- Books Name
- Private Course Testing Social Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
INTRODUCTION
Food is the basic requirement of the man so man started cultivation as the civilization began. So agriculture is one of the basic or primary activity. India is a large country with variety of soil and climatic conditions so there is variety in the crops and agricultural methods and practices. India lies in tropical and subtropical zones having a very long period of insolation or sunshine. Variety of soil variety of climatic conditions, makes India a rich agrarian country. In this topic we will deal with different types of farming. Agricultural seasons, crop varieties and other aspects like reforms and problems of this sector.
Important terms and concepts
Agriculture: It is an economic activity related to cultivation of crops, animal rearing and fishing.
Blue Revolution: A package programme introduced to increase the production of fish and fish products.
Commercial Farming: Farming in which crops are grown with the use of modern technology mainly for commercial purposes to obtain high productivity.
Gene Revolution: It refers to the production of genetically modified seeds that give higher yield per hectare which is the contribution of genetic engineering.
Green Revolution: A package programme to increase the production of food grains with the help of HYV seeds, machines, irrigation and fertilisers, etc.
Horticulture: Specialised cultivation of fruits and vegetables.
Intensive Subsistence Farming: A type of farming which emphasises maximum use of minimum land.
Kharif: An agricultural season where crops are grown with the onset of rains and harvested by the retreat of the monsoon, mainly from June to September.
Plantation Agriculture: A large scale single crop farming which resembles factory production. It is both labour intensive and capital intensive.
Primitive Subsistence Farming: A type of farming done on small fields using primitive tools mainly in the form of shifting agriculture.
White Revolution: A package programme meant for increasing the productivity of milk.
Sericulture: Rearing of silkworms to produce raw silk.
Zaid: It is a short season summer crop where fruits like watermelon and vegetables like cucumber and grown.
Sericulture: Rearing of silk worms for the production of silk is called sericulature.
Jhumming: Burning a piece of land for cultivation by the forest tribes.
India is an agriculturally important country why?
(i) Two-thirds of its population is engaged in agricultural activities
(ii) Contribution of agriculture is 22% in GDP.
(iii) Agriculture is a primary activity, which produce most of food that we consume.
(iv) Besides food grains, it also produce raw material for various industuries Like, Cotton, Jute, Silk etc.
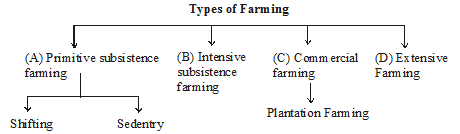
Primitive Subsistence Farming
(i) Practised in North-Eastern states on small Patches of Land with the help of Primitive tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks.
(ii) Done with the help of family/community labour.
Shifting
(i) It is also known as ‘Slash and burn’ agricultural
(ii) Farmers clear a patch of land and produce cereals and other food crops to sustain their family.
(iii) When the soil fertility decreases, the farmers shift and clear a fresh patch of land for cultivation.
(iv) This type of shifting allows nature to replenish the fertility of the soil through natural processes.
(v) It in known by different names in different parts of the country like Jhumming in north-eastern states (Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland), Pamlou in Manipur, Dipa in bastar district of Chattishgarh and in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Now a days shifting farming is discouraged because it leads to deforestation and soil erosion.
Intensive Subsistence Farming
(i) This type of farming is practised in areas of high population pressure on land.
(ii) It is labour-intensive farming, where high doses of biochemical inputs and irrigation are used for obtaining higher production.
(iii) Land holding size is uneconomical due to right of inheritence but the farmers continue to take maximum output from the limited land in the absence of alternative source of livelihood.
Commerical Farming
(i) The main characteristic of this type of farming is the use of higher doses of modern inputs, e.g. high yielding variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides and pesticides in order to obtain higher productivity.
(ii) Plantation is also a type of commercial farming. In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area.
(iii) Plantations cover large tracts of land, using capital intensive inputs, with the help of migrant labourers.
