notes added by teacher sudhanshu in section a
no need to add by Manas from section B
- Books Name
- Iti Shree Science Book
- Publication
- Vaishnav Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Science
Respiration
Introduction
- Respiration broadly means the exchange of gases.
- Animals and plants have different means of exchange of gases.
- At a cellular level, respiration means the burning of the food for generating the energy needed for other life processes.
- Cellular respiration may take place in the presence or absence of oxygen.
Cellular Respiration
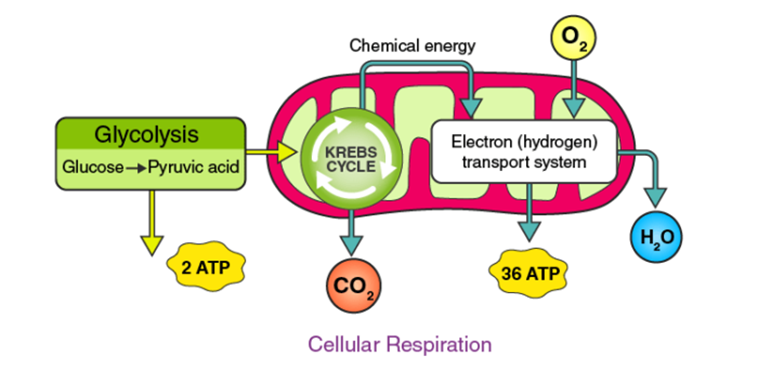
Cellular respiration is set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
- Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism. These can be divided into two categories:These can be divided into two categories:
- Catabolism – the process of breaking molecules to obtain energy.
- Anabolism – the process of synthesizing all compounds required by the cells.
- Therefore, respiration is a catabolic process, which breaks large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy to fuel cellular activities.
- Glycolysis, Krebs cycle and electron transport chain are the important processes of the cellular respiration.
ATP
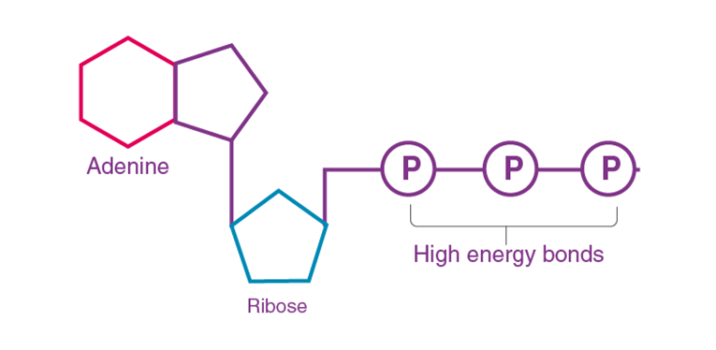
- It is the energy currency of the cell.
- ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate.
- This molecule is created as a result reactions like photosynthesis, respiration etc.
- The three phosphate bonds present in the molecule are high-energy bonds and when they are broken, a large amount of energy is released.
- Such released energy is then used for other metabolic reactions.
Types of Respiration
1. Aerobic respiration
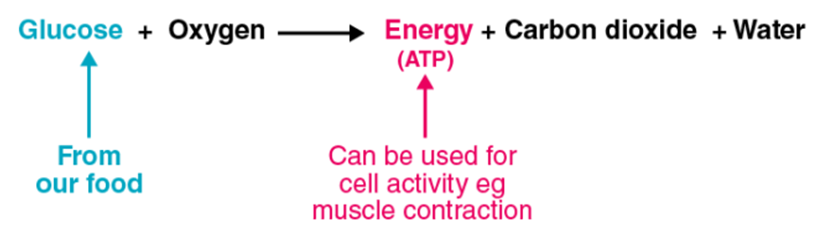
Aerobic respiration is a process in which the food i.e. glucose is converted into energy in the presence of oxygen.
- The general equation of aerobic respiration as a whole is as given below-
Glucose + oxygen ⇒ Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
- This type of respiration takes place in animals, plants and other living organisms.
2. Anaerobic respiration
- Respiration in muscles can be anaerobic when there is not enough oxygen.
- Glucose gets broken down into carbon dioxide and lactic acid.
- This results in the accumulation of lactic acid that makes the muscles sore.
- This type of anaerobic respiration is also known as lactic acid fermentation.
Respiration in Humans
- The human respiratory system is more complex and involves breathing, exchange of gases and cellular respiration.
- A well-defined respiratory system helps breathing and exchange of gases.
- Breathing involves the inhalation of oxygen and exhalation of carbon dioxide.
- The gaseous exchange takes place in the lungs and oxygen is supplied to all cells of the body.
- Cellular respiration takes place in each and every cell.
Human Respiratory system
- The human respiratory system involves the nose, nasal cavities, pharynx, larynx, trachea/windpipe, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli.
- Bronchioles and alveoli are enclosed in a pair of lungs.
- The rib cage, muscles associated with the rib cage and diaphragm, all help in inhalation and exhalation of gases.
- Exchange of gases takes place between an alveolar surface and surrounding blood vessels.
- Alveoli provide a large surface area for exchange of gases.
Physiology of Respiration
- Breathing in humans is facilitated by the action of internal intercostal and external intercostal muscles attached to the ribs and the diaphragm.
- When the dome-shaped diaphragm contracts and becomes flattened and the rib cage is expanded due to the action of intercostal muscles, the volume of the lungs increases, pressure there drops down and the air from outside gushes in. This is inhalation.
- To exhale, the diaphragm relaxes, becomes dome-shaped again, chest cavity contracts due to the action of intercostal muscles, the volume inside the lungs decreases, pressure increases and the air is forced out of the lungs.
- Inhaled air increases the concentration of oxygen in the alveoli, so oxygen simply diffuses into the surrounding blood vessels.
- Blood coming from cells has more concentration of carbon dioxide than outside air and thus carbon dioxide simply diffuses out of the blood vessels into the alveoli.
- Thus, breathing takes place due to the combined action of intercostal muscles and diaphragm while the exchange of gases takes place due to simple diffusion.
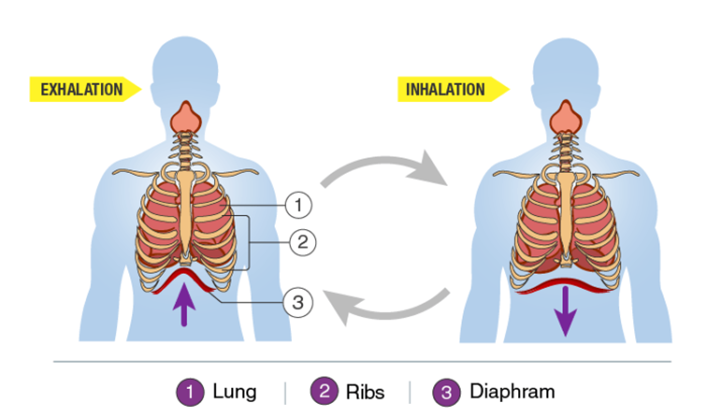
Inhalation and Exhalation
- The process of taking in air rich in oxygen is called inhalation.
- Similarly, the process of giving out air rich in carbon dioxide is called exhalation.
- One breath comprises one inhalation and one exhalation.
- A person breathes several times in a day.
- The number of times a person breathes in one minute is termed as his/her breathing rate.

 Carrier Point
Carrier Point
