1. What is Source of Energy?
Notes added by teacher Sudhanshu in Batch 1 for Test 1
[sudhanshu@kaysonseducation.co.in]
Unit V Natural Resources > Chapter 1 Sources of energy > Different forms of energy
1. What is Source of Energy?
- Books Name
- Iti Shree Science Book
- Publication
- Vaishnav Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Science
Chapter 14
Sources of Energy
A source of energy is that which is capable of providing enough useful energy at a steady rate over a long period of time.
The largest source of energy on land is sunlight. There are different purposes for which energy is needed such as for food, for lightning, transport, running machines etc.
A good source of energy should be-
- Cheap and easily available.
- Safe in handling and use.
- Do not cause any environment pollution.
- Easy to store and transport.
Characteristics of a good fuel
- High calorific value.
- Less smoke.
- Less residue after burning.
- Easy availability.
- Inexpensive.
- Easy to store and transport.
Classification of Sources of energy
The sources of energy can be classified as follows:
- Renewable sources of energy.
- Non-Renewable sources of energy.
1. Renewable sources of energy: Renewable sources of energy are those which are inexhaustible, i.e., which can be replaced as we use them and can be used to produce energy again and again.
These are available in an unlimited amount in nature and develop within a relatively short period of time.
Example of Renewable Sources of Energy:
- Solar energy.
- Wind energy.
- Water energy (hydro-energy).
- Geothermal energy.
- Ocean energy.
- Biomass energy (firewood, animal dung and biodegradable waste from cities and crop residues constitute biomass).
Advantages of Renewable Sources of Energy
- These sources will last as long as the Earth receives light from the sun.
- These sources are freely available in nature.
- These sources do not cause any pollution.
2. Non-Renewable Source of Energy: Non-renewable sources of energy are those which are exhaustible and cannot be replaced once they have been used. These sources have been accumulated in nature over a very long period of millions of years.
Examples of Non-renewable Sources of Energy:
- Coal.
- Oil.
- Natural gas.
All these fuels are called fossil fuels.
Disadvantages of Non-renewable Sources of Energy
- Due to their extensive use, these sources are fast depleting.
- It is difficult to discover and exploit new deposits of these sources.
- These sources are a major cause of environmental pollution.
Types of Sources of Energy
There are two types of Sources of Energy –
- Conventional Sources of Energy - include the fossil fuels such as coal and petroleum.
- Non-conventional Sources of Energy - include solar cooker, solar cell panel etc.
Conventional Sources of Energy
Fossil Fuels:
- Fossil fuels are the remains of prehistoric plants and animals which got buried deep inside the early millions of years ago due to some natural processes.
- These fossil fuels are non-renewable sources of energy.
- They cause environmental problems due to pollution.
Formation of Fossil Fuels:
- During its formation, an entire organism or its parts often get buried in sand or mud.
- These, then decay and disintegrate leaving no signs of their existence.
- In fact, the harder parts of organisms after their death settle down and are covered by sediments and subjected to extreme pressure and temperature or the Earth converts them into fossil fuels, the process being referred to as fossilization.
Disadvantage of Fossil Fuels
- The fossils are non-renewable sources of energy and once used cannot be renewed.
- Burning of fossil fuels causes air pollution.
- These fuels cause pollution. They release different oxides which causes acid rain which damages plants, animals, houses etc.
- Excessive release of carbon-dioxide also causes global warming.
- The fossil fuels reserves in the Earth are limited and may get exhausted soon.
Thermal Power Plants
- Thermal power plant is used to generate electricity using heat.
- Burning of fossil fuels produces the steam which is used to run the turbines.
- This method helps in efficient transmission of electricity.
Hydro Power Plants
- Use to convert potential energy of falling water into electricity.
- They are associated with dams.
- They do not cause any pollution.
- Dam construction also prevents flooding of rivers and also provide water for irrigation.
Advantages of Hydro Power Plant:
- It is readily and abundantly available everywhere free of cost.
- It is eco-friendly and does not produce any kind of environmental pollution.
- It is a renewable source as water itself is a renewable and inexhaustible resource.
- It is a cheap source of energy, as it does not involve any costly investment.
