Epithelial Tissue
Epithelium or epithelia refers to epithelial tissue. This tissue has a free surface that is exposed to either a body fluid or the outside environment and serves as a covering or lining for a body part. The cells are densely packed and there is a little intercellular matrix. Simple epithelium and compound epithelium are two forms of epithelial tissues.
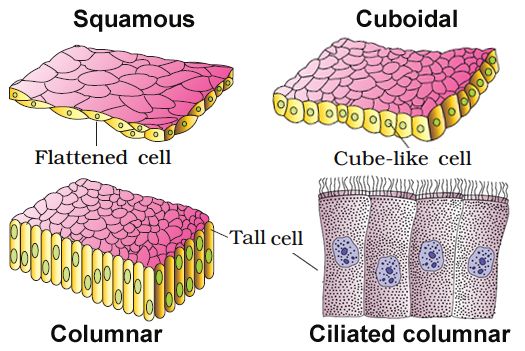
(A) SIMPLE EPITHELIUM: A single layer of cells makes up simple epithelium, which serves as a lining for bodily cavities, ducts, and tubes. Basedon structural modification of the cells, the simple epithelium is further divided into three types. These are
(i) Squamous epithelium: A single thin layer of flattened cells with uneven borders makes up the squamous epithelium. They're present in the walls of blood arteries and the air sacs of the lungs, and they help build diffusion boundaries.
(ii) Cuboidal epithelium: A single layer of cube-like cells makes up the cuboidal epithelium. Its main roles are secretion and absorption, and it is usually found in gland ducts and tubular sections of nephrons in the kidneys. Microvilli are found in the epithelium of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) of the nephron in the kidney.
(iii) Columnar epithelium: A single layer of tall and thin cells makes up the columnar epithelium. Their nuclei are near the bottom of their bodies. Microvilli may exist on a free surface. They help with secretion and absorption and are located in the lining of the stomach and intestine.
(iv) Ciliated epithelium: Ciliated epithelium is defined as columnar or cuboidal cells with cilia on their free surfaces. Their job is to transfer particles or mucus over the epithelium in a precise direction. They're mostly found on the inside of hollow organs like the bronchioles and fallopian tubes.
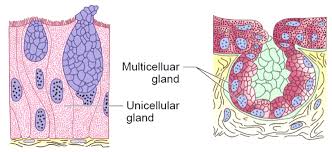
(v) Glandular epithelium: The glandular epithelium is formed when some columnar or cuboidal cells become specialized for secretion.They are divided into two types: unicellular glandular cells (goblet cells of the alimentary canal) and multicellular glandular cells (clusters of cells) (salivary gland). Exocrine and endocrine glands are split into two types based on how they secrete their secretions. Mucus, saliva, earwax, oil, milk, digestive enzymes, and other cell products are secreted by exocrine glands. Ducts or tubes are used to release these products. Endocrine glands, on the other hand, lack ducts. Hormones, which are their products, are secreted straight into the gland's fluid bath.
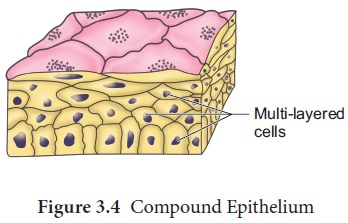
(B) COMPOUND EPITHELIUM: Compound epithelium is made up of multiple layers of cells, therefore it has little function in secretion and absorption. The compound epithelium, like our skin, is made up of two or more cell layers and serves a protective role.Their primary purpose is to protect the body against chemical and mechanical stress. They protect the skin's dry surface, the moist surface of the buccal cavity, the pharynx, the inner lining of the salivary gland, and pancreatic ducts.
The epithelium's cells are bound together by a thin layer of intercellular substance. Specified junctions offer structural and functional linkages between individual cells in practically all animal tissues. In the epithelium and other tissues, there are three types of cell junctions. Tight, adherent, and gap junctions are the three types of junctions. Tight connections prevent chemicals from leaking through a cell's surface.Adhering junctions bind cells by gluing them together. Gap junctions allow cells to communicate with one another by connecting the cytoplasm of neighboring cells, allowing for the rapid movement of ions, small molecules, and occasionally large molecules.Adhering junctions bind cells together by gluing them together.

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
