Solution of Quadratic Equations by Completing Squares
Many real life situations can result in quadratic equations. For example, consider the following situation:
A ladder is leaning against a wall. The top of the ladder touches the wall at a
height of 15 feet. The length of the ladder is one foot more than twice its distance from the foot of the wall. We need to find the length of the ladder.
We can express the given situation mathematically with the help of a quadratic equation.
Let us see how.
Let the distance from the wall to the bottom of the ladder be x feet.
It is given that the length of the ladder is one foot more than twice its distance from the foot of the wall.
Hence, the length of the ladder becomes (2x + 1).
The wall makes an angle of 90° with respect to the ground. Since the ladder is leaning against the wall, the entire arrangement forms a right triangle in which the ladder acts as the hypotenuse.
On applying Pythagoras theorem, we get
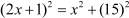
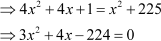
Now, to find the length of the ladder, we first need to solve the given quadratic equation. Observe that if you try to solve it by splitting the middle term, then it will become very lengthy. In such cases, it is easier to solve the quadratic equation by another method called the Completion of Squares.
Let us learn this method with the help of an example. Consider the following quadratic equation:
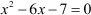
In this method, we need to convert the quadratic equation in the form
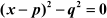
To convert a quadratic equation in this form, we will make use of the following identities:
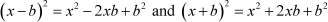
In the example taken previously, the given equation was 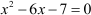 .
.
Note that the term with the coefficient x has a negative sign attached to it.
We thus need to make use of the identity 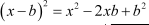 here.
here.
On comparing this equation with the given identity, we get 2b = 6, i.e., b = 3.
Thus, we need to add 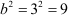 on both sides of the equation.
on both sides of the equation.
The equation now becomes .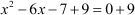
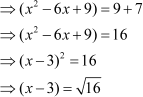
It is important to remember that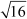 has two values, i.e., 4 and –4.
has two values, i.e., 4 and –4.
Thus, the equation can be further simplified as
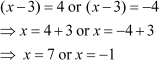
Thus, the given equation has two solutions, i.e., x = 7 and x = –1.
Let us now go back to the initial problem we were discussing.
We had arrived at a final quadratic equation, which was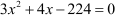 .
.
Note that in this case, the term with the coefficient x2 is not a perfect square. We thus need to multiply the equation by 3 to make it a perfect square.
On doing so, we get
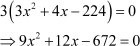
The identity can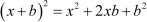 be used here.
be used here.
The equation can now be solved as
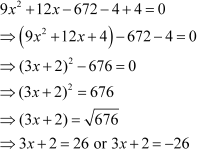
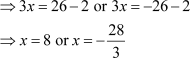
However, x represents the distance of the foot of the ladder from the base of the wall, which cannot be negative. Thus, x has only one value, i.e., 8.
Thus, length of the ladder = 2x + 1 = (2 × 8 + 1) ft = 17 ft
We can follow one more approach to solve this equation.
The equation was 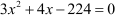 .
.
Here, the term with the coefficient x2 is not a perfect square. We thus convert it to a perfect square by multiplying the equation by 3.
Note that we could also have divided the equation by 3 and still have converted the term to a perfect square.
Let us see how.
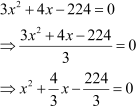
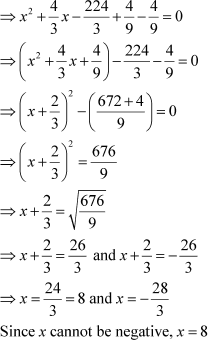
We can use any of the two methods mentioned above, as long as we covert the equation to the form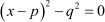 .
.
 Note: Usually, the roots of the quadratic equation ,
Note: Usually, the roots of the quadratic equation ,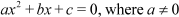 can be found by first dividing the equation by and then completing the squares of the terms in the equation.
can be found by first dividing the equation by and then completing the squares of the terms in the equation.
Example 1: Find the roots of the equation 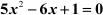 by the method of completion of squares.
by the method of completion of squares.
Solution:
The given equation is .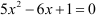
By multiplying the equation by 5, we get 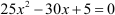 .
.
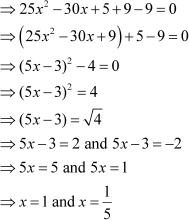
Example 2: Find the roots of the equation 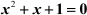 by the method of completion of squares.
by the method of completion of squares.