Disadvantages of Hydro Power Plant
- Highly expensive to construct.
- Dams cannot be constructed on all river sites.
- Large areas of human habitation and agriculture fields get submerged.
- People face social and environmental problems.
Conventional Sources of Energy using technology
Bio-Mass: Biomass is defined as living matter or its residue and is a renewable sources of energy. The dead remains of plants and animals is known as Biomass.
The biomass includes.
- all the new plant growth
- Agriculture and forest residues (like Bio-gases, dark, sea dust, wood savings, roots, animals dropping, etc.),
- Carbonaceous wastes (like sewage, garbage, night-soil, etc.)
- Biodegradable organic effluent from industries.
It is the source of the conventionally used fuels that are used in our country. For example; Cow dung cakes, fire-wood, coal, charcoal etc.
Bio-gas: It is a mixture of gases produced during decomposition of bio mass in the absence of oxygen. (Anaerobic Respiration). Methane is the major component of bio-gas.
Bio-gas plants: Animal dung, sewage, crop residues, vegetable wastes, poultry dropping, etc. are used to produce Bio-gas in Bio-gas plants.
Advantage of Bio-gas
- A Bio-gas plant, is quite simple, can easily be built in rural areas. A small plant using dung from 3 to 4 heads of cattle is capable of supplying Bio-gas for 6 hours daily for cooking purposes.
- Bio-gas is a clean fuel that burns without smoke and leaves no ash.
- The main constituent of Bio-gas, i.e., ethane has a higher calorific value (55 kj/g) that of petrol (50kj/g).
- The spent slurry, being rich in nitrogen and phosphorus is good manure.
- By using Bio-gas, firewood is saved and deforestation is reduced.
Composition of Bio-gas: Bio-gas is mainly composed of methane (up to 75%), C02 (25%) and traces of other gases such as nitrogen and hydrogen. Whereas methane is a high-value calorific fuel, carbon dioxide is an inert gas.
Wind Energy: When large masses of air move from one place to another then it is referred to as wind. During this process, kinetic energy gets associated with it which is referred to as wind energy.
It can be converted into mechanical and electrical energy.
Kinetic energy of wind is used in running of windmills, which are used to lift water, grind grains etc.
Uses of Wind Energy
The important uses of wind energy are:
- It is used to drive windmills, water lifting pumps, and flour mills, etc.
- It is used to propel sail boats.
- It is used to fly engine fewer airplanes or gilders in the air.
- It is used to generate electrically used for various purposes like lightning, heating, etc.
Advantages:
- Eco-friendly
- Renewable.
Disadvantages:
- Wind speed does not uniform always.
- Needs a large area to erect series of windmills.
- Big amount of investment is needed.
- The output is less as compared to investment.
1. Components of Eco-System
- Books Name
- Iti Shree Science Book
- Publication
- Vaishnav Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Science
Chapter 15
Our Environment
Introduction
Things around us is known as Environment. It consists of living component also known as biotic component and non-living component also known as Abiotic Components.
Ecosystem
- The interaction between abiotic and biotic components is defined as ecosystem.
- It is a self-sustaining and functional unit of biosphere.
- The term ecosystem was coined by Sir Arthur Tansley.
Types of Ecosystem
There are two types of ecosystem-natural ecosystem and artificial ecosystem.
- The ecosystem present naturally is known as Natural Ecosystem. Example of Natural Ecosystem are forests, grasslands, deserts, ponds, lakes, rivers, estuaries, sea.
- The ecosystem which is man-made is known as Artificial Ecosystem. For Example Gardens, Aquariums and Agro ecosystem which is the largest man made ecosystem.
