Graphic Interpretation Of The Number Of Zeros Of A Polynomial
A polynomial in variable x is denoted by p(x).
The highest power of the variable in the polynomial is known as its degree. For example, the highest power of variable x in the polynomial x2 − 3x + 2 is 2. Hence, it’s degree is 2.
Let us better understand this concept with a few more examples.
Example1: Find the number of zeroes of the polynomial whose graph is given below.
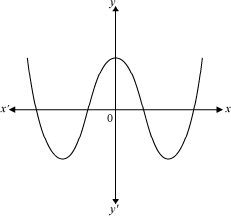
Solution:
The given graph intersects the x- axis at 4 distinct points. Hence, the number of zeroes of the given polynomial is 4.
Example 2: Find the number of zeroes of the polynomial whose graph is given below.
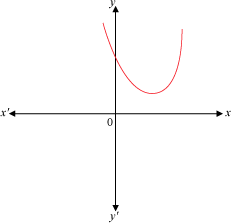
Solution:
The given graph does not intersect the x-axis.
Hence, the given polynomial has no zeroes or in other words, the number of zeroes of the given polynomial is zero.
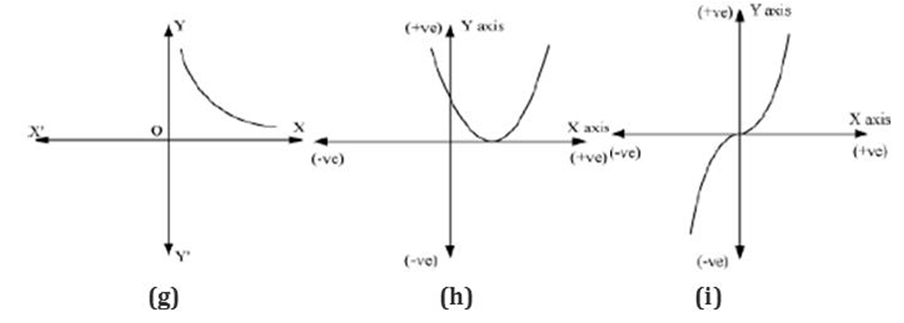
Example 3: Find the number of zeroes of the polynomials whose graphs are given below.
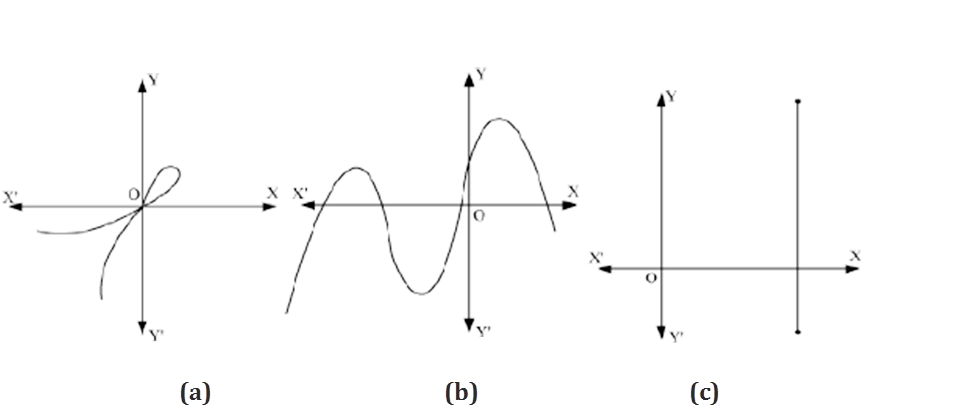

