- Books Name
- Vision classes Accountancy Book
- Publication
- Vision classes
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Accountancy
Trading and Profit and Loss Account
This account is prepared to determine the profit earned or loss sustained by the business enterprise during the accounting period. In simple words, it is a summary of revenues and expenses of the business and calculates the net figure termed as profit or loss. Trading and Profit and Loss account summarizes the performance for an accounting period. Trading and Profit and Loss account is also an account with Debit and Credit sides.
You can observe that debit balances (representing expenses) and losses are transferred to the debit side of the Trading and a Profit and Loss account and credit balance (representing revenues/gains) are transferred to its credit side.
Relevant Items in Trading and Profit and Loss Account
The different items appearing in the trading and profit and loss account are explained here under:
Items on the debit side
- Opening stock : This is the stock of goods which has been carried forward from the previous year and remains unchanged during the year and appears in the trial balance
- Purchases less returns : Goods, which have been bought for resale appears as purchases on the debit side of the trading account. They include both cash as well as credit purchases. Goods which are returned to suppliers are termed as purchases return. It is shown by way of deduction from purchases and the computed amount is known as Net purchases.
- Wages : Wages are the remuneration paid to workers who are directly engaged in factory for loading, unloading and production of goods and are debited to trading account.
- Carriage inwards/Freight inwards: The items of transport expenses, which are incurred on bringing materials/goods purchased to the place of business are this types of expenses. These items are paid in respect of purchases made during the year and are debited to the trading account.
- Fuel/Water/Power/Gas : These items are used in the production process and hence are part of expenses.
- Packaging material and Packing charges: Packaging material comes in direct expenses as is part of goods sold. However, the packing used for transporting the goods so it is an indirect expense.
- Salaries : Salaries are paid to all the staff for the services for running the business. If salaries are paid in kind by providing certain facilities (called perks) to the employees such as rent free accommodation, meals, uniform, medical facilities should also be regarded as salaries and debited to the profit and loss account.
- Rent paid : The amount of rent paid is shown on the debit side of the profit and loss account. It is all rent paid for the buinding for running a business.
- Interest paid : Interest paid on loans, bank overdraft, renewal of bills of exchange, etc. is an expense and is debited to profit and loss account.
- Commission paid: Commission paid or payable on a business transactions undertaken through the agents is an item of expense and is debited to profit and loss account.
- Repairs : Machinery, furniture, fixtures, fittings, etc. which are repairs, renewals or replacements for keeping them in working is an expenditure and comes in debited to profit and loss account.
- Miscellaneous expenses: Certain expenses of small amount clubbed together and are called miscellaneous expenses. In normal usage these expenses are called Sundry expenses or Trade expenses.
Items on the credit side
Sales less returns: It is shown on the credit side of the trading account. Goods returned by customers are called return inwards and are shown as deduction from total sales and the computed amount is known as net sales.
Other incomes: Examples of such incomes are rent received, dividend received, interest received, discount received, commission received, etc and they are recorded in the profit and loss account.
Closing Entries
The preparation of trading and profit and loss account requires that the balances of accounts of all concerned items are transferred to it for its compilation.
Opening stock account, Purchases account, Wages account, Carriage inwards account and direct expenses account are closed by transferring to the debit side of the trading and profit and loss account.
This is done by recording the following entry :
Trading A/c Dr.
To Opening stock A/c
To Purchases A/c
To Wages A/c
To Carriage inwards A/c
To All other direct expenses A/c
The purchases returns or return outwards are closed by transferring its balance to the purchases account. The following entry is recorded for this purpose :
Purchases return A/c Dr. To Purchases A/c
Similarly, the sales returns or returns inwards account is closed by transferring its balance to the sales account as :
Sales A/c Dr. To Sales return A/c
The sales account is closed by transferring its balance to the credit side of the trading and profit and loss account by recording the following entry:
Sales A/c Dr. To Trading A/c
Items of expenses, losses, etc. are closed by recording the following entries:
Profit and Loss A/c Dr.
To Expenses (individually) A/c
To Losses (individually) A/c
Items of incomes, gains, etc. are closed by recording the following entry:
Incomes (individually) A/c Dr.
Gains (individually) A/c Dr.