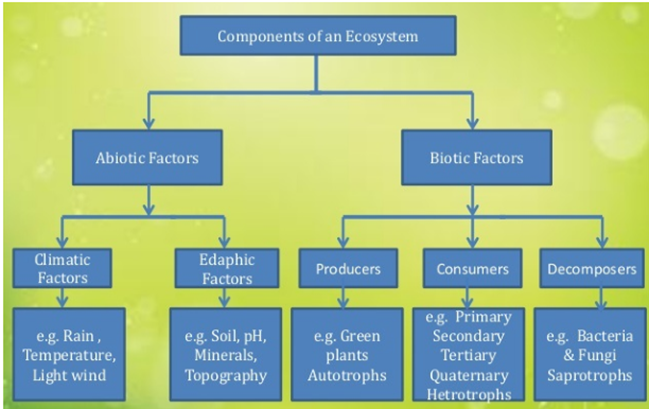
Components of ecosystem
Abiotic Factors Include - Climatic factors such as rain, temperature, wind etc. Another abiotic factor is edaphic factors such as soil, pH, minerals etc.
Biotic Factors include:
Producers which can make their own food, such as plants, blue-green algae etc.
Consumers feed on producers. Such as herbivores. In consumers there are-primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers etc.
Carnivores are flesh eating animals.
Omnivores consume both plants and animals.
Parasites live inside and depend upon living host.
Saprophytes feed on dead remains of plants and animals.
Food Chain is defined as series of organisms in order in which organisms feeds on another organism. There are various steps in food chain in which energy is transferred, each level is known as trophic level. Energy is always transferred uni directionally.
Characteristics of Food Chain
- There is a unidirectional flow of energy from producers to consumers.
- There are generally 3 to 4 trophic levels.
- It is always straight
- Organism can occupy different trophic levels in different food chain.
A 10 percent law is followed in energy transfer which was given by Raymond Lindeman. This law states that “only 10 percent of energy is transferred from one trophic level to another trophic level”. The remaining 90 percent will be used by the present trophic level in different processes. Therefore there are usually 3-4 trophic levels in a food chain.
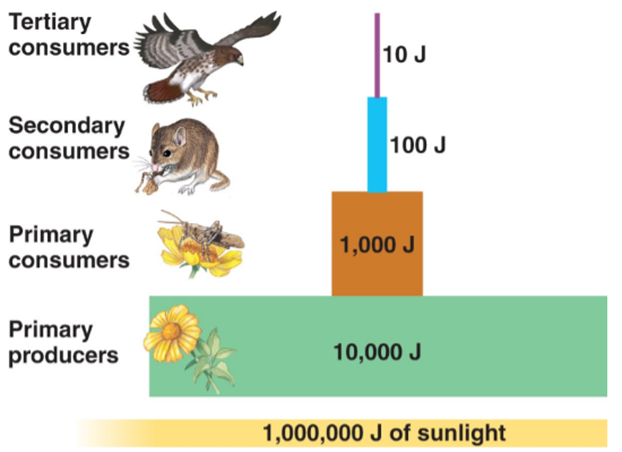
Energy transfer in trophic level
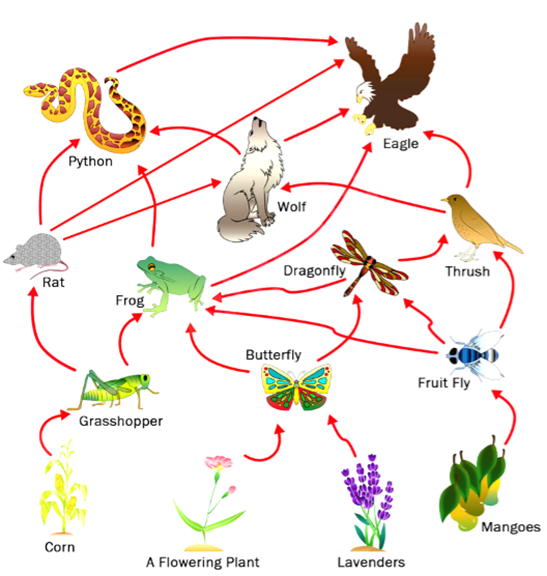
Food Web
Interconnection of food chain is known as Food Web. It shows how food chain are interdependent.
Characteristic of food web
- Food webs are never straight as they are formed by interlinking of food chains.
- Food web provides alternative pathways of food availability. If a particular species is destroyed, the predator can feed on an alternative species.
- Food webs increase ecosystem stability.