(iv) All the produce is used as raw material in respective industries.
(v) A well-developed network of transport and communication connecting the plantation areas, processing industries and markets plays, an important role in the development of plantations.
Illustration 1
Can you name some, industries based on agriculture raw materials?
Solution
Sugar industry, Rubber industry, Cotton Textile, Jute industry, Silk industry, Tea industry, Coffee industry, Species etc.
Illustration 2
Why cultivation methods have changed significantly?
Solution
Cultivation methods have changed according to
(a) Characterstics of physical environment.
(b) Technological know how.
(c) Socio-cultural practices
Illustration 3
On which factors the primitive subsistence farming depends
Solution
(i) Monsoon
(ii) Natural fertility of soil
(iii) Suitability of other environmental conditions to the crops grown.
- Books Name
- Testing Private Course Social Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
INTRODUCTION
Food is the basic requirement of the man so man started cultivation as the civilization began. So agriculture is one of the basic or primary activity. India is a large country with variety of soil and climatic conditions so there is variety in the crops and agricultural methods and practices. India lies in tropical and subtropical zones having a very long period of insolation or sunshine. Variety of soil variety of climatic conditions, makes India a rich agrarian country. In this topic we will deal with different types of farming. Agricultural seasons, crop varieties and other aspects like reforms and problems of this sector.
Important terms and concepts
Agriculture: It is an economic activity related to cultivation of crops, animal rearing and fishing.
Blue Revolution: A package programme introduced to increase the production of fish and fish products.
Commercial Farming: Farming in which crops are grown with the use of modern technology mainly for commercial purposes to obtain high productivity.
Gene Revolution: It refers to the production of genetically modified seeds that give higher yield per hectare which is the contribution of genetic engineering.
Green Revolution: A package programme to increase the production of food grains with the help of HYV seeds, machines, irrigation and fertilisers, etc.
Horticulture: Specialised cultivation of fruits and vegetables.
Intensive Subsistence Farming: A type of farming which emphasises maximum use of minimum land.
Kharif: An agricultural season where crops are grown with the onset of rains and harvested by the retreat of the monsoon, mainly from June to September.
Plantation Agriculture: A large scale single crop farming which resembles factory production. It is both labour intensive and capital intensive.
Primitive Subsistence Farming: A type of farming done on small fields using primitive tools mainly in the form of shifting agriculture.
White Revolution: A package programme meant for increasing the productivity of milk.
Sericulture: Rearing of silkworms to produce raw silk.
Zaid: It is a short season summer crop where fruits like watermelon and vegetables like cucumber and grown.
Sericulture: Rearing of silk worms for the production of silk is called sericulature.
Jhumming: Burning a piece of land for cultivation by the forest tribes.
India is an agriculturally important country why?
(i) Two-thirds of its population is engaged in agricultural activities
(ii) Contribution of agriculture is 22% in GDP.
(iii) Agriculture is a primary activity, which produce most of food that we consume.
(iv) Besides food grains, it also produce raw material for various industuries Like, Cotton, Jute, Silk etc.

Primitive Subsistence Farming
(i) Practised in North-Eastern states on small Patches of Land with the help of Primitive tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks.
(ii) Done with the help of family/community labour.
Shifting
(i) It is also known as ‘Slash and burn’ agricultural
(ii) Farmers clear a patch of land and produce cereals and other food crops to sustain their family.
(iii) When the soil fertility decreases, the farmers shift and clear a fresh patch of land for cultivation.
(iv) This type of shifting allows nature to replenish the fertility of the soil through natural processes.
(v) It in known by different names in different parts of the country like Jhumming in north-eastern states (Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland), Pamlou in Manipur, Dipa in bastar district of Chattishgarh and in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Now a days shifting farming is discouraged because it leads to deforestation and soil erosion.
Intensive Subsistence Farming
(i) This type of farming is practised in areas of high population pressure on land.
(ii) It is labour-intensive farming, where high doses of biochemical inputs and irrigation are used for obtaining higher production.