To Profit and Loss A/c
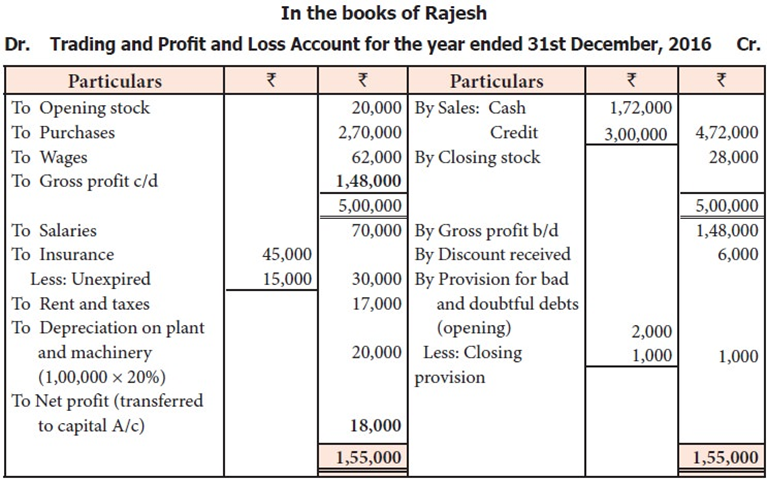
The posting for closing the seven accounts of expenses and revenues as they appear in the trial balance are given below:
(i) For closing the accounts of expenses
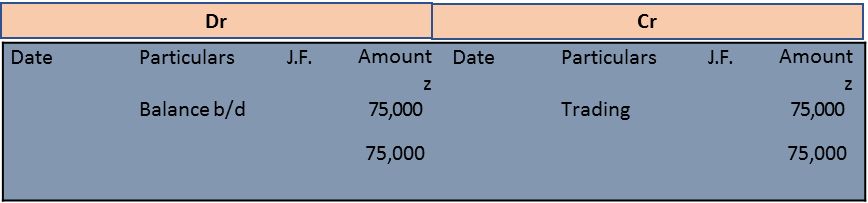
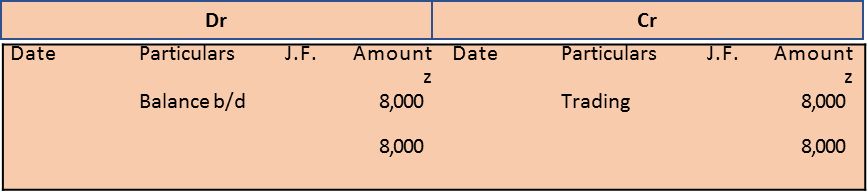
Trading A/c Dr. 83,000
To Purchases A/c 75,000
To Wages A/c 8,000
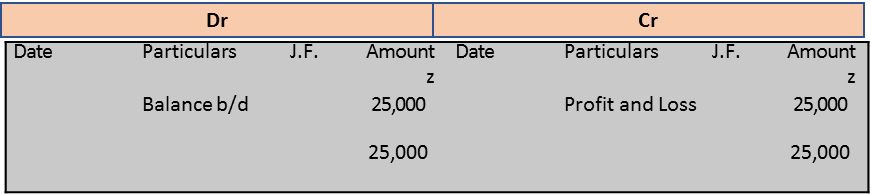
(ii) Profit and Loss A/c Dr. 43,500
To Salaries 25,000
To Rent of building 13,000
To Bad debts 4,500
(i) For closing the accounts of revenues
Sales A/c Dr. 1,25,000
To Trading A/c 1,25,000
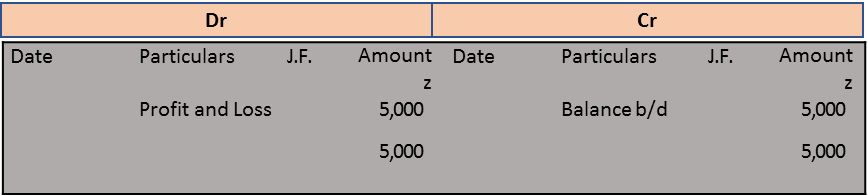
(ii) Commission received A/c Dr. 5,000
To Profit and Loss A/c 5,000
The posting done in ledger will appear as follows :
Purchases Account
Wages Account
Salaries Account
Rent of Building Account
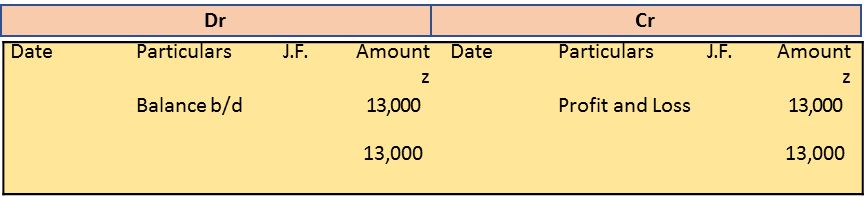
Bad Debts Account
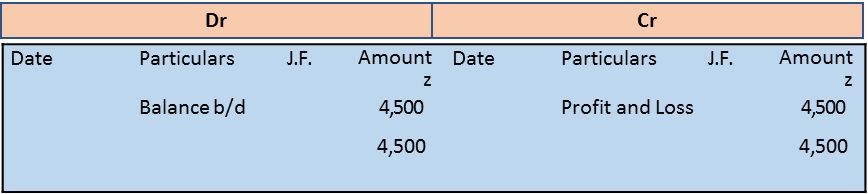
Sales Account
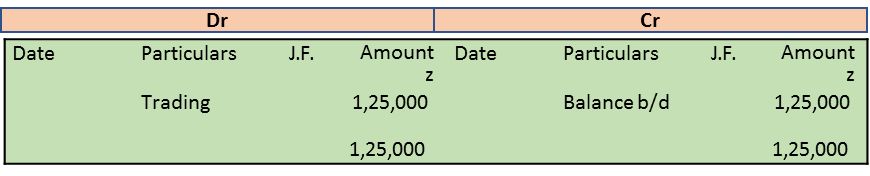
Commission Received Account
Concept of Gross Profit and Net Profit

The trading and profit and loss can be seen as combination of two accounts - Trading account and Profit and Loss account. The trading account or the first part ascertains the gross profit and profit and loss account or the second part ascertains net profit.
