery and specialised podocytes in the remaining part.
A podocyte has a number of interdigitated evaginations called pedicels or feet.
The pedicels rest over the basement membrane.
They enclose slit pores or filtration slits.
The diameter of these slits is about 25 nm.
Pedicels also possess contractile filaments which help in passage of filtrate through the filtration slits.
(ii) Parietal Layer (Outer Wall):
It consists of flat squamous epithelium.
The space between the two layers of Bowman's capsule is called lumen or capsular space.
Glomerulus:
It is a tuft of capillaries formed by fine blood vessels lying in the Bowman's capsule.
Glomerulus receives blood from an afferent arteriole.
Blood is taken away from the glomerulus by an efferent arteriole.
The latter has a narrower diameter than that of afferent arteriole.
Blood vessels of glomerulus are similar to those of blood capillaries in being covered by a single layer of endothelial cells.
However, they are 100-500 times more permeable with fenestrations or pores having a size of 50-100 nm.
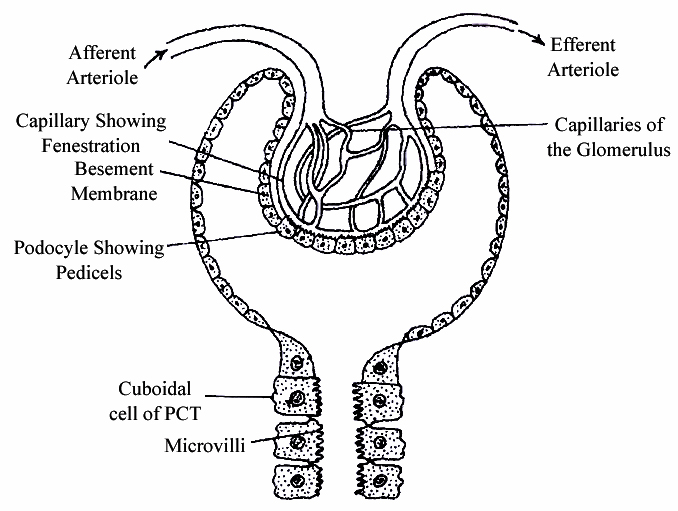
Malpighian body (renal corpuscle) : The complex formed by glomerulus, connective tissue and Bowman's capsule is called Malphighian body or renal corpuscle.
2. Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT):
Lower part of Bowman's capsule leads into proximal convoluted tubule.
The latter is present in the cortex.
It is twisted and surrounded by peritubular blood capillaries.
PCT is lined by cuboidal epithelium having brush borders with long microvilli for increasing absorptive area.
The cells contain abundant mitochondria and food reserve for providing energy to perform active absorption and secretion.
3. Loop of Henle:
Loop of Henle is made of two parallel limbs joined by curved base.
There is a descending limb and an ascending limb.
(i) Descending Limb:
Thick segment constitutes about four-fifth of the descending limb.
It lies both inside cortex and medulla.
The cells lining it are cuboidal.
They have sparse microvilli and fewer mitochondria indicating that active absorption and secretion are absent.
Thin segment is narrow part of descending limb.
It lies in the medulla and is lined by flat epithelial cells having sparse microvilli and few mitochondria.
Thin segment gets curved to become part of ascending limb.
(ii) Ascending Limb:
Ascending limb consists of thin segment in the proximal part and thick segment afterwards.
Thin segment is lined by flat epithelial cells which allow passive diffusion of some solutes (e.g., Na+, Cl–) depending upon their concentration gradient.
Thick segment of ascending limb is wider and lined by cuboidal cells having microvilli as well as mitochondria.
Thick ascending segment is involved in active secretion of NaCl in the medulla.
Vasa Recta : Loop of Henle is covered by a stair case of network of blood capillaries arising from efferent glomerular arteriole called vasa recta. It forms a counter-current system with the loop of Henle having ascending branch in the area of descending limb and descending branch in the area of ascending limb.
4. Distal Convoluted Tubule (OCT):
Distal convoluted tubule is highly coiled part of nephron and lies close to Malpighian body.
The epithelial lining of the distal convoluted tubule consists of cuboidal cells having sparse microvilli and deep mitochondria.
Distal convoluted tubule is covered by peritubular blood capillaries.
The last part of distal nephron is nearly straight, called connecting or junctional tubule and open into collecting duct.
Collecting Ducts:
Each nephron opens into a wider collecting tubule in the area of cortex.
Collecting tubules are lined by specialized cuboidal epithelium with very few microvilli.
They open into still wider collecting ducts.
Collecting ducts enter medulla and form ducts of Bellini.
The ducts run through renal pyramids.

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
