The traditional notion of development;
- Books Name
- Private Course Testing Social Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
INTRODUCTION :
Development in the basic nature of human beings. All the people institutions state and national government are working for achieving development at all levels. In this topic we will be studying about various aspects of development, why few economies are highly developed and why few economies are poor. We will also see that how can we achieve a high development level without harming our nature and without sacrificing the needs of present and future generation.
Basic concepts related to development :
We have aspirations or desires about what what we would like to do and how we would like to live, Similarly. We have ideas about what a country should be like, what are the essential things that we require? Can life be better for all ? Can there be more equality ?
For development, people look at a mix of goal :
For example:- It is true that if women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society increases. However, it is also the case that if there is respect for women there would be more sharing of housework and a greater acceptance of women working outside. A safe and secure environment may allow more women to take up a variety of jobs or run a business.
Hence, the development goals that people have are not only about better income but also about other important things in life.
It is very important to keep in mind that different persons could have different as well as conflicting notions of a country’s development.
To get more electricity, industrialist may want more dams. But this may submerge the land and disrupt the lives of people who are displaced- such as tribals. They might resent this and may prefer small check dams or tanks to irrigate their land.
What Development Promises - Different people, Different Goals
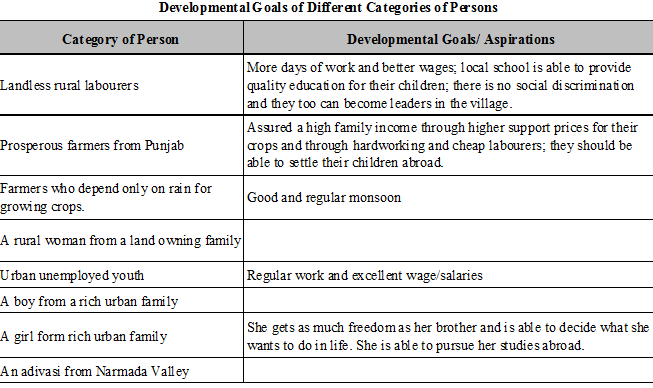
Two things are quite clear :
1. Different persons can have different developmental goals.
2. What may be development for one may not be development for the other. It may even be destructive for the other.
The traditional notion of development;
- Books Name
- Testing Private Course Social Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
INTRODUCTION :
Development in the basic nature of human beings. All the people institutions state and national government are working for achieving development at all levels. In this topic we will be studying about various aspects of development, why few economies are highly developed and why few economies are poor. We will also see that how can we achieve a high development level without harming our nature and without sacrificing the needs of present and future generation.
Basic concepts related to development :
We have aspirations or desires about what what we would like to do and how we would like to live, Similarly. We have ideas about what a country should be like, what are the essential things that we require? Can life be better for all ? Can there be more equality ?
For development, people look at a mix of goal :
For example:- It is true that if women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society increases. However, it is also the case that if there is respect for women there would be more sharing of housework and a greater acceptance of women working outside. A safe and secure environment may allow more women to take up a variety of jobs or run a business.
Hence, the development goals that people have are not only about better income but also about other important things in life.
It is very important to keep in mind that different persons could have different as well as conflicting notions of a country’s development.
To get more electricity, industrialist may want more dams. But this may submerge the land and disrupt the lives of people who are displaced- such as tribals. They might resent this and may prefer small check dams or tanks to irrigate their land.
What Development Promises - Different people, Different Goals

Two things are quite clear :
1. Different persons can have different developmental goals.
2. What may be development for one may not be development for the other. It may even be destructive for the other.
The traditional notion of development;
- Books Name
- Testing Private Course English Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
INTRODUCTION :
Development in the basic nature of human beings. All the people institutions state and national government are working for achieving development at all levels. In this topic we will be studying about various aspects of development, why few economies are highly developed and why few economies are poor. We will also see that how can we achieve a high development level without harming our nature and without sacrificing the needs of present and future generation.
Basic concepts related to development :
We have aspirations or desires about what what we would like to do and how we would like to live, Similarly. We have ideas about what a country should be like, what are the essential things that we require? Can life be better for all ? Can there be more equality ?
For development, people look at a mix of goal :
For example:- It is true that if women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society increases. However, it is also the case that if there is respect for women there would be more sharing of housework and a greater acceptance of women working outside. A safe and secure environment may allow more women to take up a variety of jobs or run a business.
Hence, the development goals that people have are not only about better income but also about other important things in life.
It is very important to keep in mind that different persons could have different as well as conflicting notions of a country’s development.
To get more electricity, industrialist may want more dams. But this may submerge the land and disrupt the lives of people who are displaced- such as tribals. They might resent this and may prefer small check dams or tanks to irrigate their land.
What Development Promises - Different people, Different Goals

Two things are quite clear :
1. Different persons can have different developmental goals.
2. What may be development for one may not be development for the other. It may even be destructive for the other.
The traditional notion of development;
- Books Name
- Testing Private Course Hindi Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
INTRODUCTION :
Development in the basic nature of human beings. All the people institutions state and national government are working for achieving development at all levels. In this topic we will be studying about various aspects of development, why few economies are highly developed and why few economies are poor. We will also see that how can we achieve a high development level without harming our nature and without sacrificing the needs of present and future generation.
Basic concepts related to development :
We have aspirations or desires about what what we would like to do and how we would like to live, Similarly. We have ideas about what a country should be like, what are the essential things that we require? Can life be better for all ? Can there be more equality ?
For development, people look at a mix of goal :
For example:- It is true that if women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society increases. However, it is also the case that if there is respect for women there would be more sharing of housework and a greater acceptance of women working outside. A safe and secure environment may allow more women to take up a variety of jobs or run a business.
Hence, the development goals that people have are not only about better income but also about other important things in life.
It is very important to keep in mind that different persons could have different as well as conflicting notions of a country’s development.
To get more electricity, industrialist may want more dams. But this may submerge the land and disrupt the lives of people who are displaced- such as tribals. They might resent this and may prefer small check dams or tanks to irrigate their land.
What Development Promises - Different people, Different Goals