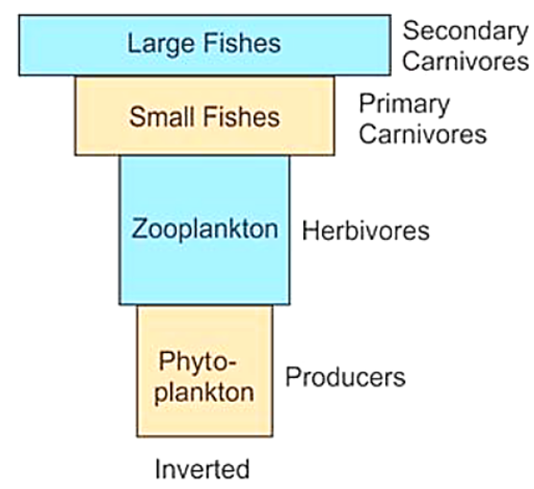
Ecological Pyramid
- Ecological Pyramid is a graphical representation to show biomass or bio productivity.
- There are different ecological pyramids such as pyramid of biomass, pyramid of number and pyramid of energy.
- Pyramid of number indicates number of individuals at different trophic levels.
- Pyramid of biomass indicates biomass of the members of the food chain present at different trophic levels.
Pyramid of energy indicates energy at different trophic levels.
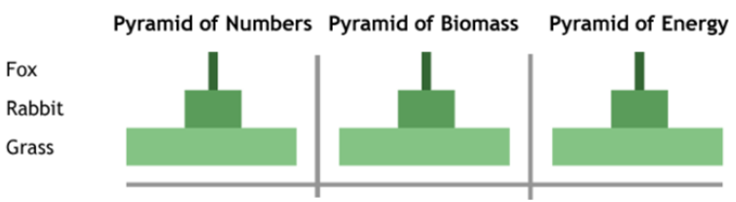
Upright Pyramids
- Pyramid of number and pyramid of biomass can be inverted also. In aquatic ecosystem pyramid of biomass is inverted.
1. Five R's to Save the Environment
- Books Name
- Iti Shree Science Book
- Publication
- Vaishnav Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Science
Chapter 16
Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
Ganga Action Plan
This plan was launched by Shri Rajeev Gandhi in 1986. It is to improve the water quality of Ganga by treatment, diversion and interception etc. It also includes treatment of domestic sewage and industrial effluents before releasing them into water bodies.
Natural Resources are obtained from earth and its environment. Natural resources are classified as-
Renewable resources which are continuously available for use. They do not get exhausted with time. For Example, Sunlight, Wind, Water etc.
Non-renewable Resources are those which gets exhausted with time. They are present in limited amount on the earth. For Example, Minerals.
Natural Resources are also classified as biotic and abiotic resources.
Biotic Resources can be obtained from forests, animals etc. For Example, Fossil Fuels.
Abiotic Resources are those that come from non-living and non-organic material.
There are five important terminologies used which are as follows-
Refuse: Say no to things that are offered to an individual. For Example, an individual say no to buy plastic products.
Reduce: Minimize the use of anything. For Example, minimize the use of fans, tube lights etc.
Reuse: To use the things again and again is defined as reuse.
Repurpose: When a particular thing cannot be used for a purpose, it can be used for another purpose.
Recycle: When the material can be used to make the needed things.
Why do we need to manage resources?
- We need to manage the resources because they are present in limited quantity.
- With the increase in population, the demand for resources are increasing.
- So, there is a need to manage the resources to minimize their use and preventing the exploitation of resources.
2. Non-Conventional Sources of Energy
Notes added by teacher sudhanshu@kaysonseducation.co.in for Batch Combined
Unit V Natural Resources > Chapter 1 Sources of energy > Conventional and non-conventional sources of energy.
2. Non-Conventional Sources of Energy
- Books Name
- Iti Shree Science Book
- Publication
- Vaishnav Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Science
Non-Conventional Sources of Energy
Solar Energy:
- The sun is the main source of energy for all living beings on this earth.
- The energy produced by the sun in the form of heat and light energy is called as solar energy.
- Solar radiations can be converted electricity through solar cells (Photovoltaic cells).
- Photovoltaic cells convert solar radiations directly into electricity through silicon solar cells.
- Solar cells arrange on a large flat sheets form a Mirror solar panel.