(iii) Land holding size is uneconomical due to right of inheritence but the farmers continue to take maximum output from the limited land in the absence of alternative source of livelihood.
Commerical Farming
(i) The main characteristic of this type of farming is the use of higher doses of modern inputs, e.g. high yielding variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides and pesticides in order to obtain higher productivity.
(ii) Plantation is also a type of commercial farming. In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area.
(iii) Plantations cover large tracts of land, using capital intensive inputs, with the help of migrant labourers.
(iv) All the produce is used as raw material in respective industries.
(v) A well-developed network of transport and communication connecting the plantation areas, processing industries and markets plays, an important role in the development of plantations.
Illustration 1
Can you name some, industries based on agriculture raw materials?
Solution
Sugar industry, Rubber industry, Cotton Textile, Jute industry, Silk industry, Tea industry, Coffee industry, Species etc.
Illustration 2
Why cultivation methods have changed significantly?
Solution
Cultivation methods have changed according to
(a) Characterstics of physical environment.
(b) Technological know how.
(c) Socio-cultural practices
Illustration 3
On which factors the primitive subsistence farming depends
Solution
(i) Monsoon
(ii) Natural fertility of soil
(iii) Suitability of other environmental conditions to the crops grown.
- Books Name
- Testing Private Course English Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
INTRODUCTION
Food is the basic requirement of the man so man started cultivation as the civilization began. So agriculture is one of the basic or primary activity. India is a large country with variety of soil and climatic conditions so there is variety in the crops and agricultural methods and practices. India lies in tropical and subtropical zones having a very long period of insolation or sunshine. Variety of soil variety of climatic conditions, makes India a rich agrarian country. In this topic we will deal with different types of farming. Agricultural seasons, crop varieties and other aspects like reforms and problems of this sector.
Important terms and concepts
Agriculture: It is an economic activity related to cultivation of crops, animal rearing and fishing.
Blue Revolution: A package programme introduced to increase the production of fish and fish products.
Commercial Farming: Farming in which crops are grown with the use of modern technology mainly for commercial purposes to obtain high productivity.
Gene Revolution: It refers to the production of genetically modified seeds that give higher yield per hectare which is the contribution of genetic engineering.
Green Revolution: A package programme to increase the production of food grains with the help of HYV seeds, machines, irrigation and fertilisers, etc.
Horticulture: Specialised cultivation of fruits and vegetables.
Intensive Subsistence Farming: A type of farming which emphasises maximum use of minimum land.
Kharif: An agricultural season where crops are grown with the onset of rains and harvested by the retreat of the monsoon, mainly from June to September.
Plantation Agriculture: A large scale single crop farming which resembles factory production. It is both labour intensive and capital intensive.
Primitive Subsistence Farming: A type of farming done on small fields using primitive tools mainly in the form of shifting agriculture.
White Revolution: A package programme meant for increasing the productivity of milk.
Sericulture: Rearing of silkworms to produce raw silk.
Zaid: It is a short season summer crop where fruits like watermelon and vegetables like cucumber and grown.
Sericulture: Rearing of silk worms for the production of silk is called sericulature.
Jhumming: Burning a piece of land for cultivation by the forest tribes.
India is an agriculturally important country why?
(i) Two-thirds of its population is engaged in agricultural activities
(ii) Contribution of agriculture is 22% in GDP.
(iii) Agriculture is a primary activity, which produce most of food that we consume.
(iv) Besides food grains, it also produce raw material for various industuries Like, Cotton, Jute, Silk etc.

Primitive Subsistence Farming
(i) Practised in North-Eastern states on small Patches of Land with the help of Primitive tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks.
(ii) Done with the help of family/community labour.
Shifting
(i) It is also known as ‘Slash and burn’ agricultural
(ii) Farmers clear a patch of land and produce cereals and other food crops to sustain their family.
(iii) When the soil fertility decreases, the farmers shift and clear a fresh patch of land for cultivation.
