- Books Name
- Online English tutor English Book
- Publication
- Online English tutor
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- English
Active voice/Passive voice
An action that requires an object to give a complete sense (transitive verb) can be expressed in two ways:
- Active voice
In active voice subject is active performer of the action.
Ex.
- The police caught the thief.
Here,
‘The police’ is the subject which performed the action
I.e.
‘caught the thief’
- Passive voice
In Passive voice subject is the receiver of the action or it is acted upon by the agent or the doer of the action.
Ex.
The thief was caught by the police.
Here,
The subject is the thief which is receiving the action done by the agent ‘the police’ rather than doing any action
Or
We can say that the subject is passive
i.e. not performing the action but being acted upon by the agent ‘the police’
So,
The sentence where the subject of the verb is passive is called Passive Voice.
Passive voice is used
Where the object is given more importance than the subject
Or
When the person or thing which is acted upon is given more importance than the performer of the action.
Ex.
Plastic bag has been banned by the government.
Or
Plastic bag has been banned.
Plastic bags are given more importance than the government (doer of the action)
Points to be remembered to convert active into passive voice
- Passive voice can be used only with transitive verb (which requires an object to give a complete sense)
Like,
1.Ravi hit. (No meaning as the question is what is hit by Ravi)
But,
Ravi hit the ball.
Here,
Ball is the object with which the sentence gives full meaning.
It is not used with intransitive verbs which have no object.
Like,
2.He is sleeping.
Here,
Sleeping is intransitive ie. It is making full sense without any object.
- ‘By’ is used with the agent
of the action.
- To be form of the verb is used.
I.e.
is/am/are/was/were/be/been
- Main verb is changed into Past Participle (III form)
- Tense remains unchanged only its form is changed.
Ex.
Active - She bought a bungalow.
(Past tense)
Passive-A bungalow was bought by her.
Past tense – was ( to be form)
Bought- past participle
‘By’ has been used with the agent of the action, her.
Ex.2
Active- Tom throws a party often. (Present tense, is )
Passive – A party is thrown by
Tom often. (Present tense, is )
- Well known and indefinite subjects are usually dropped or not mentioned as the agent.
Ex.
Active-Someone has broken the vase.
Passive – The vase has been broken. (‘Someone’ is dropped)
- In the case of two object in active voice, any object may be used as the subject of passive voice.
Ex.
Active - He gifted me a car.
Two objects – me, car
Passive- I was gifted a pen by him.
Subjective of me is used as subject.
Passive - A pen was gifted to me by him.
Pen is used as subject.
- Preposition must not be left with the verbs requiring it.
Ex.
Active - He put on the socks.
Passive- The socks were put on by him.
Structure of Active and Passive voice:
Active voice: Subject + Verb + Object
Passive voice: Object + Verb + Subject
Rules for changing Active voice to Passive voice:
- The places of the subject and the object are exchanged.
The subject become the agent (doer of action, introduced with ‘by’) and the object becomes new subject.
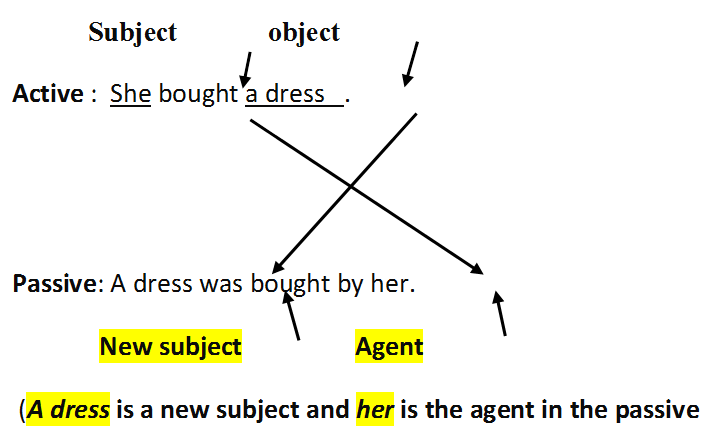
- Convert the main verb into its past participle or third form while converting from active to passive voice
- Change the tense of the auxiliary verbs according to the rules of passive voice.
- Tense of the verb containing be or been are not converted into passive.
I.e.
- Future continuous
- Present perfect continuous
- Past perfect continuous
- Future perfect continuous
Active and Passive Voice Rules for Present Simple Tense
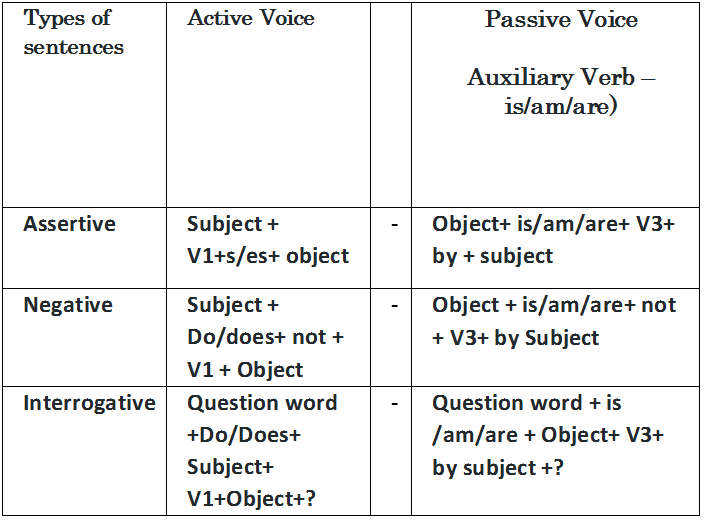
Example
Assertive
Active: The child keeps the ball.
Passive: The ball is kept by the child.
Negative
Active: The child doesn’t keep the ball.
Passive: The ball is not kept by the child.
Interrogative
Active: Does the child keep the ball?
Passive: Is the ball kept by the child?
Exercise
Active: She manages the house.
Passive: The house is managed by her.
Active: He seldom keeps quiet.
Passive: Quite is seldom kept by him.
Active: My father doesn’t scold me.
Passive: I am not scolded by my father.
Active and Passive Voice Rules for Past Simple Tense