- Solar cookers are painted black from outside and a large glass plate to trap solar radiations by greenhouse effect.
Solar Cooker:
- Solar cooker is very simple in design and mode of function.
- It is usually made from mirrors.
- Plain mirrors are placed inside a rectangular box.
- The light reflected from the plain mirrors concentrates the solar energy inside the solar cooker which generates enough heat to cook food.
Advantages of Solar Cookers
- Eco-friendly.
- Renewable.
- Used in rural areas.
- Retains all the nutrients in food due to slow cooking.
Disadvantage of Solar Cookers:
- Silicon cells are expensive.
- Solar radiations are not uniform over the Earth’s surface.
- Cannot be used at night or on cloudy days.
- Cannot be used to make chapattis, for frying as these require a temperature of 140 °C or more. (Maximum temperature of 100 °C only can be achieved in a solar cooker) Other Solar Devices are solar water heater and Solar furnace.
Solar Panel
- Solar panel is an assembly of photo -voltaic cells mounted in a framework for installation.
- Solar panels use sunlight as a source of energy to generate direct current electricity.
- A collection of PV modules is called a PV panel, and a system of PV panels is called an array.
- Arrays of a photovoltaic system supply solar electricity to electrical equipment.
Energy from Sea
Tidal Energy: Due to the gravitational pull of the moon, tides happen near seashores. Water rushes up near the seashore during high tide and goes down during low tide. Dams are built near seashores to collect the water which comes during a high tide. When the water runs back to the ocean, the flow of water can be utilized to generate electricity.
Wave Energy: Waves can also be a good source of energy. Many devices are being designed and tested to produce wave energy. For example; a hollow tower is built near the seashore. When water gushes in the tube because of wave, it forces the air upwards. The kinetic energy of air in the tube is used to run a turbine. When the wave goes down; air from up goes down the tube which is also used in running the turbine.
Ocean Thermal Energy: The water at sea surface is hot during the daytime, while the water at a lower level is cold. The temperature differential in water levels can be utilized to generate energy. If the temperature differential is more than 20°C, then ocean thermal energy can be utilized from that place. For this, a volatile liquid; like ammonia; is boiled using the heat from the hot water at the surface. The steam of the volatile liquid is utilized to run the turbine to generate electricity. Colder water from the surface below is utilized to condense ammonia vapour which is then channelized to the surface to repeat the cycle.
Geothermal Energy: Heat energy from molten rocks present inside the earth created under certain favorable conditions by natural processes is called geothermal energy. It is the only type of energy which does not use solar energy.
Magma is formed when this heat melts the rocks. The rocks and hot gases are called magma.
The magma gets collected at some depths below the Earth’s surface. These places are called ‘Hot spots’.
When underground water comes in contact these hot spots, it changes into steam, which can be used to generate electricity.
Advantages of Geo Thermal Energy
- renewable
- Inexpensive
Disadvantages of Geo Thermal Energy
- Only a few sites are available for harnessing energy.