(iv) This type of shifting allows nature to replenish the fertility of the soil through natural processes.
(v) It in known by different names in different parts of the country like Jhumming in north-eastern states (Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland), Pamlou in Manipur, Dipa in bastar district of Chattishgarh and in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Now a days shifting farming is discouraged because it leads to deforestation and soil erosion.
Intensive Subsistence Farming
(i) This type of farming is practised in areas of high population pressure on land.
(ii) It is labour-intensive farming, where high doses of biochemical inputs and irrigation are used for obtaining higher production.
(iii) Land holding size is uneconomical due to right of inheritence but the farmers continue to take maximum output from the limited land in the absence of alternative source of livelihood.
Commerical Farming
(i) The main characteristic of this type of farming is the use of higher doses of modern inputs, e.g. high yielding variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides and pesticides in order to obtain higher productivity.
(ii) Plantation is also a type of commercial farming. In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area.
(iii) Plantations cover large tracts of land, using capital intensive inputs, with the help of migrant labourers.
(iv) All the produce is used as raw material in respective industries.
(v) A well-developed network of transport and communication connecting the plantation areas, processing industries and markets plays, an important role in the development of plantations.
Illustration 1
Can you name some, industries based on agriculture raw materials?
Solution
Sugar industry, Rubber industry, Cotton Textile, Jute industry, Silk industry, Tea industry, Coffee industry, Species etc.
Illustration 2
Why cultivation methods have changed significantly?
Solution
Cultivation methods have changed according to
(a) Characterstics of physical environment.
(b) Technological know how.
(c) Socio-cultural practices
Illustration 3
On which factors the primitive subsistence farming depends
Solution
(i) Monsoon
(ii) Natural fertility of soil
(iii) Suitability of other environmental conditions to the crops grown.
- Books Name
- Testing Private Course Hindi Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
INTRODUCTION
Food is the basic requirement of the man so man started cultivation as the civilization began. So agriculture is one of the basic or primary activity. India is a large country with variety of soil and climatic conditions so there is variety in the crops and agricultural methods and practices. India lies in tropical and subtropical zones having a very long period of insolation or sunshine. Variety of soil variety of climatic conditions, makes India a rich agrarian country. In this topic we will deal with different types of farming. Agricultural seasons, crop varieties and other aspects like reforms and problems of this sector.
Important terms and concepts
Agriculture: It is an economic activity related to cultivation of crops, animal rearing and fishing.
Blue Revolution: A package programme introduced to increase the production of fish and fish products.
Commercial Farming: Farming in which crops are grown with the use of modern technology mainly for commercial purposes to obtain high productivity.
Gene Revolution: It refers to the production of genetically modified seeds that give higher yield per hectare which is the contribution of genetic engineering.
Green Revolution: A package programme to increase the production of food grains with the help of HYV seeds, machines, irrigation and fertilisers, etc.
Horticulture: Specialised cultivation of fruits and vegetables.
Intensive Subsistence Farming: A type of farming which emphasises maximum use of minimum land.
Kharif: An agricultural season where crops are grown with the onset of rains and harvested by the retreat of the monsoon, mainly from June to September.
Plantation Agriculture: A large scale single crop farming which resembles factory production. It is both labour intensive and capital intensive.
Primitive Subsistence Farming: A type of farming done on small fields using primitive tools mainly in the form of shifting agriculture.
White Revolution: A package programme meant for increasing the productivity of milk.
Sericulture: Rearing of silkworms to produce raw silk.
Zaid: It is a short season summer crop where fruits like watermelon and vegetables like cucumber and grown.
Sericulture: Rearing of silk worms for the production of silk is called sericulature.
Jhumming: Burning a piece of land for cultivation by the forest tribes.
India is an agriculturally important country why?
(i) Two-thirds of its population is engaged in agricultural activities
(ii) Contribution of agriculture is 22% in GDP.