Two things are quite clear :
1. Different persons can have different developmental goals.
2. What may be development for one may not be development for the other. It may even be destructive for the other.
The traditional notion of development;
INTRODUCTION :
Development in the basic nature of human beings. All the people institutions state and national government are working for achieving development at all levels. In this topic we will be studying about various aspects of development, why few economies are highly developed and why few economies are poor. We will also see that how can we achieve a high development level without harming our nature and without sacrificing the needs of present and future generation.
Basic concepts related to development :
We have aspirations or desires about what what we would like to do and how we would like to live, Similarly. We have ideas about what a country should be like, what are the essential things that we require? Can life be better for all ? Can there be more equality ?
For development, people look at a mix of goal :
For example:- It is true that if women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society increases. However, it is also the case that if there is respect for women there would be more sharing of housework and a greater acceptance of women working outside. A safe and secure environment may allow more women to take up a variety of jobs or run a business.
Hence, the development goals that people have are not only about better income but also about other important things in life.
It is very important to keep in mind that different persons could have different as well as conflicting notions of a country’s development.
To get more electricity, industrialist may want more dams. But this may submerge the land and disrupt the lives of people who are displaced- such as tribals. They might resent this and may prefer small check dams or tanks to irrigate their land.
What Development Promises - Different people, Different Goals

Two things are quite clear :
1. Different persons can have different developmental goals.
2. What may be development for one may not be development for the other. It may even be destructive for the other.
The traditional notion of development;
- Books Name
- Private Course Testing Modules English Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
INTRODUCTION :
Development in the basic nature of human beings. All the people institutions state and national government are working for achieving development at all levels. In this topic we will be studying about various aspects of development, why few economies are highly developed and why few economies are poor. We will also see that how can we achieve a high development level without harming our nature and without sacrificing the needs of present and future generation.
Basic concepts related to development :
We have aspirations or desires about what what we would like to do and how we would like to live, Similarly. We have ideas about what a country should be like, what are the essential things that we require? Can life be better for all ? Can there be more equality ?
For development, people look at a mix of goal :
For example:- It is true that if women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society increases. However, it is also the case that if there is respect for women there would be more sharing of housework and a greater acceptance of women working outside. A safe and secure environment may allow more women to take up a variety of jobs or run a business.
Hence, the development goals that people have are not only about better income but also about other important things in life.
It is very important to keep in mind that different persons could have different as well as conflicting notions of a country’s development.
To get more electricity, industrialist may want more dams. But this may submerge the land and disrupt the lives of people who are displaced- such as tribals. They might resent this and may prefer small check dams or tanks to irrigate their land.
What Development Promises - Different people, Different Goals

Two things are quite clear :
1. Different persons can have different developmental goals.
2. What may be development for one may not be development for the other. It may even be destructive for the other.
The traditional notion of development;
- Books Name
- Private Course Testing Modules Hindi Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
INTRODUCTION :
Development in the basic nature of human beings. All the people institutions state and national government are working for achieving development at all levels. In this topic we will be studying about various aspects of development, why few economies are highly developed and why few economies are poor. We will also see that how can we achieve a high development level without harming our nature and without sacrificing the needs of present and future generation.
Basic concepts related to development :
We have aspirations or desires about what what we would like to do and how we would like to live, Similarly. We have ideas about what a country should be like, what are the essential things that we require? Can life be better for all ? Can there be more equality ?
For development, people look at a mix of goal :
For example:- It is true that if women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society increases. However, it is also the case that if there is respect for women there would be more sharing of housework and a greater acceptance of women working outside. A safe and secure environment may allow more women to take up a variety of jobs or run a business.
Hence, the development goals that people have are not only about better income but also about other important things in life.
It is very important to keep in mind that different persons could have different as well as conflicting notions of a country’s development.
To get more electricity, industrialist may want more dams. But this may submerge the land and disrupt the lives of people who are displaced- such as tribals. They might resent this and may prefer small check dams or tanks to irrigate their land.
What Development Promises - Different people, Different Goals

Two things are quite clear :
1. Different persons can have different developmental goals.
2. What may be development for one may not be development for the other. It may even be destructive for the other.
National Income and Per capita Income.
- Books Name
- Private Course Testing Social Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
Income and other goals :
What people desire are regular work, better wages, and decent price for their crops or other products that they produce. In other words, they want more income.
People also seek things like equal treatment, freedom, security, and respect of others. They resent
discrimination.
Money, or material things that one can buy with it, is one factor on which our life depends. But the quality of our life also depends on non-material things mentioned above.
Consider an example:- If you get a job in a far off place, before accepting it you would try to consider many factors, apart from income, such as facilities for your family, working atmosphere, or opportunity to learn. In another case, a job may give you less pay but may offer regular employment that enhances your sense of security. Another job, however, may offer high pay but no job security and also leave no time for your family. This will reduce your sense of security and freedom.
How to compare different countries or states?
For comparing countries, their income is considered to be one of the most important attributes. Countries with higher income are more developed than others with less income. This is based on the understanding that more income means more of all things that human beings need.
Average income:- It is the total income of the country divided by its total population. The average income is also called per capita income.
Countries with per capita income of $12616 per annum and above in 2012, are called rich income countries. Eg.:- Japan, USA. UK. The rich countries, excluding countries of Middle East and certain other small countries, are generally called developed countries.
Those with per capita income of $1035 or less are called low-income countries. Eg.:- India. Because its per capita income was just $1530 per annum.
Income and Other Criteria :
When we think of a nation or a region, we may, besides average income, think of other equally important attributes. What could these attributes be? Let us examine this through an example.
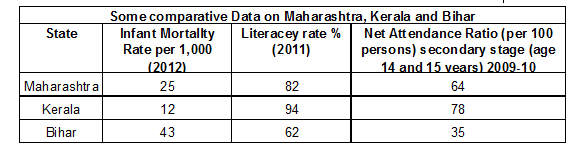
(i) Income & other criteria :
1. If we compare the states of Maharashtra, Kerala, Bihar we find that Maharashtra has PCI of Rs. 107070, Kerala has Rs. 885 and Bihar has Rs. 28774.
2. IMR of Bihar is the most that is 43/1000, Maharashtra 25/1000 and Kerala 12/1000. This indicates that most of the children below the age of 1 year die in Bihar whereas although Maharashtra has a higher PCI their Kerala. This clearly proves that money cannot buy all the goods and services you need to live well such as pollution freen environment, unadultrated medicines and prevention from infections diseases.
3. If we com pare the literacy rate we find that the least number of children attending school in Bihar, i.e., 62 and maximum is in Kerala i.e. 94.
4. 2/3rd of the children aged 14-15 years in Bit are not attending school. The maximum net attendance ratio is in Kerala.
Important : Kerala has a low IMR because is has adequate provision of basic he a and educational facilities. Some states have a good public distribution system. This ensures a healthy and nutrition a states of the people.
Other Criteria’s :
Besides PCI other criteria’s use to measure development are
1. Infant Mortality Rate : Indicates the no. of children per 1000 born in a year that die before the age of one.
2. Literacy Rate : Measure the proportion of literia population above 7 years.
3. Net attendance Ratio : Is the total number of children between the age of it 10 years who are attending school.
4. Life Expectancy : Denotes the average expected length of life of a person at the times of births. In India, it is 66.4 years.
Human Development Report (HDR) :
The Human Development Report is published by UNDP and it compares countries based on it educational level, health states income level life expectancy. If we compare India with its neighbouring countries certain relevant inform can be percieved.
1. Gross National Income of Sri Lanka is $9250 India 5150 dollors and Pakistan - 4652 dollar.
2. Life expectancy of Sri Lanka is 74.3 years, India is 66.4 years and Pakistan is 66.6 years.
3. Literacy rates for 15 years and above in Sri Lanka is 91.2, Myanmar 92.7 & India 62.8.
4. As per HDR rank in the world, Sri Lanka is 73 & India is 135.
(ii) Literacy Rate measures the proportion of literate population in the 7 and above age group.
The 2nd column shows that more that half of the children in Bihar do not even get to go to school.
Net Attendance Ratio is the total number of children of age group 6-10 attending school as a percentage of total number of children in the same age group.
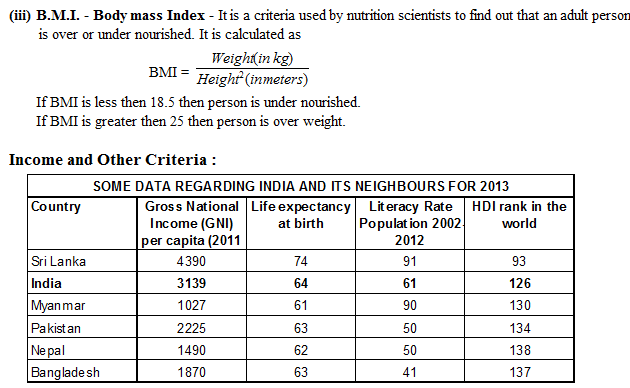
Notes :
(i) HDI stands for Human Development Index. HDI ranks in above table are out of 177 countries in all.
(ii) Life expectancy at birth denotes, as the name suggests, average expected length of life of a person at the time of birth.
(iii) Gross Enrolment Ratio for three levels means enrolment ratio for primary school, secondary school and higher education beyond secondary school.
(iv) Per Capita Income is calculated in dollars for all countries so that it can be compared. It is also done in a way so that every dollar would buy the same amount of goods and services in any country.
Sri Lanka, is much ahead of India in every respect and a big country like ours has such a low rank in the world.
Nepal has half the per capita income of India yet it is not far behind India in life expectancy and literacy levels.
What is important in development is what is happening to citizens of a country. It is people, their health, their well being, that is most important.
National Income and Per capita Income.
- Books Name
- Testing Private Course Social Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
Income and other goals :
What people desire are regular work, better wages, and decent price for their crops or other products that they produce. In other words, they want more income.
People also seek things like equal treatment, freedom, security, and respect of others. They resent
discrimination.
Money, or material things that one can buy with it, is one factor on which our life depends. But the quality of our life also depends on non-material things mentioned above.
Consider an example:- If you get a job in a far off place, before accepting it you would try to consider many factors, apart from income, such as facilities for your family, working atmosphere, or opportunity to learn. In another case, a job may give you less pay but may offer regular employment that enhances your sense of security. Another job, however, may offer high pay but no job security and also leave no time for your family. This will reduce your sense of security and freedom.
How to compare different countries or states?
For comparing countries, their income is considered to be one of the most important attributes. Countries with higher income are more developed than others with less income. This is based on the understanding that more income means more of all things that human beings need.
Average income:- It is the total income of the country divided by its total population. The average income is also called per capita income.
Countries with per capita income of $12616 per annum and above in 2012, are called rich income countries. Eg.:- Japan, USA. UK. The rich countries, excluding countries of Middle East and certain other small countries, are generally called developed countries.
Those with per capita income of $1035 or less are called low-income countries. Eg.:- India. Because its per capita income was just $1530 per annum.
Income and Other Criteria :
When we think of a nation or a region, we may, besides average income, think of other equally important attributes. What could these attributes be? Let us examine this through an example.

(i) Income & other criteria :
1. If we compare the states of Maharashtra, Kerala, Bihar we find that Maharashtra has PCI of Rs. 107070, Kerala has Rs. 885 and Bihar has Rs. 28774.
2. IMR of Bihar is the most that is 43/1000, Maharashtra 25/1000 and Kerala 12/1000. This indicates that most of the children below the age of 1 year die in Bihar whereas although Maharashtra has a higher PCI their Kerala. This clearly proves that money cannot buy all the goods and services you need to live well such as pollution freen environment, unadultrated medicines and prevention from infections diseases.
3. If we com pare the literacy rate we find that the least number of children attending school in Bihar, i.e., 62 and maximum is in Kerala i.e. 94.
4. 2/3rd of the children aged 14-15 years in Bit are not attending school. The maximum net attendance ratio is in Kerala.
Important : Kerala has a low IMR because is has adequate provision of basic he a and educational facilities. Some states have a good public distribution system. This ensures a healthy and nutrition a states of the people.
Other Criteria’s :
Besides PCI other criteria’s use to measure development are
1. Infant Mortality Rate : Indicates the no. of children per 1000 born in a year that die before the age of one.
2. Literacy Rate : Measure the proportion of literia population above 7 years.
3. Net attendance Ratio : Is the total number of children between the age of it 10 years who are attending school.
4. Life Expectancy : Denotes the average expected length of life of a person at the times of births. In India, it is 66.4 years.
Human Development Report (HDR) :
The Human Development Report is published by UNDP and it compares countries based on it educational level, health states income level life expectancy. If we compare India with its neighbouring countries certain relevant inform can be percieved.
1. Gross National Income of Sri Lanka is $9250 India 5150 dollors and Pakistan - 4652 dollar.
2. Life expectancy of Sri Lanka is 74.3 years, India is 66.4 years and Pakistan is 66.6 years.
3. Literacy rates for 15 years and above in Sri Lanka is 91.2, Myanmar 92.7 & India 62.8.
4. As per HDR rank in the world, Sri Lanka is 73 & India is 135.
(ii) Literacy Rate measures the proportion of literate population in the 7 and above age group.
The 2nd column shows that more that half of the children in Bihar do not even get to go to school.
Net Attendance Ratio is the total number of children of age group 6-10 attending school as a percentage of total number of children in the same age group.

Notes :
(i) HDI stands for Human Development Index. HDI ranks in above table are out of 177 countries in all.
(ii) Life expectancy at birth denotes, as the name suggests, average expected length of life of a person at the time of birth.
(iii) Gross Enrolment Ratio for three levels means enrolment ratio for primary school, secondary school and higher education beyond secondary school.
(iv) Per Capita Income is calculated in dollars for all countries so that it can be compared. It is also done in a way so that every dollar would buy the same amount of goods and services in any country.
Sri Lanka, is much ahead of India in every respect and a big country like ours has such a low rank in the world.
Nepal has half the per capita income of India yet it is not far behind India in life expectancy and literacy levels.
What is important in development is what is happening to citizens of a country. It is people, their health, their well being, that is most important.
National Income and Per capita Income.
- Books Name
- Testing Private Course English Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
Income and other goals :
What people desire are regular work, better wages, and decent price for their crops or other products that they produce. In other words, they want more income.
People also seek things like equal treatment, freedom, security, and respect of others. They resent
discrimination.
Money, or material things that one can buy with it, is one factor on which our life depends. But the quality of our life also depends on non-material things mentioned above.
Consider an example:- If you get a job in a far off place, before accepting it you would try to consider many factors, apart from income, such as facilities for your family, working atmosphere, or opportunity to learn. In another case, a job may give you less pay but may offer regular employment that enhances your sense of security. Another job, however, may offer high pay but no job security and also leave no time for your family. This will reduce your sense of security and freedom.
How to compare different countries or states?
For comparing countries, their income is considered to be one of the most important attributes. Countries with higher income are more developed than others with less income. This is based on the understanding that more income means more of all things that human beings need.
Average income:- It is the total income of the country divided by its total population. The average income is also called per capita income.
Countries with per capita income of $12616 per annum and above in 2012, are called rich income countries. Eg.:- Japan, USA. UK. The rich countries, excluding countries of Middle East and certain other small countries, are generally called developed countries.
Those with per capita income of $1035 or less are called low-income countries. Eg.:- India. Because its per capita income was just $1530 per annum.
Income and Other Criteria :
When we think of a nation or a region, we may, besides average income, think of other equally important attributes. What could these attributes be? Let us examine this through an example.