- Expensive
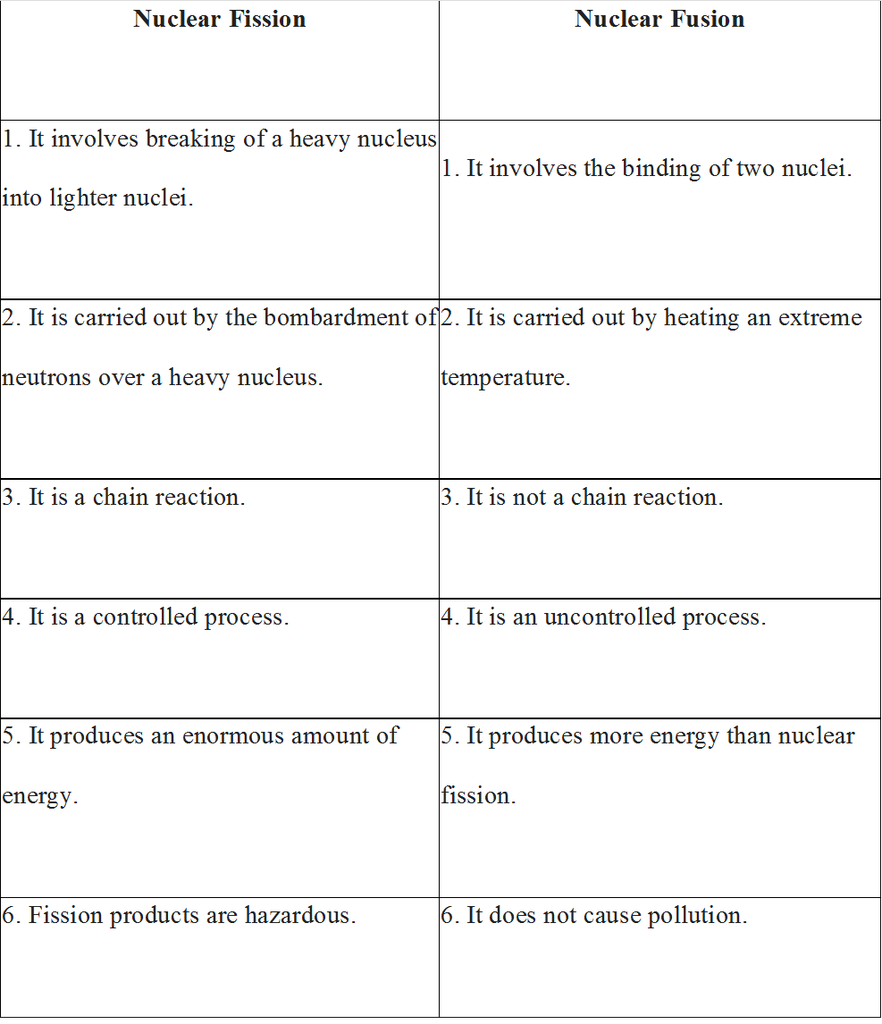
Nuclear Energy:
- Nuclear fission is the process during which a bigger nucleus breaks to produce two smaller nuclei.
- The process generates a huge amount of energy.
- This phenomenon is utilized in nuclear power plants.
- Nuclear power is safest for the environment but the risk of damage due to accidental leaks of radiation is pretty high.
- There are two distinct ways of obtaining nuclear energy, (a) Nuclear fission and (b) Nuclear fusion.
Advantages of nuclear energy.
A very large amount of energy can be produced by a nuclear process on using very small amount of nuclear fuel in a nuclear reactor.
The energy so produced can be easily transformed into electrical energy.
It does not produce harmful gases.
Disadvantages of Nuclear Energy:
- Risk of nuclear waste leakage.
- High cost of setting up of nuclear plant.
- Pollution of environment.
Difference between Nuclear Fission and Fusion
Environmental consequences of the increasing demand for energy:
- The combustion for fossil fuels produces acid rain and damages plants (crops), soil and aquatic life.
- The burning of fossil fuels is increasing the amount of greenhouse gas, carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- The construction of hydropower plants is a disturbing ecological balance.
- Nuclear power plants are increasing radioactivity in the environment.
2. Activities Affect the Environment
- Books Name
- Iti Shree Science Book
- Publication
- Vaishnav Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Science
Impact of Human activities
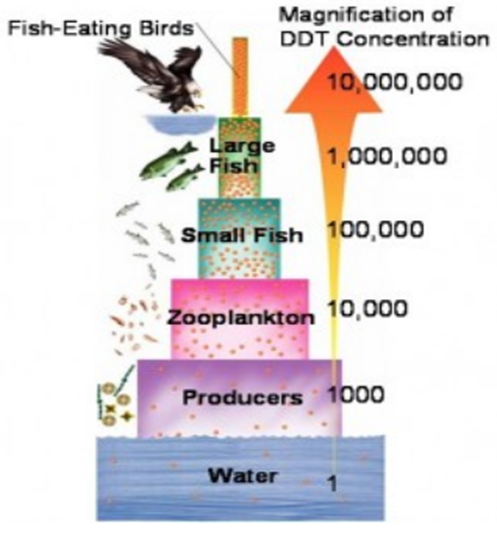
Biological Magnification
- The concentration of harmful substances increases with every trophic level. This is known as Bio magnification.