Example
Assertive
Active: She managed the house.
Passive: The house was managed by her
Negative
Active: He didn’t care for his health.
Passive: His health was not cared for by the him.
interrogative
Active: My neighbours listened to the music in high volume.
Passive: The music was listened to by my neighbours in high volume.
Exercise
Active: Someone knocked at the door.
Passive: The door was knocked at by someone.
Or
The door was knocked at.
Active: They did not proclaim him king.
Passive: He was not proclaimed king by him.
Active: Why did he not purchased the book?
Passive: Why was the book not purchased by him?
Active: Where did she drop the key?
Passive: Where was the key dropped by her?
Active and Passive Voice Rules Future Indefinite Tense

Example
Assertive
Active: She will arrange the ceremony.
Passive: The ceremony will be arranged by her.
Negative
Active: Tom will not blame me .
Passive: I will not be blamed by him.
interrogative
Active: Why will they listen to the music in high volume?
Passive: Why will the music be listened to by them in high volume?
Exercise
Active: Sam will love the gift.
Passive: The gift will be loved by Sam.
Active: Will the court do the justice?
Passive: Will the justice be done by the court?
Active: Why will he claim the property?
Passive: Why will the property be claimed by him?
Active: Will she act upon my advice?
Passive: will my advice be acted upon by her?
Active and Passive Voice Rules for Present continuous tense.

Example
Assertive
Active: She is learning the guitar.
Passive: The guitar is being learned by her.
Negative
Active: They are not making noise.
Passive: Noise is not being made by them.
interrogative
Active: What is he asking for?
Passive: What is being asked by him?
Exercise
Active: The saint is blessing the child.
Passive: The child is being blessed by the saint.
Active: Is the dog chasing the cat?
Passive: Is the cat being chased by the dog?
Active: Why is he building the cottage outside?
Passive: Why the cottage is being build by him outside?
Active: Is she getting at you?
Passive: Are you being getting at by her?
Example
Assertive
Active: She will arrange the ceremony.
Passive: The ceremony will be arranged by her.
Negative
Active: Tom will not blame me.
Passive: I will not be blamed by him.
interrogative
Active: Why will they listen to the music in high volume?
Passive: Why will the music be listened to by them in high volume?
Exercise
Active: Sam will love the gift.
Passive: The gift will be loved by Sam.
Active: Will the court do the justice?
Passive: Will the justice be done by the court?
Active: Why will he claim the property?
Passive: Why will the property be claimed by him?
Active: Will she act upon my advice?
Passive: Will my advice be acted upon by her?
Active and Passive Voice Rules for Past continuous Tense

Example
Assertive
Active: She was teaching the kids.
Passive: Were the kids being taught by her.
Negative
Active: They were not speaking to him.
Passive: He was not being spoken to by them.
Interrogative
Active: Why was he withdrawing money?
Passive: Why the money was being withdrawn by him?
Exercise
Active: The thief was begging the judge to forgive him.
Passive: The judge was being begged by the thief to forgive him.
Active: Was the boy riding the bicycle?
Passive: Was the bicycle being rode by the boy?
Active: Why was he not returning the book?
Passive: Why the book was not being returned by him?
Active and Passive Voice Rules for Present Perfect Tense.