(i) Income & other criteria :
1. If we compare the states of Maharashtra, Kerala, Bihar we find that Maharashtra has PCI of Rs. 107070, Kerala has Rs. 885 and Bihar has Rs. 28774.
2. IMR of Bihar is the most that is 43/1000, Maharashtra 25/1000 and Kerala 12/1000. This indicates that most of the children below the age of 1 year die in Bihar whereas although Maharashtra has a higher PCI their Kerala. This clearly proves that money cannot buy all the goods and services you need to live well such as pollution freen environment, unadultrated medicines and prevention from infections diseases.
3. If we com pare the literacy rate we find that the least number of children attending school in Bihar, i.e., 62 and maximum is in Kerala i.e. 94.
4. 2/3rd of the children aged 14-15 years in Bit are not attending school. The maximum net attendance ratio is in Kerala.
Important : Kerala has a low IMR because is has adequate provision of basic he a and educational facilities. Some states have a good public distribution system. This ensures a healthy and nutrition a states of the people.
Other Criteria’s :
Besides PCI other criteria’s use to measure development are
1. Infant Mortality Rate : Indicates the no. of children per 1000 born in a year that die before the age of one.
2. Literacy Rate : Measure the proportion of literia population above 7 years.
3. Net attendance Ratio : Is the total number of children between the age of it 10 years who are attending school.
4. Life Expectancy : Denotes the average expected length of life of a person at the times of births. In India, it is 66.4 years.
Human Development Report (HDR) :
The Human Development Report is published by UNDP and it compares countries based on it educational level, health states income level life expectancy. If we compare India with its neighbouring countries certain relevant inform can be percieved.
1. Gross National Income of Sri Lanka is $9250 India 5150 dollors and Pakistan - 4652 dollar.
2. Life expectancy of Sri Lanka is 74.3 years, India is 66.4 years and Pakistan is 66.6 years.
3. Literacy rates for 15 years and above in Sri Lanka is 91.2, Myanmar 92.7 & India 62.8.
4. As per HDR rank in the world, Sri Lanka is 73 & India is 135.
(ii) Literacy Rate measures the proportion of literate population in the 7 and above age group.
The 2nd column shows that more that half of the children in Bihar do not even get to go to school.
Net Attendance Ratio is the total number of children of age group 6-10 attending school as a percentage of total number of children in the same age group.

Notes :
(i) HDI stands for Human Development Index. HDI ranks in above table are out of 177 countries in all.
(ii) Life expectancy at birth denotes, as the name suggests, average expected length of life of a person at the time of birth.
(iii) Gross Enrolment Ratio for three levels means enrolment ratio for primary school, secondary school and higher education beyond secondary school.
(iv) Per Capita Income is calculated in dollars for all countries so that it can be compared. It is also done in a way so that every dollar would buy the same amount of goods and services in any country.
Sri Lanka, is much ahead of India in every respect and a big country like ours has such a low rank in the world.
Nepal has half the per capita income of India yet it is not far behind India in life expectancy and literacy levels.
What is important in development is what is happening to citizens of a country. It is people, their health, their well being, that is most important.
National Income and Per capita Income.
- Books Name
- Testing Private Course Hindi Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
Income and other goals :
What people desire are regular work, better wages, and decent price for their crops or other products that they produce. In other words, they want more income.
People also seek things like equal treatment, freedom, security, and respect of others. They resent
discrimination.
Money, or material things that one can buy with it, is one factor on which our life depends. But the quality of our life also depends on non-material things mentioned above.
Consider an example:- If you get a job in a far off place, before accepting it you would try to consider many factors, apart from income, such as facilities for your family, working atmosphere, or opportunity to learn. In another case, a job may give you less pay but may offer regular employment that enhances your sense of security. Another job, however, may offer high pay but no job security and also leave no time for your family. This will reduce your sense of security and freedom.
How to compare different countries or states?
For comparing countries, their income is considered to be one of the most important attributes. Countries with higher income are more developed than others with less income. This is based on the understanding that more income means more of all things that human beings need.
Average income:- It is the total income of the country divided by its total population. The average income is also called per capita income.
Countries with per capita income of $12616 per annum and above in 2012, are called rich income countries. Eg.:- Japan, USA. UK. The rich countries, excluding countries of Middle East and certain other small countries, are generally called developed countries.
Those with per capita income of $1035 or less are called low-income countries. Eg.:- India. Because its per capita income was just $1530 per annum.
Income and Other Criteria :
When we think of a nation or a region, we may, besides average income, think of other equally important attributes. What could these attributes be? Let us examine this through an example.

