- Books Name
- Chemistry Class 10 NCERT based
- Publication
- Grow Career Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
Chemical Properties
Combustion Reactions
Combustion means burning of carbon or carbon-containing compounds in the presence of air or oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, heat and light.
Flame Characteristics
Saturated hydrocarbons give clean flame while unsaturated hydrocarbons give smoky flame. In the presence of limited oxygen, even saturated hydrocarbons give smoky flame.
Oxidation
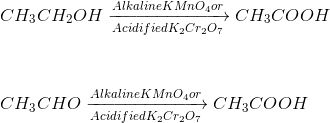
Addition
The reactions in which two molecules react to form a single product having all the atoms of the combining molecules are called addition reactions.
The hydrogenation reaction is an example of the addition reaction. In this reaction, hydrogen is added to a double bond or a triple bond in the presence of a catalyst like nickel, palladium or platinum.
![]()
Substitution
The reaction in which an atom or group of atoms in a molecule is replaced or substituted by different atoms or group of atoms is called substitution reaction. In alkanes, hydrogen atoms are replaced by other elements.
CH4+Cl2+Sunlight → CH3Cl+HCl

 PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication

