Division Algorithm Of Polynomials
We are aware of the process of division of numbers. Let us divide 487 by 3. We can divide 487 by 3 as follows:
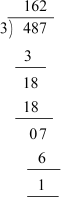
From the above division, we can see that when we divide 487 by 3, we get 1 as remainder and 162 as quotient.
We can also write the dividend 487 in terms of divisor, quotient and remainder as follows: 487 = 3 × 162 + 1
Thus, for real numbers we can write
Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
In the same way, we can also divide a polynomial p(x) by another polynomial g(x) when the degree of the polynomial p(x) is greater than or equal to the degree of polynomial g(x). The above relation is also true in case of polynomials and then it is known as division algorithm of polynomials.
Using the division algorithm of polynomials, we can also find any one of the values among p(x), g(x), q(x) and r(x) if other three are known.
Note that degree of q(x) = degree of p(x) – degree of g(x)
Let us discuss more examples based on division algorithm of polynomials.
Example 1: Find the quotient, if the polynomial −2x3 + 7x2 − 7x − 2 when divided by 2x2 − 5x + 2 gives remainder −4.
Solution:
Let the quotient be q(x).
It is given that when we divide the polynomial (−2x3 + 7x2 − 7x − 2) by (2x2 − 5x + 2), we get the q(x) as quotient and −4 as remainder.
Thus, we have
p(x) = −2x3 + 7x2 − 7x − 2
g(x) = 2x2 − 5x + 2
r(x) = −4
We know that the division algorithm for polynomials is:
p(x) = g(x) × q(x) + r(x)
Now, on putting the values in this equation, we have
−2x3 + 7x2 − 7x − 2 = (2x2 − 5x + 2) × q(x) − 4
⇒ −2x3 + 7x2 − 7x − 2 + 4 = (2x2 − 5x + 2) × q(x)
⇒ −2x3 + 7x2 − 7x + 2 = (2x2 − 5x + 2) × q(x)
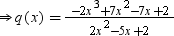
We can divide −2x3 + 7x2 − 7x + 2 by (2x2 − 5x + 2) as follows:
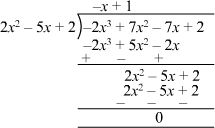
Now, we have q(x) = 1 − x
Therefore, the quotient is 1 − x.
Example 2: Find the quotient, if the polynomial 3x3 − 3x2 + 9x + 2 when divided by x2 + 5x + 1 gives remainder 4x3.
Solution:
Let the quotient be q(x).
It is given that when we divide the polynomial (3x3 − 3x2 + 9x + 2) by (x2 + 5x + 1), we get the q(x) as quotient and 4x3 as remainder.
Thus, we have
p(x) = 3x3 − 3x2 + 9x + 2
g(x) = x2 + 5x + 1
r(x) = 4x3
We know that the division algorithm for polynomials is:
p(x) = g(x) × q(x) + r(x)
Now, on putting the values in this equation, we have
3x3 − 3x2 + 9x + 2 = (x2 + 5x + 1) × q(x) + 4x3
⇒ 3x3 − 3x2 + 9x + 2 − 4x3 = (x2 + 5x + 1) × q(x)
⇒ −x3 − 3x2 + 9x + 2 = (x2 + 5x + 1) × q(x)
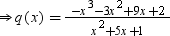
We can divide −x3 − 3x2 + 9x + 2 by (x2 + 5x + 1) as follows:
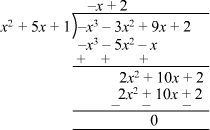
Now, we have q(x) = 2 − x
Therefore, the quotient is 2 − x.
Example 3: By applying division algorithm, find the quotient and remainder when p(x)
= x4 + 3x3 + 2x2 + 5x – 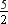 is divided by g(x) = x3 + 2x – 1.
is divided by g(x) = x3 + 2x – 1.
Solution:
p(x) = x4 + 3x3 + 2x2 + 5x – 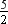 , g(x) = x3 + 2x – 1
, g(x) = x3 + 2x – 1
deg p(x) = 4, deg g(x) = 3
Degree of quotient q(x) = 4 – 3 = 1, and deg of remainder r(x) < deg g(x) = 3 Let q(x) = ax + b, r(x) = cx2 + dx + e
By division algorithm,
p(x) = g(x) × q(x) + r(x)
⇒ x4 + 3x3 + 2x2 + 5x – 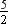 = (ax + b)(x3 + 2x – 1) + (cx2 + dx + e)
= (ax + b)(x3 + 2x – 1) + (cx2 + dx + e)
= ax4 + 2ax2 – ax + bx3 + 2bx – b + cx2 + dx + e
= ax4 + bx3 + (2a + c)x2 + (–a + 2b + d)x + (–b + e)
Equating the coefficients of respective powers, we obtain
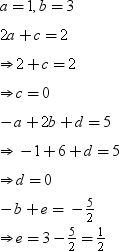
Quotient, q (x) = x + 3
Remainder, r (x) = 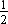

 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