Solution:
The given equation is 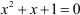 .
.
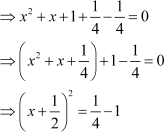
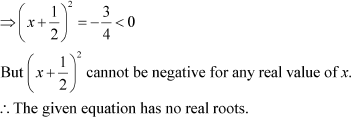
Example 3: Find three consecutive even integers so that the product of the first two numbers is three times the third number.
Solution:
Let the three numbers be x, (x + 2), and (x + 4).
From the given condition, we have x(x + 2) = 3(x + 4).
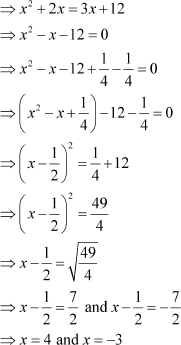
However, the three numbers are positive integers.
Thus, x cannot be equal to –3.
Thus, the three consecutive even integers are 4, 6, and 8.
Example 4: Denominator of a fraction is 3 more than its numerator such that both are positive integers. If the sum of the fraction and its reciprocal is 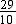 then find the fraction.
then find the fraction.
Solution:
Let the numerator be x. Then the denominator will be x + 3.
According to the question, we have
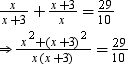
⇒ 10(x2 + x2 + 6x + 9) = 29x(x + 3)
⇒ 20x2 + 60x + 90 = 29x2 + 87x
⇒ 9x2 + 27x – 90 = 0
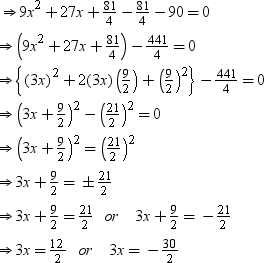
⇒ x = 2 or x = –5
–5 is a negative integer, so it is discarded.
Consider x = 2
∴ Numerator = 2 and Denominator = 2 + 3 = 5
∴ Fraction = 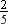
Example 5: Base of a small triangular garden is 7 m more than its height. If the area of the garden is 60 m2 then find its base and height.
Solution:
Let the height of the triangular garden be x m. Then its base will be (x + 7) m.
Area of triangular garden = 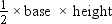
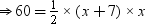
⇒120 = x2 + 7x
⇒ x2 + 7x – 120 = 0
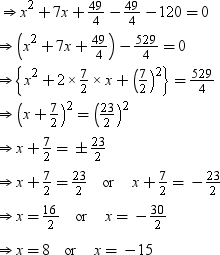
Length cannot be negative, so we consider x = 8.
∴ Height of triangular garden = 8 m
∴ Base of triangular garden = (8 + 7) m = 15 m
Solution of Quadratic Equations by Using Quadratic Formula
The following equations are quadratic in nature:
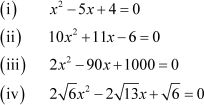
If we were to solve these equations, we could have either factorized the equations (i), (ii), and (iii) or completed their squares.
However, note that we would face a lot of difficulty in solving equation (iv) by either of these two methods.
Apart from factorizing a quadratic equation or completing its square, we can also use the quadratic formula to factorize an equation.
Let us go back to equation (iv), which was 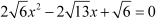 . Comparing this equation with the general form of a quadratic equation:
. Comparing this equation with the general form of a quadratic equation:
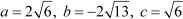
Thus, according to the quadratic formula:
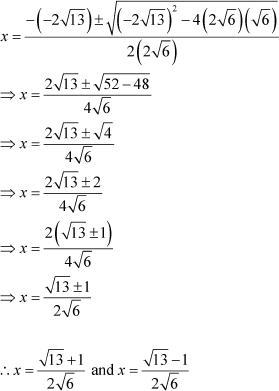
Let us now solve some more quadratic equations by using the quadratic formula.
Example 1: Solve the quadratic equation 5x2 + x− 22 = 0 by using the quadratic formula.
Solution:
On comparing the given equation with the general form ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 5, b = 1, c = −22
On putting these values in the quadratic formula, we get
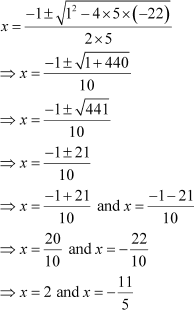
Example 2: Find the roots of the equation 3x2 + 5x + 10 = 0 by using the quadratic equation formula.
