The Concept Of Arithmetic Progression
Any given series of numbers may exhibit some special properties. A sequence of numbers in arithmetic progression is one of these special series.
Let us look at the following example.
Example 1: Check whether the following sequences form an A.P. or not.
(i)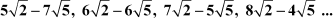
(ii)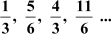
(iii)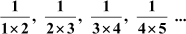
(iv) A list of prime numbers greater than 2
(v) A list of the squares of natural numbers
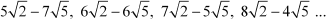
(i) The given sequence is
Difference between the second and the first term
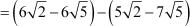
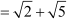
Difference between the third and the second term
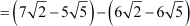
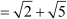
Difference between the fourth and the third term
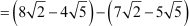
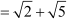
Since the difference between any two consecutive terms is a constant, the sequence is an arithmetic progression.
(ii) The given sequence is 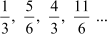
Difference between the second and the first term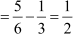
Difference between the third and the second term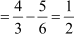
Difference between the fourth and the third term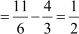
Since the difference between any two consecutive terms is a constant, the sequence is an arithmetic progression.
(iii) The given sequence is 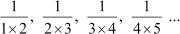
This sequence can be rewritten as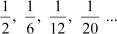
Difference between the second and the first term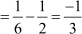
Difference between the third and the second term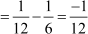
Difference between the fourth and the third term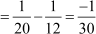
Since the difference between the consecutive terms is not a constant, the sequence is not an arithmetic progression.
(iv) The list of the prime numbers greater than 2 is: 3, 5, 7, 11 …
Difference between the second and the first term = 5 – 3 = 2
Difference between the third and the second term = 7 – 5 = 2
Difference between the fourth and the third term = 11 – 7 = 4
Since the difference between the consecutive terms is not a constant, the sequence is not an arithmetic progression.
(v) The list of the squares of natural numbers is: 12, 22, 32, 42 …
= 1, 4, 9, 16 …
Difference between the second and the first term = 4 – 1 = 3
Difference between the third and the second term = 9 – 4 = 5
Difference between the fourth and the third term = 16 – 9 = 7
Since the difference between the consecutive terms is not a constant, the sequence is not an arithmetic progression.
The Terminologies Related To Arithmetic Progressions
An arithmetic progression (A.P.) is a sequence in which the difference between any two consecutive terms is constant.
Now there are many common terms associated with an arithmetic progression, which one has to understand to solve any A.P. related problem.
Let us solve some more examples to understand this concept better.
Example 1: Find the common difference of the A.P.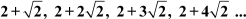
Also, state whether it is finite or infinite and write down its first term.
Solution:
The given A.P. is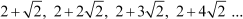
a1 = 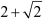
a2 = 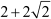
a3 = 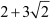
a4 =![]()
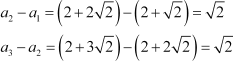
∴Common difference of the A.P. = 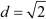
First term of the A.P. =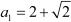
The given A.P. is infinite because its last term cannot be calculated.
Example 2: State whether the following statements are true or false.
(i) The sequence 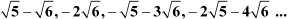 forms an A.P. with the first term as
forms an A.P. with the first term as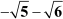 and the common difference as
and the common difference as 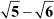 .
.
(ii) The common difference of the A.P. 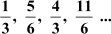 is .
is .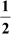
(iii) The nth term of an A.P. is given by 3n – 4. Its common difference is 4.
Solution:
(i) The given sequence is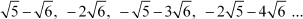
Difference between the first and the second term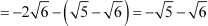
Difference between the second and the third term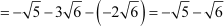
Difference between the third and the fourth term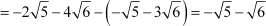
Since the difference between the consecutive terms of the sequence is constant, the given sequence is an A.P. with the first term as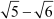 and the common difference as
and the common difference as 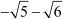 .
.
Thus, the statement is false.
(ii) The given A.P. is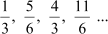
Common difference of the A.P. =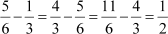
Thus, the statement is true.
(iii) It is given that the nth term of the A.P. is given by 3n – 4.
Thus, first term of the A.P. = a = 3 × 1 – 4 = 3 – 4 = –1
Second term of the A.P. = a2 = 3 × 2 – 4 = 6 – 4 = 2
Third term of the A.P. = a3 = 3 × 3 – 4 = 9 – 4 = 5
Fourth term of the A.P. = a4 = 3 × 4 – 4 = 12 – 4 = 8
Thus, common difference of the A.P. = 8 – 5 = 5 – 2 = 2 – (–1) = 3
Thus, the statement is false.
Missing Terms In Arithmetic Progressions
An arithmetic progression (A.P.) is a sequence in which the difference between any two consecutive terms is constant.
Now if we are given an A.P. 3, 6, 9, ?, 15 and asked to find the missing term, then how will we go about it?
Let us now solve some problems based on this concept.
Example 1: Find the missing terms in the following arithmetic progressions.
(i) 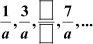
(ii) 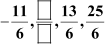
Solution:
(i) In the given A.P.,
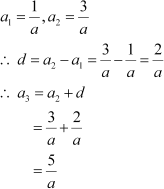
Thus, missing term, a3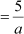
(ii) In the given A.P.,
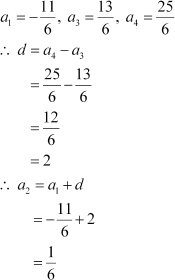
Thus, missing term, a2 =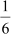
Example 2: Find the first two terms of an A.P. in which the third term is 10 and the common difference is 7.
Solution:
Here, d = 7 and a3 = 10
Hence, the value of a2 can be found by subtracting 7 from a3.
∴ a2 = 10 − 7 = 3
Similarly, the value of a1 can be found by subtracting 7 from a2.
∴ a1 = 3 − 7 = −4
Thus, the first two terms of the A.P. are –4 and 3.

 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