Example
Assertive
Active: She has missed the train.
Passive: The train has been missed by her.
Negative
Active: We have not invested the money in that project.
Passive: The money has not been invested by us in that project.
interrogative
Active: Why has he wasted the time?
Passive: Why the time has been wasted by him?
Exercise
Active: The owner has suffered a great loss.
Passive: A great loss has been suffered by the owner.
Active: Has the lady gone through many challenges?
Passive: Have many challenges been gone through by the lady?
Active: Why has he not put on that coat?
Passive: Why has that coat been not put on by him?
Active and Passive Voice Rules for Past Perfect Tense

Example
Assertive
Active: The lorry had dashed the car.
Passive: The car had been dashed by the lorry.
Negative
Active: The police had not solved the case.
Passive: The case had not been solved by the police.
interrogative
Active: Why had the management asked him to resign?
Passive: Why had he asked by the management to resign?
Exercise
Active: His conduct had surprised me.
Passive: I had been surprised with his conduct.
Active: Had the incident spoiled the party?
Passive: Had the party been spoilt by that incident?
Active: Why had she compared me with that girl?
Passive: Why had I been compared with that girl by her?
Active and Passive Voice Rules for Future Perfect Tense

Example
Assertive
Active: The teacher will have revealed the marks.
Passive: The marks will have been revealed by the teacher.
Negative
Active: He will have not caught the train.
Passive: The train will have not been caught by him.
interrogative
Active: Who will have called you today?
Passive: By whom will you have been called today?
Exercise
Active: I will have disposed of my old car by next year.
Passive: My car will have been disposed of by me next year .
Active: Will they solve the matter before father comes?
Passive: Will the matter have been solved by them before father comes?
Active: When will you have done this task?
Passive: When this task will have been done by you?
Active and Passive Voice Rules for Future Perfect Tense
Structure 1
Assertive- subject +modal verb + be + past participle
Negative- subject +Modal verb +not+ be + past participle
Interrogative- Question words+Modal verb + subject+ be + past participle
Example
Assertive
Active: He can speak French.
Passive: French can be spoken by him.
Negative
Active: The police could not get the clue.
Passive: The clue couldn’t be got by the police.
Interrogative
Active: When should we greet him?
Passive: When should he be greeted?
Structure 2
Assertive- subject +modal verb +have + been + past participle
Negative- subject +Modal verb+ have +not+ been + past participle
Interrogative- Question word +Modal verb+ subject + have+ been+ past participle.
Example
Assertive
Active: The boss must have fired him.
Passive: He must have been fired by the boss.
Negative
Active: The police could not have lost the evidence.
Passive: The evidence could have not been lost. (by the police)
interrogative
Active: Should we have informed him?
Passive: Should he has been informed by us?
Exercise
Active: She can drive a car.
Passive: A car can be driven by her.
Active: We ought to do our duty
Passive: Our duty is ought to be done by us.
Active: He might visit us.
Passive: We might be visited by him?
Active and Passive Voice Rules for Infinitives
Structure:
Sub + helping Verb +To+ be+ V3
Example
Assertive
Active: You will have to inform him.
Passive: He will have to be informed.
Negative
Active: There are no house to let.
Passive: There are no house to be let.
interrogative
Active: Is it the time to do this work?
Passive: Is it the time this work to be done?
Exercise
Active: A pen is to write with.
Passive: A pen is to be written with.
Active: We ought to do our duty.
Passive: Duty is ought to be done by us.
Active: He wished to write a poem.
Passive: A poem is wished to be written by him.
Active and Passive Voice Rules for preposition other than ‘by'.
In some special cases with main verb ‘by' is dropped and a preposition is used only.
- Use of preposition ‘At’ instead of ‘by’ with the verbs - surprised, annoyed, shocked, alarmed, disappointed, displeased, distressed, astonished, laughed
- Use of preposition ‘to’ instead of ‘by’ with the verbs - married, known, obliged etc.
- Use of preposition ‘with’ instead of ‘by’ with the verbs - pleased, disgusted, impressed, charmed, etc.
- Use preposition ‘in’ instead of ‘by’ with the verbs - interested, consisted, absorbed, contained, etc.’
Example:
Assertive
Active: She knows me.
Passive: I am known to her.
Negative
Active: His remarks don’t offend me.
Passive: I am not offended with his remarks.
interrogative
Active: Does his success satisfy his parents?
Passive: Do his parents satisfied with his success.
Exercise
Active: Sam's performance please the boss.
Passive: The boss is pleased with Sam's performance.
Active: His poor condition surprised me.
Passive: I got surprised with his poor condition.
Active: He wished to write a poem.
Passive: A poem is wished to be written by him.

 Online English tutor
Online English tutor