Solution:
(a) The graph intersects the x-axis at only 1 point.
Hence, the number of zeroes of this polynomial is 1.
(b) The graph intersects the x-axis at 4 distinct points.
Hence, the number of zeroes of this polynomial is 4.
(c) The graph intersects the x-axis at only 1 point.
Hence, the number of zeroes of this polynomial is 1.
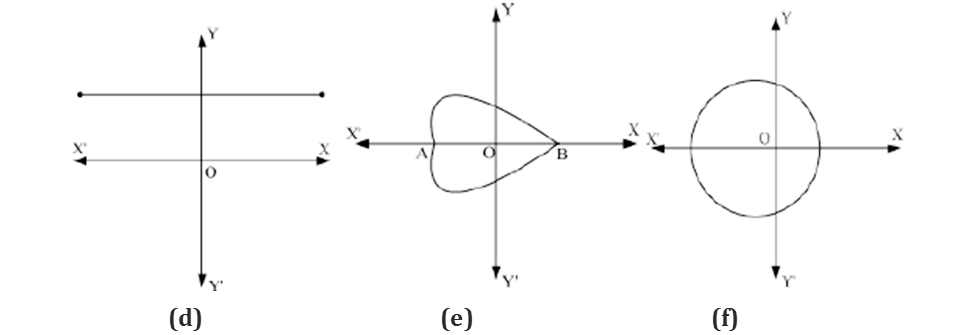
(d) The graph of the polynomial does not intersect the x-axis.
Hence, this polynomial has no zeroes.
(e) The graph intersects the x-axis at 2 distinct points.
Hence, the number of zeroes of this polynomial is 2.
(f) The graph intersects the x-axis at 2 distinct points.
Hence, the number of zeroes of this polynomial is 2.
(g) The graph of the polynomial does not intersect the x-axis.
Hence, this polynomial has no zeroes.
(h) The graph intersects the x-axis at only 1 point.
Hence, the number of zeroes of this polynomial is 1.
(i) The graph intersects the x-axis at only 1 point.
Hence, the number of zeroes of this polynomial is 1.
(j) The graph intersects the x-axis at 4 distinct points.
Hence, the number of zeroes of this polynomial is 4.
(k) The graph intersects the x-axis at 5 distinct points.
Hence, the number of zeroes of this polynomial is 5.
(l) The graph intersects the x-axis at 3 distinct points.
Hence, the number of zeroes of this polynomial is 3.
Geometrical Interpretation Of Zeros Of Polynomials
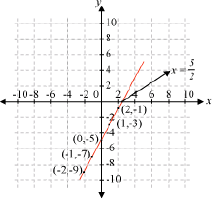
Let us consider a polynomial p(x) = 2x – 5. Its graph can be drawn as follows:
If we notice the above graph carefully, then we can see that the graph of the polynomial p(x) = 2x – 5 passes through the x-axis at a point .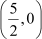
Do you know what is the value of the polynomial p(x) at the x-coordinate of this point? Let us find out how.
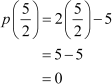
Thus,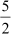 is a zero of the polynomial.
is a zero of the polynomial.
Thus, we can say that

Using the above statement, we can find out the zeroes of the polynomials. The method of finding zeroes can be easily understood with the help of the following example.
Let us find the zeroes of the polynomial p(x) = x2 – 4x + 3. The graph of this polynomial can be drawn as follows:
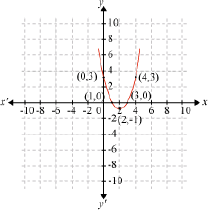
From the graph, we can see that the graph of the polynomial p(x) = x2 – 4x + 3 cuts the x- axis at two points respectively (1, 0) and (3, 0). Now, the x-coordinates of these points are 1 and 3 respectively. Thus, 1 and 3 are the zeroes of the given polynomial p(x) = x2 – 4x + 3.
In this way we can interpret the zeroes of the polynomial geometrically.
Let us discuss one more example based on geometrical interpretation of zeroes of a polynomial.
Example1: Find the zeroes of the polynomials whose graphs are shown below.
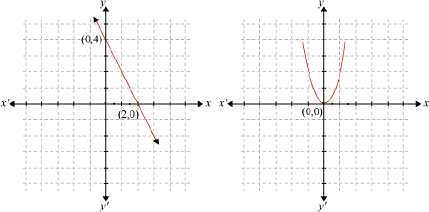

Solution:
(i) The graph of the polynomial intersects the x-axis at the point (2, 0).
The x coordinate of the point (2, 0) is 2.
Thus, 2 is a zero of the polynomial whose graph has been shown.
(ii) The graph of the polynomial intersects the x-axis at the point (0, 0).
The x co-ordinate of the point (0, 0) is 0. Thus, 0 is a zero of the polynomial.
(iii) The graph does not intersect the x-axis, so there is no zero of the polynomial whose graph has been shown.

 SonikaAnandAcademy
SonikaAnandAcademy
 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