(iii) Agriculture is a primary activity, which produce most of food that we consume.
(iv) Besides food grains, it also produce raw material for various industuries Like, Cotton, Jute, Silk etc.

Primitive Subsistence Farming
(i) Practised in North-Eastern states on small Patches of Land with the help of Primitive tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks.
(ii) Done with the help of family/community labour.
Shifting
(i) It is also known as ‘Slash and burn’ agricultural
(ii) Farmers clear a patch of land and produce cereals and other food crops to sustain their family.
(iii) When the soil fertility decreases, the farmers shift and clear a fresh patch of land for cultivation.
(iv) This type of shifting allows nature to replenish the fertility of the soil through natural processes.
(v) It in known by different names in different parts of the country like Jhumming in north-eastern states (Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland), Pamlou in Manipur, Dipa in bastar district of Chattishgarh and in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Now a days shifting farming is discouraged because it leads to deforestation and soil erosion.
Intensive Subsistence Farming
(i) This type of farming is practised in areas of high population pressure on land.
(ii) It is labour-intensive farming, where high doses of biochemical inputs and irrigation are used for obtaining higher production.
(iii) Land holding size is uneconomical due to right of inheritence but the farmers continue to take maximum output from the limited land in the absence of alternative source of livelihood.
Commerical Farming
(i) The main characteristic of this type of farming is the use of higher doses of modern inputs, e.g. high yielding variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides and pesticides in order to obtain higher productivity.
(ii) Plantation is also a type of commercial farming. In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area.
(iii) Plantations cover large tracts of land, using capital intensive inputs, with the help of migrant labourers.
(iv) All the produce is used as raw material in respective industries.
(v) A well-developed network of transport and communication connecting the plantation areas, processing industries and markets plays, an important role in the development of plantations.
Illustration 1
Can you name some, industries based on agriculture raw materials?
Solution
Sugar industry, Rubber industry, Cotton Textile, Jute industry, Silk industry, Tea industry, Coffee industry, Species etc.
Illustration 2
Why cultivation methods have changed significantly?
Solution
Cultivation methods have changed according to
(a) Characterstics of physical environment.
(b) Technological know how.
(c) Socio-cultural practices
Illustration 3
On which factors the primitive subsistence farming depends
Solution
(i) Monsoon
(ii) Natural fertility of soil
(iii) Suitability of other environmental conditions to the crops grown.
INTRODUCTION
Food is the basic requirement of the man so man started cultivation as the civilization began. So agriculture is one of the basic or primary activity. India is a large country with variety of soil and climatic conditions so there is variety in the crops and agricultural methods and practices. India lies in tropical and subtropical zones having a very long period of insolation or sunshine. Variety of soil variety of climatic conditions, makes India a rich agrarian country. In this topic we will deal with different types of farming. Agricultural seasons, crop varieties and other aspects like reforms and problems of this sector.
Important terms and concepts
Agriculture: It is an economic activity related to cultivation of crops, animal rearing and fishing.
Blue Revolution: A package programme introduced to increase the production of fish and fish products.
Commercial Farming: Farming in which crops are grown with the use of modern technology mainly for commercial purposes to obtain high productivity.
Gene Revolution: It refers to the production of genetically modified seeds that give higher yield per hectare which is the contribution of genetic engineering.
Green Revolution: A package programme to increase the production of food grains with the help of HYV seeds, machines, irrigation and fertilisers, etc.
Horticulture: Specialised cultivation of fruits and vegetables.
Intensive Subsistence Farming: A type of farming which emphasises maximum use of minimum land.
Kharif: An agricultural season where crops are grown with the onset of rains and harvested by the retreat of the monsoon, mainly from June to September.
Plantation Agriculture: A large scale single crop farming which resembles factory production. It is both labour intensive and capital intensive.
Primitive Subsistence Farming: A type of farming done on small fields using primitive tools mainly in the form of shifting agriculture.
White Revolution: A package programme meant for increasing the productivity of milk.