(i) Income & other criteria :
1. If we compare the states of Maharashtra, Kerala, Bihar we find that Maharashtra has PCI of Rs. 107070, Kerala has Rs. 885 and Bihar has Rs. 28774.
2. IMR of Bihar is the most that is 43/1000, Maharashtra 25/1000 and Kerala 12/1000. This indicates that most of the children below the age of 1 year die in Bihar whereas although Maharashtra has a higher PCI their Kerala. This clearly proves that money cannot buy all the goods and services you need to live well such as pollution freen environment, unadultrated medicines and prevention from infections diseases.
3. If we com pare the literacy rate we find that the least number of children attending school in Bihar, i.e., 62 and maximum is in Kerala i.e. 94.
4. 2/3rd of the children aged 14-15 years in Bit are not attending school. The maximum net attendance ratio is in Kerala.
Important : Kerala has a low IMR because is has adequate provision of basic he a and educational facilities. Some states have a good public distribution system. This ensures a healthy and nutrition a states of the people.
Other Criteria’s :
Besides PCI other criteria’s use to measure development are
1. Infant Mortality Rate : Indicates the no. of children per 1000 born in a year that die before the age of one.
2. Literacy Rate : Measure the proportion of literia population above 7 years.
3. Net attendance Ratio : Is the total number of children between the age of it 10 years who are attending school.
4. Life Expectancy : Denotes the average expected length of life of a person at the times of births. In India, it is 66.4 years.
Human Development Report (HDR) :
The Human Development Report is published by UNDP and it compares countries based on it educational level, health states income level life expectancy. If we compare India with its neighbouring countries certain relevant inform can be percieved.
1. Gross National Income of Sri Lanka is $9250 India 5150 dollors and Pakistan - 4652 dollar.
2. Life expectancy of Sri Lanka is 74.3 years, India is 66.4 years and Pakistan is 66.6 years.
3. Literacy rates for 15 years and above in Sri Lanka is 91.2, Myanmar 92.7 & India 62.8.
4. As per HDR rank in the world, Sri Lanka is 73 & India is 135.
(ii) Literacy Rate measures the proportion of literate population in the 7 and above age group.
The 2nd column shows that more that half of the children in Bihar do not even get to go to school.
Net Attendance Ratio is the total number of children of age group 6-10 attending school as a percentage of total number of children in the same age group.

Notes :
(i) HDI stands for Human Development Index. HDI ranks in above table are out of 177 countries in all.
(ii) Life expectancy at birth denotes, as the name suggests, average expected length of life of a person at the time of birth.
(iii) Gross Enrolment Ratio for three levels means enrolment ratio for primary school, secondary school and higher education beyond secondary school.
(iv) Per Capita Income is calculated in dollars for all countries so that it can be compared. It is also done in a way so that every dollar would buy the same amount of goods and services in any country.
Sri Lanka, is much ahead of India in every respect and a big country like ours has such a low rank in the world.
Nepal has half the per capita income of India yet it is not far behind India in life expectancy and literacy levels.
What is important in development is what is happening to citizens of a country. It is people, their health, their well being, that is most important.
National Income and Per capita Income.
Income and other goals :
What people desire are regular work, better wages, and decent price for their crops or other products that they produce. In other words, they want more income.
People also seek things like equal treatment, freedom, security, and respect of others. They resent
discrimination.
Money, or material things that one can buy with it, is one factor on which our life depends. But the quality of our life also depends on non-material things mentioned above.
Consider an example:- If you get a job in a far off place, before accepting it you would try to consider many factors, apart from income, such as facilities for your family, working atmosphere, or opportunity to learn. In another case, a job may give you less pay but may offer regular employment that enhances your sense of security. Another job, however, may offer high pay but no job security and also leave no time for your family. This will reduce your sense of security and freedom.
How to compare different countries or states?
For comparing countries, their income is considered to be one of the most important attributes. Countries with higher income are more developed than others with less income. This is based on the understanding that more income means more of all things that human beings need.
Average income:- It is the total income of the country divided by its total population. The average income is also called per capita income.
Countries with per capita income of $12616 per annum and above in 2012, are called rich income countries. Eg.:- Japan, USA. UK. The rich countries, excluding countries of Middle East and certain other small countries, are generally called developed countries.
Those with per capita income of $1035 or less are called low-income countries. Eg.:- India. Because its per capita income was just $1530 per annum.
Income and Other Criteria :
When we think of a nation or a region, we may, besides average income, think of other equally important attributes. What could these attributes be? Let us examine this through an example.

(i) Income & other criteria :
1. If we compare the states of Maharashtra, Kerala, Bihar we find that Maharashtra has PCI of Rs. 107070, Kerala has Rs. 885 and Bihar has Rs. 28774.
2. IMR of Bihar is the most that is 43/1000, Maharashtra 25/1000 and Kerala 12/1000. This indicates that most of the children below the age of 1 year die in Bihar whereas although Maharashtra has a higher PCI their Kerala. This clearly proves that money cannot buy all the goods and services you need to live well such as pollution freen environment, unadultrated medicines and prevention from infections diseases.
3. If we com pare the literacy rate we find that the least number of children attending school in Bihar, i.e., 62 and maximum is in Kerala i.e. 94.
4. 2/3rd of the children aged 14-15 years in Bit are not attending school. The maximum net attendance ratio is in Kerala.
Important : Kerala has a low IMR because is has adequate provision of basic he a and educational facilities. Some states have a good public distribution system. This ensures a healthy and nutrition a states of the people.
Other Criteria’s :
Besides PCI other criteria’s use to measure development are
1. Infant Mortality Rate : Indicates the no. of children per 1000 born in a year that die before the age of one.
2. Literacy Rate : Measure the proportion of literia population above 7 years.
3. Net attendance Ratio : Is the total number of children between the age of it 10 years who are attending school.
4. Life Expectancy : Denotes the average expected length of life of a person at the times of births. In India, it is 66.4 years.
Human Development Report (HDR) :
The Human Development Report is published by UNDP and it compares countries based on it educational level, health states income level life expectancy. If we compare India with its neighbouring countries certain relevant inform can be percieved.
1. Gross National Income of Sri Lanka is $9250 India 5150 dollors and Pakistan - 4652 dollar.
2. Life expectancy of Sri Lanka is 74.3 years, India is 66.4 years and Pakistan is 66.6 years.
3. Literacy rates for 15 years and above in Sri Lanka is 91.2, Myanmar 92.7 & India 62.8.
4. As per HDR rank in the world, Sri Lanka is 73 & India is 135.
(ii) Literacy Rate measures the proportion of literate population in the 7 and above age group.
The 2nd column shows that more that half of the children in Bihar do not even get to go to school.
Net Attendance Ratio is the total number of children of age group 6-10 attending school as a percentage of total number of children in the same age group.