Trading Account
The trading account ascertains the result from basic operational activities of the business. The basic operational activity involves the manufacturing, purchasing and selling of goods. It is prepared to ascertain whether the selling of goods and/or rendering of services to customers have proved profitable for the business or not. A purchase is one of the main constituents of expenses in business organization. Besides purchases, the remaining expenses are divided into two categories - direct expenses and indirect expenses.
Direct expenses means all expenses directly connected with the manufacture, purchase of goods and bringing them to the point of sale. Direct expenses include carriage inwards, freight inwards, wages, factory lighting, coal, water and feul, royalty on production, etc.
Similarly, sales is the main item of revenue for the business. The excess of sales over purchases and direct expenses is called gross profit. If the amount of purchases including direct expenses is more than the sales revenue, the resultant figure is gross loss. The gross profit or the gross loss is transferred to profit and loss account. The computation of gross profit can be shown in the form of equation as :
Gross Profit = Sales - (Purchases + Direct Expenses)
The indirect expenses are transferred to the debit side of the second part - profit and loss account. All revenue/gains other than sales are transferred to the credit side of the profit and loss account.
Note - When the total of the credit side of the profit and loss account is more than the total of the debit side, the difference is the net profit for the period of which it is being prepared and if the total of the debit side is more than the total of the credit side, the difference is the net loss incurred by the business firm.
In an equation form, it is shown as follows :
Net Profit = Gross Profit + Other Incomes - Indirect Expenses
Net profit or net loss so computed is transferred to the capital account in the balance sheet by way of the following entry :
(i) For transfer of net profit
Profit and Loss A/c Dr. To Capital A/c
(ii) For transfer of net loss
Capital A/c Dr. To Profit and Loss A/c
Cost of Goods Sold and Closing Stock-Trading Account Revisited
The trading and profit and loss account prepared in the figure presents useful information as to the profitability from the basic operations of the business enterprise. It is reproduced for further perusal.
Trading Account for the year ended March 31, 2017
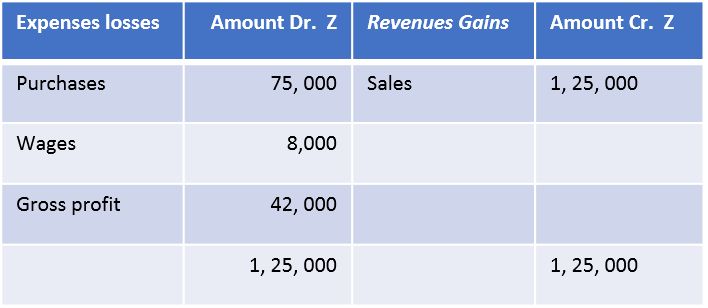
An illustrative trading account
If there is no opening or closing stock, the total of purchases and direct expenses is taken as Cost of goods sold. The cost of goods sold will be computed using the following formula :
Cost of Goods Sold = Purchases + Direct Expenses
=Rs 75,000 + Rs 8,000
= Rs 83,000
As there is no unsold stock, the presumption here is that all the goods purchased have been sold. But in practice, there is some unsold goods at the end of the accounting period.
let us assume that out of the goods purchased amounting to Rs 75,000 in the current year, the business owner is able to sell goods costing Rs 60,000 only. In such a situation, the business will have an unsold stock of goods costing Rs 15,000 in hand, also called closing stock. The amount of cost of goods sold will be computed as per the following equation:
Cost of Goods Sold = Purchases + Direct Expenses - Closing Stock
= Rs 75,000 + Rs 8,000 - Rs 15,000
It may be noted that closing stock does not normally form part of trial balance, and is brought into books with the help of the following journal entry :
Closing stock A/c Dr.
To Trading A/c
It opens a new account of asset, i.e. closing stock Rs 15,000 which is transferred to the balance sheet. The closing stock shall be an opening stock for the next year and shall be sold during the year. In most cases, therefore, the business shall have opening stock as well as closing stock every year, and the cost of goods sold should be worked as per the following equation:
Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Purchases Direct Expenses-Closing Stock
Operating Profit (EBIT)
It is earned through the normal operations and activities of the business. Operating profit is the excess of operating revenue over operating expenses.
While calculating operating profit, the incomes and expenses of a purely financial nature are not taken into account. Thus, operating profit is profit before interest and tax (EBIT). Similarly, abnormal items such as loss by fire, etc. are also not taken into account. It is calculated as follows:
Operating profit = Net Profit + Non Operating Expenses - Non Operating Incomes

 Vision classes
Vision classes
