- Books Name
- Iti Shree Science Book
- Publication
- Vaishnav Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Science
Chemical properties of Carbon Compounds
Combustion
Carbon along with its compound is used as a fuel as it burns in presence of oxygen to release energy. Saturated hydrocarbons produce blue and non-sooty flame whereas unsaturated hydrocarbons produce a yellow sooty flame.
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
Oxidation
Alcohol can be oxidised to aldehydes whereas aldehydes, in turn, can be oxidised to carboxylic acid. Oxidising agents such as potassium permanganate can be used for oxidation.

Addition Reaction
Hydrogenation of vegetable oil is an example of an additional reaction. Addition of hydrogen in presence of catalysts such as nickel or palladium. This converts the oil into ghee.
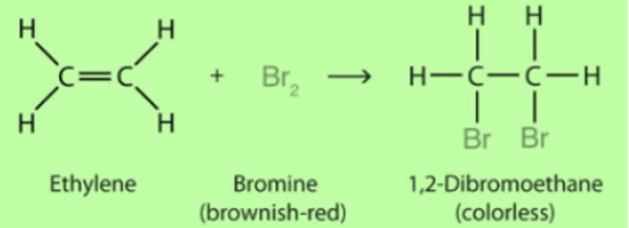
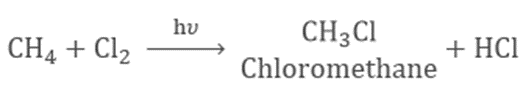
Substitution Reaction
When one atom in hydrocarbon is replaced by chlorine, bromine, etc. this is known as a Substitution Reaction.

 Vaishnav Publication
Vaishnav Publication