- Addition of pesticides in one trophic level increases the concentration of pesticides in other trophic level.
Ozone Layer
High UV radiation break down oxygen into oxygen atoms. These oxygen atoms when combine with oxygen, they form ozone.
Depletion of Ozone layer
- The thickness of the ozone layer over Antarctica was found to be decreased in the year 1985. This is defined as ozone depletion.
- This is due to excessive use of chlorofluorocarbons in refrigerators, ACs, aerosols, etc.
- Thinning of ozone would allow penetration of Ultraviolet rays into earth’s atmosphere causing blindness, skin cancers and mutations.
In 1987 United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) signed an agreement to limit the usage of CFCS. This is known as Montreal Protocol.
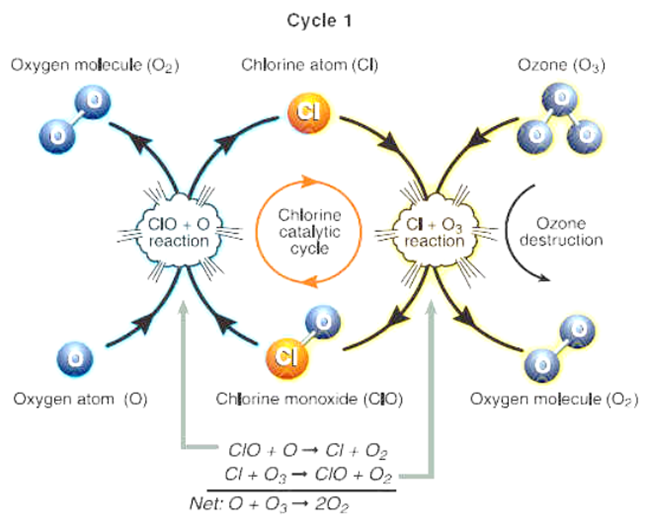
Reaction of CFC with ozone
Consequences of Ozone depletion
Exposure of UV rays causes skin cancer. UV-rays damage the eyes also. It affects humans, plants as well as animals.
Garbage Disposal
- Waste materials are known as garbage. There are two types garbage - Biodegradable Garbage and Non-biodegradable Garbage.
- Garbage that can be completely decomposed by the microorganism are called Biodegradable Garbage., such as fruit and vegetable peel, sewage.
- Substances which cannot be decomposed through microorganisms are known as Non-biodegradable Garbage, For Example, Plastic, Glass, Pesticide, Metals, and Radioactive Elements etc.
Methods of Waste Management
Waste disposal is a very important part of day to day life. There are different methods of waste disposal management- sewage treatment plant, biogas plant, land fillings, recycling, incineration, composting and reuse.
2. Forest and Wildlife
- Books Name
- Iti Shree Science Book
- Publication
- Vaishnav Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Science
Forests & Wildlife
Forests are biodiversity hotspots. Biodiversity is defined as different types of organism present on the earth. The main aim of conservation is to preserve the biodiversity. The loss of biodiversity will lead to loss of ecological stability.
Stakeholders
- They are the people living around the forests are dependent on forest and its products.
- Forest department of the government owns the land and also control the resources from forests.
- Industries that use forest produce .For Example Timber, Paper, Resin, Gum medicines, Sports equipment industries.
- Wildlife and natural enthusiast who want to conserve the nature.
Bamboo is used to manufacture huts, baskets and also for food storage. Implements used in agriculture, fishing is largely made up of wood. The government of India has recently instituted an Amrita devi bishnoi national award for wildlife conservation in the memory of an Amrita Devi bishnoi who sacrificed her life to protect the trees in 1731.
Management of Forests
- Local communities have been working traditionally for conservation of forests and trees.
- Magsaysay Award recipient Sunderlal Bahuguna gave momentum to the Chipko Andolan.
- The Chipko Andolan was started in Reni in Garhwal.
- It was started by villagers especially by women at Reni village who tried to stop the commercial wood contractors from cutting the tree by hugging the trunk of the trees.
People Participation in Management of forest resources
- The acceptance of locals who live in harmony with natural resources is vital for forest conservation measures.