Sericulture: Rearing of silkworms to produce raw silk.
Zaid: It is a short season summer crop where fruits like watermelon and vegetables like cucumber and grown.
Sericulture: Rearing of silk worms for the production of silk is called sericulature.
Jhumming: Burning a piece of land for cultivation by the forest tribes.
India is an agriculturally important country why?
(i) Two-thirds of its population is engaged in agricultural activities
(ii) Contribution of agriculture is 22% in GDP.
(iii) Agriculture is a primary activity, which produce most of food that we consume.
(iv) Besides food grains, it also produce raw material for various industuries Like, Cotton, Jute, Silk etc.

Primitive Subsistence Farming
(i) Practised in North-Eastern states on small Patches of Land with the help of Primitive tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks.
(ii) Done with the help of family/community labour.
Shifting
(i) It is also known as ‘Slash and burn’ agricultural
(ii) Farmers clear a patch of land and produce cereals and other food crops to sustain their family.
(iii) When the soil fertility decreases, the farmers shift and clear a fresh patch of land for cultivation.
(iv) This type of shifting allows nature to replenish the fertility of the soil through natural processes.
(v) It in known by different names in different parts of the country like Jhumming in north-eastern states (Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland), Pamlou in Manipur, Dipa in bastar district of Chattishgarh and in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Now a days shifting farming is discouraged because it leads to deforestation and soil erosion.
Intensive Subsistence Farming
(i) This type of farming is practised in areas of high population pressure on land.
(ii) It is labour-intensive farming, where high doses of biochemical inputs and irrigation are used for obtaining higher production.
(iii) Land holding size is uneconomical due to right of inheritence but the farmers continue to take maximum output from the limited land in the absence of alternative source of livelihood.
Commerical Farming
(i) The main characteristic of this type of farming is the use of higher doses of modern inputs, e.g. high yielding variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides and pesticides in order to obtain higher productivity.
(ii) Plantation is also a type of commercial farming. In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area.
(iii) Plantations cover large tracts of land, using capital intensive inputs, with the help of migrant labourers.
(iv) All the produce is used as raw material in respective industries.
(v) A well-developed network of transport and communication connecting the plantation areas, processing industries and markets plays, an important role in the development of plantations.
Illustration 1
Can you name some, industries based on agriculture raw materials?
Solution
Sugar industry, Rubber industry, Cotton Textile, Jute industry, Silk industry, Tea industry, Coffee industry, Species etc.
Illustration 2
Why cultivation methods have changed significantly?
Solution
Cultivation methods have changed according to
(a) Characterstics of physical environment.
(b) Technological know how.
(c) Socio-cultural practices
Illustration 3
On which factors the primitive subsistence farming depends
Solution
(i) Monsoon
(ii) Natural fertility of soil
(iii) Suitability of other environmental conditions to the crops grown.
- Books Name
- Private Course Testing Modules English Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
INTRODUCTION
Food is the basic requirement of the man so man started cultivation as the civilization began. So agriculture is one of the basic or primary activity. India is a large country with variety of soil and climatic conditions so there is variety in the crops and agricultural methods and practices. India lies in tropical and subtropical zones having a very long period of insolation or sunshine. Variety of soil variety of climatic conditions, makes India a rich agrarian country. In this topic we will deal with different types of farming. Agricultural seasons, crop varieties and other aspects like reforms and problems of this sector.
Important terms and concepts
Agriculture: It is an economic activity related to cultivation of crops, animal rearing and fishing.
Blue Revolution: A package programme introduced to increase the production of fish and fish products.
Commercial Farming: Farming in which crops are grown with the use of modern technology mainly for commercial purposes to obtain high productivity.
Gene Revolution: It refers to the production of genetically modified seeds that give higher yield per hectare which is the contribution of genetic engineering.
Green Revolution: A package programme to increase the production of food grains with the help of HYV seeds, machines, irrigation and fertilisers, etc.
