- Books Name
- Iti Shree Science Book
- Publication
- Vaishnav Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Science
Refraction of Light through Prism
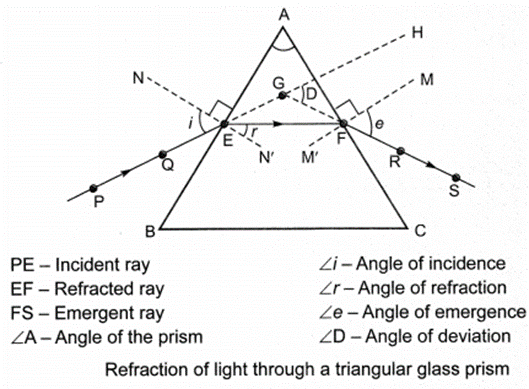
(i) The refraction of light takes place at two surfaces firstly when light enters from air to prism and j secondly when light emerges from prism.
(ii) Angle of prism: The angle between the two lateral faces of the prism is called angle of prism.
(iii) Angle of deviation: The angle between incident ray (produced forward) and emergent ray I (produced backward).
Dispersion of White Light by a Glass Prism
When light falls on the prism it splits the incident light into band of colours. The sequence of colours observed are VIBGYOR (Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red). This band of colour is known as Spectrum. So, this splitting of incident light into different colours is known as Dispersion. This splitting is due to bending of light rays at different angles. Violet light bends most whereas red light bends least. The phenomenon of rainbow is also due to dispersion of light.
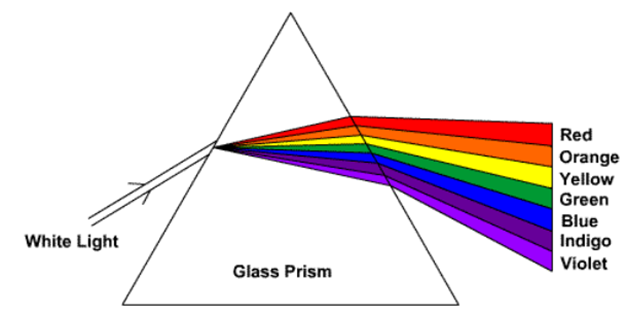
Dispersion of White Light through Prism
The band of these seven colours formed because of dispersion of light is known as Spectrum.
Atmospheric Refraction
Twinkling of Stars
When star light enters the atmosphere, it undergoes refraction. Due to this refractive index changes as the light bends towards the normal. The apparent position of the stars appears slightly different from the actual position. Since the physical conditions of the earth’s atmosphere are not stationary, the apparent positions of stars keep on changing. That is why they appear to twinkle.
Advance Sunlight and Delayed Sunset
The sun is visible 2 minutes before the actual sunrise or sunset appears 2 minutes after the actual sunset has taken place is due to atmospheric refraction.
When the sun is slightly below the horizon, the sunlight coming from the less dense (vacuum) to the denser (air) medium is refracted downwards. Therefore, the Sun appears to be above the horizon. Similarly, even after sunset, the Sun can be seen for some time due to refraction of sunlight.

 Vaishnav Publication
Vaishnav Publication
