- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Biology Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Biology
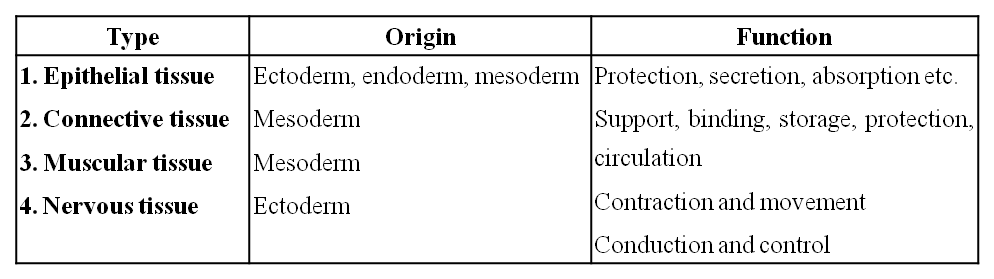
Tissue : A group of cells similar in structure, function and origin.
In a tissue cells may be dissimilar in structure and function but they are always similar in origin.
– Word animal tissue was coined by – Bichat
– N. Grew coined the term for Plant Anatomy.
– Study of tissue – Histology
– Histology word was given by – Mayr
– Father of Histology – Bichat
– Study of tissue is also called Microscopic anatomy.
– Founder of microscopic anatomy – Marcello Malpighi
TYPES OF TISSUES
Based on the location and function the animal tissues are classified into four types :
Chapter 7
STRUCTURAL ORGANISATION IN ANIMALS
In unicellular organisms, a single cell performs all tasks such as digesting, respiration, and reproduction. The same basic duties are carried out by different groups of cells in a well-organized manner in the complex body of multicellular organisms. The body of a basic organism like Hydra is made up of many distinct types of cells, each with thousands of them. The human body is made up of billions of cells that each perform a different purpose. A set of related cells, as well as intercellular chemicals, execute a defined purpose in multicellular creatures. Tissue is the name for this type of arrangement.
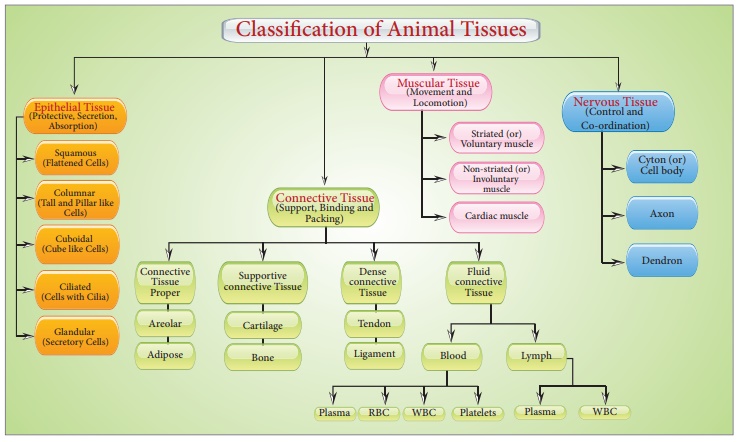
There are just four fundamental types of tissues in all complex creatures. To form an organ such as the stomach, lung, heart, or kidney, these tissues are organized in a certain proportion and pattern. When two or more organs interact physically and/or chemically to fulfill a shared function, they create an organ system, such as the digestive system or the respiratory system. Cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems divide up the work and contribute to the body's overall survival through the division of labor.
Animal Tissues
Cells have different structures depending on their purpose. As a result, the tissues differ and can be divided into four categories:

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