Horticulture: Specialised cultivation of fruits and vegetables.
Intensive Subsistence Farming: A type of farming which emphasises maximum use of minimum land.
Kharif: An agricultural season where crops are grown with the onset of rains and harvested by the retreat of the monsoon, mainly from June to September.
Plantation Agriculture: A large scale single crop farming which resembles factory production. It is both labour intensive and capital intensive.
Primitive Subsistence Farming: A type of farming done on small fields using primitive tools mainly in the form of shifting agriculture.
White Revolution: A package programme meant for increasing the productivity of milk.
Sericulture: Rearing of silkworms to produce raw silk.
Zaid: It is a short season summer crop where fruits like watermelon and vegetables like cucumber and grown.
Sericulture: Rearing of silk worms for the production of silk is called sericulature.
Jhumming: Burning a piece of land for cultivation by the forest tribes.
India is an agriculturally important country why?
(i) Two-thirds of its population is engaged in agricultural activities
(ii) Contribution of agriculture is 22% in GDP.
(iii) Agriculture is a primary activity, which produce most of food that we consume.
(iv) Besides food grains, it also produce raw material for various industuries Like, Cotton, Jute, Silk etc.

Primitive Subsistence Farming
(i) Practised in North-Eastern states on small Patches of Land with the help of Primitive tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks.
(ii) Done with the help of family/community labour.
Shifting
(i) It is also known as ‘Slash and burn’ agricultural
(ii) Farmers clear a patch of land and produce cereals and other food crops to sustain their family.
(iii) When the soil fertility decreases, the farmers shift and clear a fresh patch of land for cultivation.
(iv) This type of shifting allows nature to replenish the fertility of the soil through natural processes.
(v) It in known by different names in different parts of the country like Jhumming in north-eastern states (Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland), Pamlou in Manipur, Dipa in bastar district of Chattishgarh and in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Now a days shifting farming is discouraged because it leads to deforestation and soil erosion.
Intensive Subsistence Farming
(i) This type of farming is practised in areas of high population pressure on land.
(ii) It is labour-intensive farming, where high doses of biochemical inputs and irrigation are used for obtaining higher production.
(iii) Land holding size is uneconomical due to right of inheritence but the farmers continue to take maximum output from the limited land in the absence of alternative source of livelihood.
Commerical Farming
(i) The main characteristic of this type of farming is the use of higher doses of modern inputs, e.g. high yielding variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides and pesticides in order to obtain higher productivity.
(ii) Plantation is also a type of commercial farming. In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area.
(iii) Plantations cover large tracts of land, using capital intensive inputs, with the help of migrant labourers.
(iv) All the produce is used as raw material in respective industries.
(v) A well-developed network of transport and communication connecting the plantation areas, processing industries and markets plays, an important role in the development of plantations.
Illustration 1
Can you name some, industries based on agriculture raw materials?
Solution
Sugar industry, Rubber industry, Cotton Textile, Jute industry, Silk industry, Tea industry, Coffee industry, Species etc.
Illustration 2
Why cultivation methods have changed significantly?
Solution
Cultivation methods have changed according to
(a) Characterstics of physical environment.
(b) Technological know how.
(c) Socio-cultural practices
Illustration 3
On which factors the primitive subsistence farming depends
Solution
(i) Monsoon
(ii) Natural fertility of soil
(iii) Suitability of other environmental conditions to the crops grown.
- Books Name
- Private Course Testing Modules Hindi Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
INTRODUCTION
Food is the basic requirement of the man so man started cultivation as the civilization began. So agriculture is one of the basic or primary activity. India is a large country with variety of soil and climatic conditions so there is variety in the crops and agricultural methods and practices. India lies in tropical and subtropical zones having a very long period of insolation or sunshine. Variety of soil variety of climatic conditions, makes India a rich agrarian country. In this topic we will deal with different types of farming. Agricultural seasons, crop varieties and other aspects like reforms and problems of this sector.
