What is Lorem Ipsum?
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry's standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a type specimen book. It has survived not only five centuries, but also the leap into electronic typesetting, remaining essentially unchanged. It was popularised in the 1960s with the release of Letraset sheets containing Lorem Ipsum passages, and more recently with desktop publishing software like Aldus PageMaker including versions of Lorem Ipsum.
- Books Name
- Iti Shree Science Book
- Publication
- Vaishnav Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Science
Chapter 6
Life Processes
Introduction
- Nutrition: The process by which an organism takes food and utilizes it, is called nutrition.
- Need for Nutrition: Organisms need the energy to perform various activities. The energy is supplied by the nutrients. Organisms need various raw materials for growth and repair. These raw materials are provided by nutrients.
- Nutrients: Materials which provide nutrition to organisms are called nutrients. Carbohydrates, proteins and fats are the main nutrients and are called macronutrients. Minerals and vitamins are required in small amounts and hence are called micronutrients.
- Modes of Nutrition
1. Autotrophic Nutrition.
2. Heterotrophic Nutrition.
Autotrophic Nutrition
- The mode of nutrition in which an organism prepares its own food is called autotrophic nutrition. Green plants and blue-green algae follow the autotrophic mode of nutrition.
- The organisms which carry out autotrophic nutrition are called autotrophs (green plants).
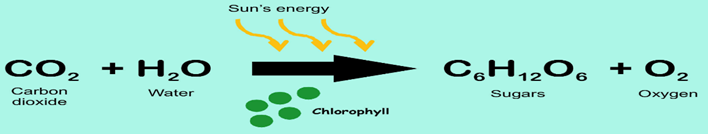
- Autotrophic nutrition is fulfilled by the process, by which autotrophs intake CO2 and H2O, and convert these into carbohydrates in the presence of chlorophyll, sunlight is called photosynthesis.
- Nutrition in Plants: Green plants prepare their own food. They make food in the presence of sunlight. Sunlight provides energy’, carbon dioxide and water are the raw materials and chloroplast is the site where food is made.
The site where photosynthesis occurs is known as chloroplast. They contain a green colour pigment known as chlorophyll that traps sunlight for photosynthesis.
The steps of photosynthesis are as follows-
- Absorption of light by chlorophyll.
- Conversion of light energy into chemical energy.
- Splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Finally, reduction of carbon dioxide into carbohydrates.
Leaves contain small openings known as stomata which helps in the exchange of gases. The stomata/stoma is surrounded by a guard cell which guards the opening and closing of stomata. Guard cells also contain chloroplast.
Heterotrophic Nutrition
In this mode of nutrition, an organism is unable to synthesise its food. It is of the following types-
- Holozoic nutrition is a type of nutrition where an organism takes in whole food and breaks it inside the body. For example, Amoeba.
- Saprophytic nutrition is nutrition in which organisms feed on dead and decaying matter. For example, fungi.
- Parasitic nutrition is nutrition in which an organism feeds on a living host. For example, Cuscuta.
Nutrition in Amoeba
- Amoeba feeds by holozoic mode of nutrition.
- It engulfs the food particle using pseudopodia, the process is called phagocytosis.
- The engulfed food gets enclosed in a food vacuole.
- As the food vacuole passes through the cytoplasm, digestion, absorption and assimilation take place.
- When the food vacuole opens to outside, the egestion of undigested food takes place.
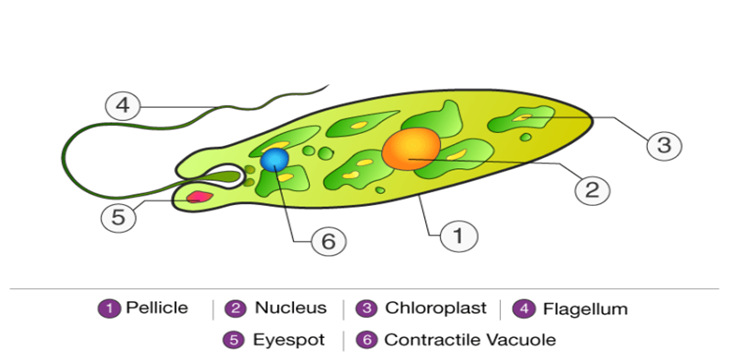
Nutrition in Paramecium
- Paramecium also exhibits holozoic nutrition.
- However, they have cilia that help them to engulf the food through the oral groove.
- A food vacuole is created enclosing the food.
- It moves through the cytoplasm, the process is called cyclosis.
- Food digested in the food vacuole is absorbed by the cytoplasm.
- Undigested food is given out to a tiny pore called anal pore or cytopyge.
Nutrition in Human beings
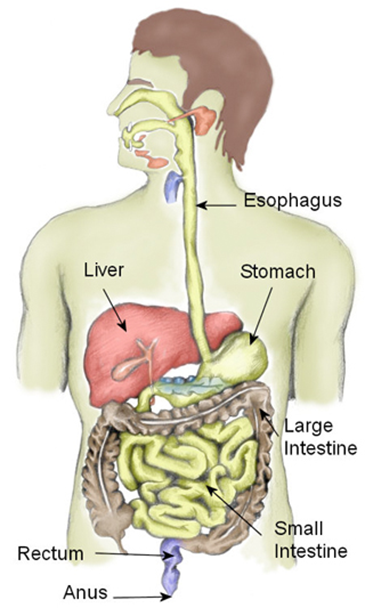
Humans consist of the alimentary canal which starts from the mouth and ends at the anus. The parts of the alimentary canal are as follows-
- Mouth
- Pharynx
- Oesophagus/food pipe
- Stomach
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Rectum
- Anus
Human Digestive System
Mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal. The mouth consists of a muscular tongue and teeth. The cavity inside the mouth is known as the oral cavity.
Mechanism of Digestion of Food
- Food digestion process begins in the mouth. Food is complex in nature.
- To break down food and absorb it, we need biological catalysts known as enzymes.
- The mouth contains salivary glands that secrete saliva. Saliva contains an important enzyme known as the salivary enzyme that breaks down starch into simple sugars.
- The food then passes via the oesophagus into the stomach. The movement of the food inside the oesophagus occurs via rhythmic contraction of muscles, this is known as peristalsis.
- The stomach contains gastric glands that secrete mucus, hydrochloric acid and pepsin. Pepsin is a protein-digesting enzyme.
- After the stomach, food then enters the small intestine. The small intestine is larger in herbivores due to cellulose digestion compared to carnivores.
- Complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats occurs in the small intestine.
- The small intestine receives secretions from the pancreas and bile from the liver. Bile helps in the emulsification of fats whereas the pancreas secretes enzymes such as trypsin for protein digestion. The intestinal wall also contains glands that secrete intestinal juice.
- The small intestine has villi that increase the surface area for the absorption of food.
- The unabsorbed food is then transferred to the large intestine where water is absorbed.
- Undigested food is then expelled out from the anus.

 Carrier Point
Carrier Point