Solution:
On comparing the given equation with the general form ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 3, b = 5, c = 10
∴ b2 − 4ac = (5)2 − 4 × 3 × 10
= 25 − 120
= −95 <</span> 0
Thus, 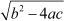 does not have any real value.
does not have any real value.
Thus, there are no real roots for the given equation.
Example 3: The denominator of a fraction is 2. If the sum of the fraction and its
reciprocal is ![]() , then find the fraction.
, then find the fraction.
Solution:
Let the numerator of the fraction be x.
Hence, the rational number is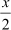 .
.
It is given that the sum of the fraction and its reciprocal is 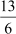 .
.
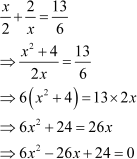
On comparing this equation with the general form ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 6, b = −26, c = 24
On putting these values in the quadratic formula, we get
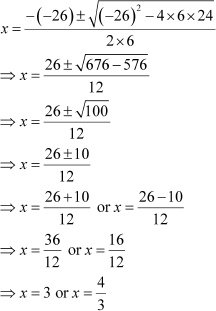
Since x is the numerator of the fraction, it has to be an integer.
∴ x = 3
Thus, the fraction is 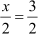 .
.
Example 4: The perimeter of a rectangle is 34 cm and its area is 70 cm2. Find the length and the breadth of the rectangle.
Solution:
Let the length and breadth of the rectangle be x and y respectively.
Thus, perimeter of the rectangle = 2(x + y) = 34 cm
⇒ x + y = 17
⇒ y = 17 – x … (1)
Thus, area of the rectangle = x × y = 70 cm2 … (2)
Substituting the value of y from (1) in (2):
x(17 – x) = 70
⇒ 17x – x2 = 70
⇒ x2 – 17x + 70 = 0
By using the quadratic formula, we get
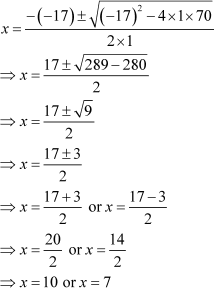
Thus, the length and the breadth of the rectangle are 10 cm and 7 cm respectively.
Example 5: A ball is thrown upwards from a height of 6 m with a particular speed. The height h of the ball after t seconds is given by 6 + 13t – 5t2. How long the ball will take to touch the ground?
Solution:
Height of the ball after t seconds is given as follows:
h = 6 + 13t – 5t2
When ball will touch the ground, the height will be 0 m.
⇒ 0 = 6 + 13t – 5t2
⇒ 5t2 – 13t – 6 = 0
By using the quadratic formula, we get
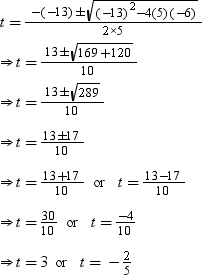
Time cannot be negative, so we will consider t = 3.
Thus, the ball will touch the ground after 3 seconds.
Example 6: A super fast train takes 6 hours less than a passenger train to reach the destination which is 1440 km away. If the speed of the super fast train is 40 km/hr more than that of passenger train then find the average speed of both trains.
Solution:
Let the average speed of passenger train be x km/hr.
Then the average speed of super fast train will be x + 40 km/hr.
Total distance to be covered = 1440 km
Total time taken by passenger train = 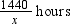
Total time taken by super fast train = 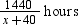
According to the question, we have
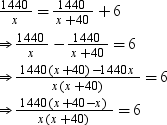
⇒ 1440(40) = 6x(x + 40)
⇒ x2 + 40x – 9600 = 0
By using the quadratic formula, we get
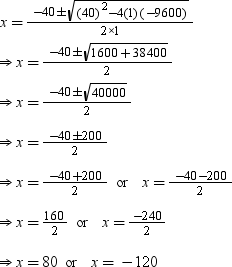
Speed cannot be negative, so we consider x = 80.
∴ Average speed of passenger train = 80 km/hr
∴ Average speed of super fast train = (80 + 40) km/hr = 120 km/hr

 SonikaAnandAcademy
SonikaAnandAcademy
 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
