- Books Name
- Iti Shree Science Book
- Publication
- Vaishnav Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Science
Chemical properties of Metals
Metals react with air or oxygen to form metal oxide.
For Example, Copper reacts with oxygen to form copper oxide.
Metal + O2 → Metal oxide
2Cu + O2 → 2CuO
4Al + 3O2 → 2Al2O3
Oxides of metals can react with both acids and bases to produce salt and water. Such oxides are known as Amphoteric Oxides.
Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + H2O

Metals also react with water to form metal oxide. Metal oxide in turn can react with water to form metal hydroxide.
For Example
2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + 1H2
2Al + 3H2O → Al2O3 + 3H2
Metals also react with dilute acids to form salt and hydrogen.
For example, magnesium reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to form magnesium chloride and hydrogen.
Metal + Acid → Metal Salt + Hydrogen
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
Reaction of metals with solutions of other metal salts
Reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their compounds in solution or molten form.
Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu
Cu + 2AgNO3 → Cu (NO3) + 2Ag
Reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their compounds in solution or molten form.
Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu
Cu + 2AgNO3 → Cu (NO3) + 2Ag
Special cases
- Metals such as potassium and sodium react so vigorously that they catch fire if kept in the open. Hence, to protect them and to prevent accidental fires, they are kept immersed in kerosene oil.
- At ordinary temperature, the surfaces of metals such as magnesium, aluminum, zinc, lead, etc., are covered with a thin layer of oxide. The protective oxide layer prevents the metal from further oxidation.
- Iron does not burn on heating but iron filings burn vigorously when sprinkled in the flame of the burner.
- Copper does not burn, but the hot metal is coated with a black coloured layer of copper (II) oxide.
- Silver and gold do not react with oxygen even at high temperatures.
Chemical properties of Non-metals
Non-metals react with oxygen to form non-metal oxide.
Non-metal + Oxygen → Non-metal oxide
C + O2 → CO2
Non-metals do not react with water and acids to evolve hydrogen gas.
Non-metals can react with salt solution; the more reactive element will displace the less reactive non-metal.
2 NaBr (aq) + Cl2(aq) → 2NaCl (aq) + Br2 (aq)
Non-metals can also react with hydrogen to form hydrides.
H2(g) + S(l) → H2S(g)
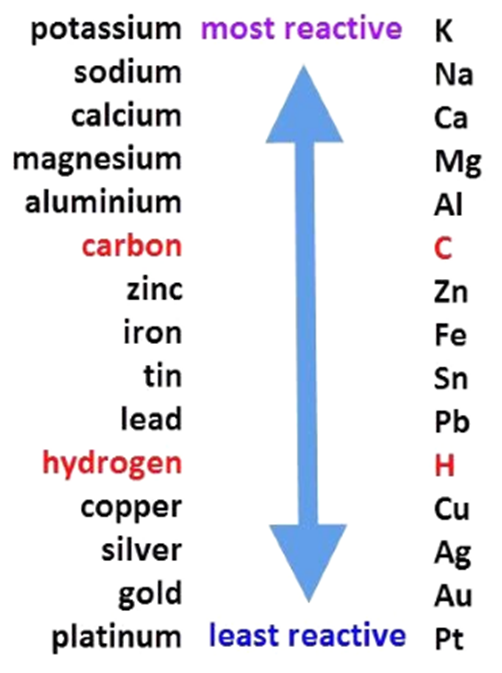
Reactivity Series
The series in which metals are arranged in the decreasing order of reactivity is known as the Reactivity Series.

 Vaishnav Publication
Vaishnav Publication
