What is Lorem Ipsum?
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry's standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a type specimen book. It has survived not only five centuries, but also the leap into electronic typesetting, remaining essentially unchanged. It was popularised in the 1960s with the release of Letraset sheets containing Lorem Ipsum passages, and more recently with desktop publishing software like Aldus PageMaker including versions of Lorem Ipsum.
- Books Name
- Iti Shree Science Book
- Publication
- Vaishnav Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Science
Refraction through a rectangular Glass slab
- The ray of light enters from rarer to denser medium at point O that is from air to glass and bends towards the normal.
- At ‘O’, the light ray enters from glass to air, that is, from a denser medium to a rarer medium. The light here bends away from normal.
- The emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray. However the light ray shifts slightly sideward.
- Refraction is due to change in speed of light when it enters from one medium to another.
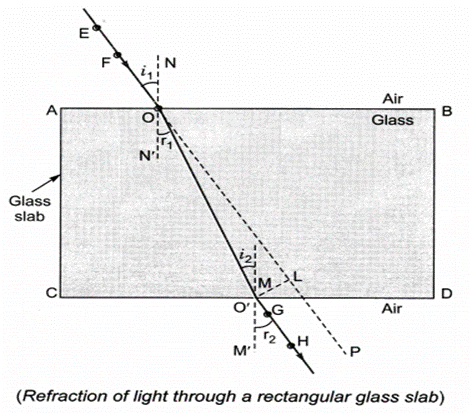
Refraction of light: Bending of the light rays as it passes from one medium to another medium is known as refraction of light.
Laws of refraction
Two laws of reflection are:
(i) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface of two transparent media at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is constant for the light of a given colour and for the given pair of media. This law is also known as Snell’s law of refraction.
![]()
Refractive index: The extent of the change in direction of light that takes place in a given pair of media is expressed in terms of the refractive index. This can be expressed in an equation form as
![]()
Absolute refractive index: Refractive index of medium 2 with respect to vacuum is called the absolute refractive index of the medium. It is represented as n2.
Spherical lens: A transparent medium bound by two surfaces, of which one or both surfaces are curved is called a spherical lens.
Concave lens: It is a spherical lens in which two spherical surfaces bulge inwards. It is also called diverging lens.
Convex lens: It is a spherical lens in which two spherical surfaces bulge outwards. It is also called converging lens.
Refraction of light by spherical lens:
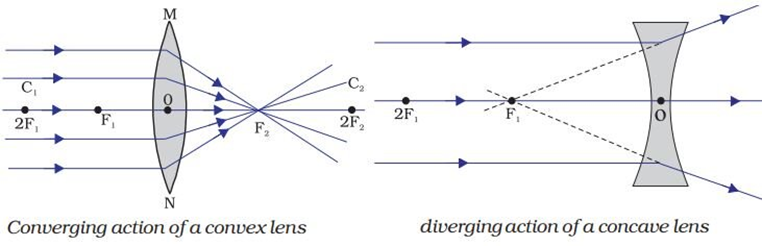
Image formation by Convex Lens
(i) When the object is at infinity
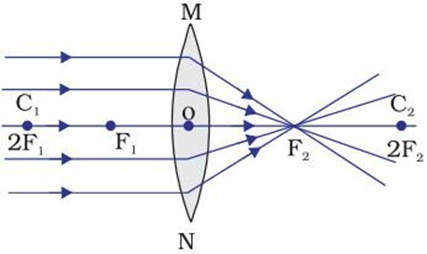
→ Image is formed at focus F2
→ Image is highly diminished or point-sized
→ Image is real and inverted
(ii) When the object is beyond 2F1
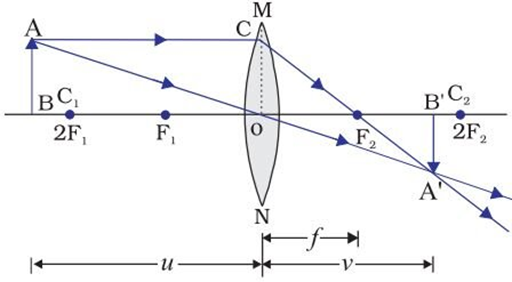
→ Image is formed between F2 and 2F2
→ Image is diminished
→ Image is real and inverted
(iii) When the object is at 2F1
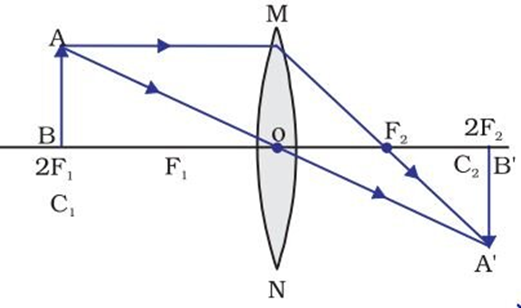
→ Image is formed at 2F2
→ Image is same size as that of object
→ Image is real and inverted
(iv) When the object is between F1 and 2F1
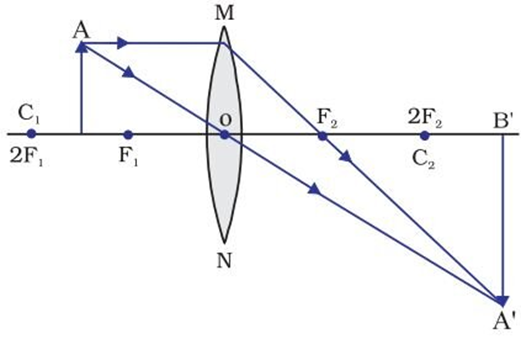
→ Image is formed beyond 2F2
→ Image is enlarged
→ Image is real and inverted
(v) When the object is at focus F1
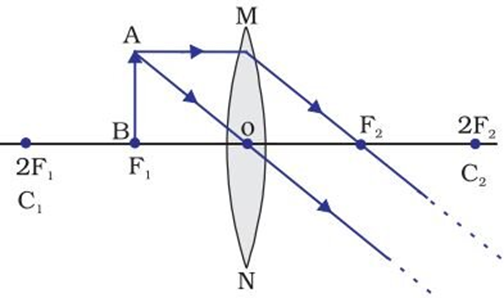
→ Image is formed at infinity
→ Image is infinitely large or highly enlarged
→ Image is real and inverted
(vi) When the object is between focus F1 and optical centre O
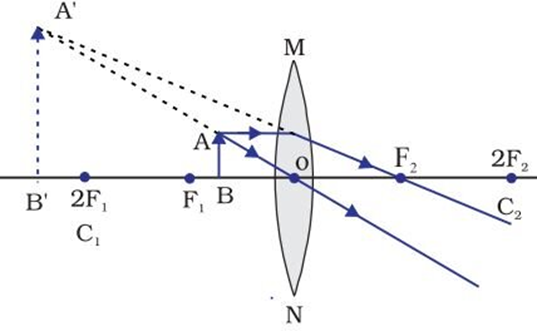
→ Image is formed on the same side of the lens as the object
→ Image is enlarged
→ Image is virtual and erect

 Carrier Point
Carrier Point