- In 1972, the West Bengal forest department found that they have failed in maintaining the degraded Sal forests.
- Surveillance and policing had led to complete alienation of the people which led to clashes between forest officials and villagers.
- So, to overcome this, department was forced to changed the strategy.
- Forest officer A.K. Banerjee involved villagers in protection of 1272 hectares of badly degraded Sal forests in Arabari forest range of Midnapore district.
- In return he allowed villagers to collect fuel wood and fodder on payment of nominal fee. Also 25% of final harvest was given to village community.
Method of Forest Conservation
- One of the most common method of forest conservation is silviculture. It is a method in which trees are grown and cultivated.
- Social forestry deals with the management and protection of the forest.
- Agroforestry includes land management for the cultivation of trees or shrubs.
Red Data Book
It is a document for recording the list of the endangered and rare species of animals, plants, fungi as well as some local species also.
Water for All
Water is required for fulfilling the basic needs of individuals. Human activities have altered the availability of water in various regions. Rain in India are due to monsoon. Common irrigation methods such as dams, canals and tanks are used in various parts of India. These methods are maintained by local people. This helps in storing water which can be used in agriculture. Not only in agriculture, can daily needs of the common people be met through this water.
Dams
- Large dams are made to store water that can be used in irrigation, in generating electricity etc. Indira Gandhi canal in Rajasthan areas has helped a lot in bringing greenery in different regions.
- Dams control floods, provide water supply, electricity, waste management, recreation and wildlife habitat etc.
- Criticism about large dams addresses three problems in particular- social problems, economic problems and environment problems
- Construction of dams causes problems such as excessive sedimentation, water logging, sudden floods, soil erosion, large scale deforestation, health hazards, loss of livelihood etc.
Ancient method of Waste watershed Management
Different methods of watershed management system are known since ancient times. One of the method known as Khadins in Rajasthan which consists of a long earthen embankment built across the lower hill slopes. The area enclosed by the embankment is called as ‘bund’ which collects huge amount of rainwater which flows down the slopes. Subsequently this water saturated land is used for crop production.
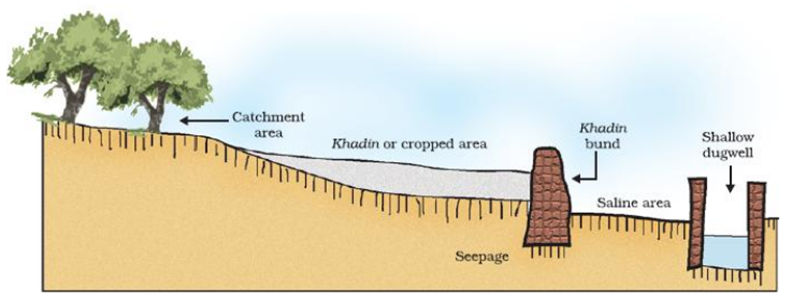
Khadin in Rajasthan- An ancient method of watershed management.
Talabs are other mode of watershed management system known so far. It stores water for drinking and household consumption purposes. Others include kulhs in Himachal Pradesh,, Ahar and Pynes in Bihar, Eris in Tamil Nadu, Bundhis in Madhya Pradesh, Surangams in Kerala etc.
Coal & Petroleum
- They are the non-renewable natural resources.
- Coal is formed by the remains of the trees buried inside the earth.
- Petroleum is formed by the bacterial decomposition of dead plants and dead animals. High pressure and temperature are needed for the formation of petroleum.
- Both coal and petroleum are fossil fuels.
- They are getting used up at higher rate, so there are more chances that they get exhausted soon.
Disadvantages of Fossil Fuels - Burning of fossil fuels release large amount of carbon-dioxide, sulphur dioxide and other harmful gases. This causes air pollutions and the harmful effects of air pollution. This also raises the earth temperature and thus leads to global warming.
Steps to minimize the pollution from fossil fuels
- Reduce the use and burning of fossil fuels.
- Use of CNG in transport vehicles to reduce pollution.
- Alternative sources of energy such as Hydroelectricity, nuclear, solar, wind power and biogas should be used.

 Carrier Point
Carrier Point
