- Books Name
- Iti Shree Science Book
- Publication
- Vaishnav Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Science
Forests & Wildlife
Forests are biodiversity hotspots. Biodiversity is defined as different types of organism present on the earth. The main aim of conservation is to preserve the biodiversity. The loss of biodiversity will lead to loss of ecological stability.
Stakeholders
- They are the people living around the forests are dependent on forest and its products.
- Forest department of the government owns the land and also control the resources from forests.
- Industries that use forest produce .For Example Timber, Paper, Resin, Gum medicines, Sports equipment industries.
- Wildlife and natural enthusiast who want to conserve the nature.
Bamboo is used to manufacture huts, baskets and also for food storage. Implements used in agriculture, fishing is largely made up of wood. The government of India has recently instituted an Amrita devi bishnoi national award for wildlife conservation in the memory of an Amrita Devi bishnoi who sacrificed her life to protect the trees in 1731.
Management of Forests
- Local communities have been working traditionally for conservation of forests and trees.
- Magsaysay Award recipient Sunderlal Bahuguna gave momentum to the Chipko Andolan.
- The Chipko Andolan was started in Reni in Garhwal.
- It was started by villagers especially by women at Reni village who tried to stop the commercial wood contractors from cutting the tree by hugging the trunk of the trees.
People Participation in Management of forest resources
- The acceptance of locals who live in harmony with natural resources is vital for forest conservation measures.
- In 1972, the West Bengal forest department found that they have failed in maintaining the degraded Sal forests.
- Surveillance and policing had led to complete alienation of the people which led to clashes between forest officials and villagers.
- So, to overcome this, department was forced to changed the strategy.
- Forest officer A.K. Banerjee involved villagers in protection of 1272 hectares of badly degraded Sal forests in Arabari forest range of Midnapore district.
- In return he allowed villagers to collect fuel wood and fodder on payment of nominal fee. Also 25% of final harvest was given to village community.
Method of Forest Conservation
- One of the most common method of forest conservation is silviculture. It is a method in which trees are grown and cultivated.
- Social forestry deals with the management and protection of the forest.
- Agroforestry includes land management for the cultivation of trees or shrubs.
Red Data Book
It is a document for recording the list of the endangered and rare species of animals, plants, fungi as well as some local species also.
Water for All
Water is required for fulfilling the basic needs of individuals. Human activities have altered the availability of water in various regions. Rain in India are due to monsoon. Common irrigation methods such as dams, canals and tanks are used in various parts of India. These methods are maintained by local people. This helps in storing water which can be used in agriculture. Not only in agriculture, can daily needs of the common people be met through this water.
Dams
- Large dams are made to store water that can be used in irrigation, in generating electricity etc. Indira Gandhi canal in Rajasthan areas has helped a lot in bringing greenery in different regions.
- Dams control floods, provide water supply, electricity, waste management, recreation and wildlife habitat etc.
- Criticism about large dams addresses three problems in particular- social problems, economic problems and environment problems
- Construction of dams causes problems such as excessive sedimentation, water logging, sudden floods, soil erosion, large scale deforestation, health hazards, loss of livelihood etc.
Ancient method of Waste watershed Management
Different methods of watershed management system are known since ancient times. One of the method known as Khadins in Rajasthan which consists of a long earthen embankment built across the lower hill slopes. The area enclosed by the embankment is called as ‘bund’ which collects huge amount of rainwater which flows down the slopes. Subsequently this water saturated land is used for crop production.
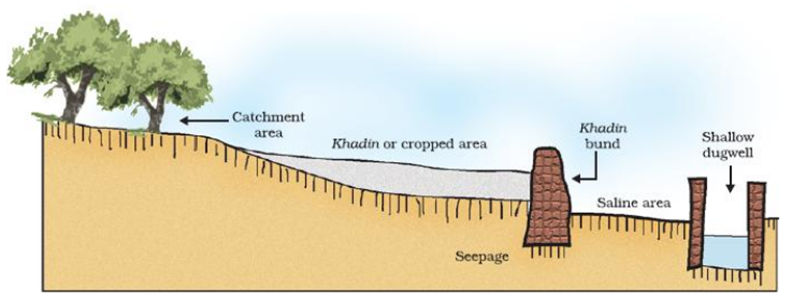
Khadin in Rajasthan- An ancient method of watershed management.
Talabs are other mode of watershed management system known so far. It stores water for drinking and household consumption purposes. Others include kulhs in Himachal Pradesh,, Ahar and Pynes in Bihar, Eris in Tamil Nadu, Bundhis in Madhya Pradesh, Surangams in Kerala etc.
Coal & Petroleum
- They are the non-renewable natural resources.
- Coal is formed by the remains of the trees buried inside the earth.
- Petroleum is formed by the bacterial decomposition of dead plants and dead animals. High pressure and temperature are needed for the formation of petroleum.
- Both coal and petroleum are fossil fuels.
- They are getting used up at higher rate, so there are more chances that they get exhausted soon.
Disadvantages of Fossil Fuels - Burning of fossil fuels release large amount of carbon-dioxide, sulphur dioxide and other harmful gases. This causes air pollutions and the harmful effects of air pollution. This also raises the earth temperature and thus leads to global warming.
Steps to minimize the pollution from fossil fuels
- Reduce the use and burning of fossil fuels.
- Use of CNG in transport vehicles to reduce pollution.
- Alternative sources of energy such as Hydroelectricity, nuclear, solar, wind power and biogas should be used.

 Vaishnav Publication
Vaishnav Publication