Notes :
(i) HDI stands for Human Development Index. HDI ranks in above table are out of 177 countries in all.
(ii) Life expectancy at birth denotes, as the name suggests, average expected length of life of a person at the time of birth.
(iii) Gross Enrolment Ratio for three levels means enrolment ratio for primary school, secondary school and higher education beyond secondary school.
(iv) Per Capita Income is calculated in dollars for all countries so that it can be compared. It is also done in a way so that every dollar would buy the same amount of goods and services in any country.
Sri Lanka, is much ahead of India in every respect and a big country like ours has such a low rank in the world.
Nepal has half the per capita income of India yet it is not far behind India in life expectancy and literacy levels.
What is important in development is what is happening to citizens of a country. It is people, their health, their well being, that is most important.
National Income and Per capita Income.
- Books Name
- Private Course Testing Modules English Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
Income and other goals :
What people desire are regular work, better wages, and decent price for their crops or other products that they produce. In other words, they want more income.
People also seek things like equal treatment, freedom, security, and respect of others. They resent
discrimination.
Money, or material things that one can buy with it, is one factor on which our life depends. But the quality of our life also depends on non-material things mentioned above.
Consider an example:- If you get a job in a far off place, before accepting it you would try to consider many factors, apart from income, such as facilities for your family, working atmosphere, or opportunity to learn. In another case, a job may give you less pay but may offer regular employment that enhances your sense of security. Another job, however, may offer high pay but no job security and also leave no time for your family. This will reduce your sense of security and freedom.
How to compare different countries or states?
For comparing countries, their income is considered to be one of the most important attributes. Countries with higher income are more developed than others with less income. This is based on the understanding that more income means more of all things that human beings need.
Average income:- It is the total income of the country divided by its total population. The average income is also called per capita income.
Countries with per capita income of $12616 per annum and above in 2012, are called rich income countries. Eg.:- Japan, USA. UK. The rich countries, excluding countries of Middle East and certain other small countries, are generally called developed countries.
Those with per capita income of $1035 or less are called low-income countries. Eg.:- India. Because its per capita income was just $1530 per annum.
Income and Other Criteria :
When we think of a nation or a region, we may, besides average income, think of other equally important attributes. What could these attributes be? Let us examine this through an example.

(i) Income & other criteria :
1. If we compare the states of Maharashtra, Kerala, Bihar we find that Maharashtra has PCI of Rs. 107070, Kerala has Rs. 885 and Bihar has Rs. 28774.
2. IMR of Bihar is the most that is 43/1000, Maharashtra 25/1000 and Kerala 12/1000. This indicates that most of the children below the age of 1 year die in Bihar whereas although Maharashtra has a higher PCI their Kerala. This clearly proves that money cannot buy all the goods and services you need to live well such as pollution freen environment, unadultrated medicines and prevention from infections diseases.
3. If we com pare the literacy rate we find that the least number of children attending school in Bihar, i.e., 62 and maximum is in Kerala i.e. 94.
4. 2/3rd of the children aged 14-15 years in Bit are not attending school. The maximum net attendance ratio is in Kerala.
Important : Kerala has a low IMR because is has adequate provision of basic he a and educational facilities. Some states have a good public distribution system. This ensures a healthy and nutrition a states of the people.
Other Criteria’s :
Besides PCI other criteria’s use to measure development are
1. Infant Mortality Rate : Indicates the no. of children per 1000 born in a year that die before the age of one.
2. Literacy Rate : Measure the proportion of literia population above 7 years.
3. Net attendance Ratio : Is the total number of children between the age of it 10 years who are attending school.
4. Life Expectancy : Denotes the average expected length of life of a person at the times of births. In India, it is 66.4 years.
Human Development Report (HDR) :
The Human Development Report is published by UNDP and it compares countries based on it educational level, health states income level life expectancy. If we compare India with its neighbouring countries certain relevant inform can be percieved.
1. Gross National Income of Sri Lanka is $9250 India 5150 dollors and Pakistan - 4652 dollar.
2. Life expectancy of Sri Lanka is 74.3 years, India is 66.4 years and Pakistan is 66.6 years.
3. Literacy rates for 15 years and above in Sri Lanka is 91.2, Myanmar 92.7 & India 62.8.
4. As per HDR rank in the world, Sri Lanka is 73 & India is 135.
(ii) Literacy Rate measures the proportion of literate population in the 7 and above age group.
The 2nd column shows that more that half of the children in Bihar do not even get to go to school.
Net Attendance Ratio is the total number of children of age group 6-10 attending school as a percentage of total number of children in the same age group.

