- Books Name
- ACME SMART COACHING Biology Book
- Publication
- ACME SMART PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Biology
Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic respiration is a process in which there is a complete oxidation of organic substances in the presence of oxygen and releases CO₂ , water and a large amount of energy present in the substrate . This type of respiration is most common in higher organisms .
The aerobic respiration takes place in the mitochondria .The final product of glycolysis , pyruvate is transported from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria .
The crucial events in aerobic respiration are :
( i ) The complete oxidation of pyruvate by the stepwise removal of all the hydrogen atoms , leaving three molecules of CO2
( ii ) The passing on of the electrons removed as part of the hydrogen atoms to molecular O₂ with simultaneous synthesis of ATP
The first t process takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria while the second process is located on the inner membrane of the mitochondria .
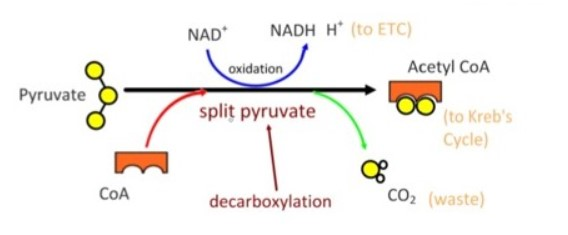
Pyruvate oxidation : Pyruvate , the end product of glycolysis enters mitochondrial matrix through a specific transport protein . It is decarboxylated oxidatively to produce CO₂ and NADH . The product combines with sulphur containing coenzyme A to form acetyl CoA or activated acetate . The reaction occurs in the presence of an enzyme complex pyruvate dehydrogenase . This step is called gateway step or link reaction because acetyl CoA acts as a connecting link between glycolysis and Krebs ' cycle .

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