Important terms and concepts
Agriculture: It is an economic activity related to cultivation of crops, animal rearing and fishing.
Blue Revolution: A package programme introduced to increase the production of fish and fish products.
Commercial Farming: Farming in which crops are grown with the use of modern technology mainly for commercial purposes to obtain high productivity.
Gene Revolution: It refers to the production of genetically modified seeds that give higher yield per hectare which is the contribution of genetic engineering.
Green Revolution: A package programme to increase the production of food grains with the help of HYV seeds, machines, irrigation and fertilisers, etc.
Horticulture: Specialised cultivation of fruits and vegetables.
Intensive Subsistence Farming: A type of farming which emphasises maximum use of minimum land.
Kharif: An agricultural season where crops are grown with the onset of rains and harvested by the retreat of the monsoon, mainly from June to September.
Plantation Agriculture: A large scale single crop farming which resembles factory production. It is both labour intensive and capital intensive.
Primitive Subsistence Farming: A type of farming done on small fields using primitive tools mainly in the form of shifting agriculture.
White Revolution: A package programme meant for increasing the productivity of milk.
Sericulture: Rearing of silkworms to produce raw silk.
Zaid: It is a short season summer crop where fruits like watermelon and vegetables like cucumber and grown.
Sericulture: Rearing of silk worms for the production of silk is called sericulature.
Jhumming: Burning a piece of land for cultivation by the forest tribes.
India is an agriculturally important country why?
(i) Two-thirds of its population is engaged in agricultural activities
(ii) Contribution of agriculture is 22% in GDP.
(iii) Agriculture is a primary activity, which produce most of food that we consume.
(iv) Besides food grains, it also produce raw material for various industuries Like, Cotton, Jute, Silk etc.

Primitive Subsistence Farming
(i) Practised in North-Eastern states on small Patches of Land with the help of Primitive tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks.
(ii) Done with the help of family/community labour.
Shifting
(i) It is also known as ‘Slash and burn’ agricultural
(ii) Farmers clear a patch of land and produce cereals and other food crops to sustain their family.
(iii) When the soil fertility decreases, the farmers shift and clear a fresh patch of land for cultivation.
(iv) This type of shifting allows nature to replenish the fertility of the soil through natural processes.
(v) It in known by different names in different parts of the country like Jhumming in north-eastern states (Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland), Pamlou in Manipur, Dipa in bastar district of Chattishgarh and in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Now a days shifting farming is discouraged because it leads to deforestation and soil erosion.
Intensive Subsistence Farming
(i) This type of farming is practised in areas of high population pressure on land.
(ii) It is labour-intensive farming, where high doses of biochemical inputs and irrigation are used for obtaining higher production.
(iii) Land holding size is uneconomical due to right of inheritence but the farmers continue to take maximum output from the limited land in the absence of alternative source of livelihood.
Commerical Farming
(i) The main characteristic of this type of farming is the use of higher doses of modern inputs, e.g. high yielding variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides and pesticides in order to obtain higher productivity.
(ii) Plantation is also a type of commercial farming. In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area.
(iii) Plantations cover large tracts of land, using capital intensive inputs, with the help of migrant labourers.
(iv) All the produce is used as raw material in respective industries.
(v) A well-developed network of transport and communication connecting the plantation areas, processing industries and markets plays, an important role in the development of plantations.
Illustration 1
Can you name some, industries based on agriculture raw materials?
Solution
Sugar industry, Rubber industry, Cotton Textile, Jute industry, Silk industry, Tea industry, Coffee industry, Species etc.
Illustration 2
Why cultivation methods have changed significantly?
Solution
Cultivation methods have changed according to
(a) Characterstics of physical environment.
(b) Technological know how.
(c) Socio-cultural practices
Illustration 3
On which factors the primitive subsistence farming depends
Solution
(i) Monsoon
(ii) Natural fertility of soil
(iii) Suitability of other environmental conditions to the crops grown.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