Notes :
(i) HDI stands for Human Development Index. HDI ranks in above table are out of 177 countries in all.
(ii) Life expectancy at birth denotes, as the name suggests, average expected length of life of a person at the time of birth.
(iii) Gross Enrolment Ratio for three levels means enrolment ratio for primary school, secondary school and higher education beyond secondary school.
(iv) Per Capita Income is calculated in dollars for all countries so that it can be compared. It is also done in a way so that every dollar would buy the same amount of goods and services in any country.
Sri Lanka, is much ahead of India in every respect and a big country like ours has such a low rank in the world.
Nepal has half the per capita income of India yet it is not far behind India in life expectancy and literacy levels.
What is important in development is what is happening to citizens of a country. It is people, their health, their well being, that is most important.
National Income and Per capita Income.
- Books Name
- Private Course Testing Modules Hindi Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Social Science
Income and other goals :
What people desire are regular work, better wages, and decent price for their crops or other products that they produce. In other words, they want more income.
People also seek things like equal treatment, freedom, security, and respect of others. They resent
discrimination.
Money, or material things that one can buy with it, is one factor on which our life depends. But the quality of our life also depends on non-material things mentioned above.
Consider an example:- If you get a job in a far off place, before accepting it you would try to consider many factors, apart from income, such as facilities for your family, working atmosphere, or opportunity to learn. In another case, a job may give you less pay but may offer regular employment that enhances your sense of security. Another job, however, may offer high pay but no job security and also leave no time for your family. This will reduce your sense of security and freedom.
How to compare different countries or states?
For comparing countries, their income is considered to be one of the most important attributes. Countries with higher income are more developed than others with less income. This is based on the understanding that more income means more of all things that human beings need.
Average income:- It is the total income of the country divided by its total population. The average income is also called per capita income.
Countries with per capita income of $12616 per annum and above in 2012, are called rich income countries. Eg.:- Japan, USA. UK. The rich countries, excluding countries of Middle East and certain other small countries, are generally called developed countries.
Those with per capita income of $1035 or less are called low-income countries. Eg.:- India. Because its per capita income was just $1530 per annum.
Income and Other Criteria :
When we think of a nation or a region, we may, besides average income, think of other equally important attributes. What could these attributes be? Let us examine this through an example.

(i) Income & other criteria :
1. If we compare the states of Maharashtra, Kerala, Bihar we find that Maharashtra has PCI of Rs. 107070, Kerala has Rs. 885 and Bihar has Rs. 28774.
2. IMR of Bihar is the most that is 43/1000, Maharashtra 25/1000 and Kerala 12/1000. This indicates that most of the children below the age of 1 year die in Bihar whereas although Maharashtra has a higher PCI their Kerala. This clearly proves that money cannot buy all the goods and services you need to live well such as pollution freen environment, unadultrated medicines and prevention from infections diseases.
3. If we com pare the literacy rate we find that the least number of children attending school in Bihar, i.e., 62 and maximum is in Kerala i.e. 94.
4. 2/3rd of the children aged 14-15 years in Bit are not attending school. The maximum net attendance ratio is in Kerala.
Important : Kerala has a low IMR because is has adequate provision of basic he a and educational facilities. Some states have a good public distribution system. This ensures a healthy and nutrition a states of the people.
Other Criteria’s :
Besides PCI other criteria’s use to measure development are
1. Infant Mortality Rate : Indicates the no. of children per 1000 born in a year that die before the age of one.
2. Literacy Rate : Measure the proportion of literia population above 7 years.
3. Net attendance Ratio : Is the total number of children between the age of it 10 years who are attending school.
4. Life Expectancy : Denotes the average expected length of life of a person at the times of births. In India, it is 66.4 years.
Human Development Report (HDR) :
The Human Development Report is published by UNDP and it compares countries based on it educational level, health states income level life expectancy. If we compare India with its neighbouring countries certain relevant inform can be percieved.
1. Gross National Income of Sri Lanka is $9250 India 5150 dollors and Pakistan - 4652 dollar.
2. Life expectancy of Sri Lanka is 74.3 years, India is 66.4 years and Pakistan is 66.6 years.
3. Literacy rates for 15 years and above in Sri Lanka is 91.2, Myanmar 92.7 & India 62.8.
4. As per HDR rank in the world, Sri Lanka is 73 & India is 135.
(ii) Literacy Rate measures the proportion of literate population in the 7 and above age group.
The 2nd column shows that more that half of the children in Bihar do not even get to go to school.
Net Attendance Ratio is the total number of children of age group 6-10 attending school as a percentage of total number of children in the same age group.

Notes :
(i) HDI stands for Human Development Index. HDI ranks in above table are out of 177 countries in all.
(ii) Life expectancy at birth denotes, as the name suggests, average expected length of life of a person at the time of birth.
(iii) Gross Enrolment Ratio for three levels means enrolment ratio for primary school, secondary school and higher education beyond secondary school.
(iv) Per Capita Income is calculated in dollars for all countries so that it can be compared. It is also done in a way so that every dollar would buy the same amount of goods and services in any country.
Sri Lanka, is much ahead of India in every respect and a big country like ours has such a low rank in the world.
Nepal has half the per capita income of India yet it is not far behind India in life expectancy and literacy levels.
What is important in development is what is happening to citizens of a country. It is people, their health, their well being, that is most important.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
