- Books Name
- Chemistry Book based on NCERT
- Publication
- PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
Chemical properties of Metals
(i) Reaction with air :-
All metals combine with oxygen to form metal oxide .
Metal +
For example,
2
4Al + 3
- Sodium and potassium react so vigorously that they catch fire in open so they are kept immersed in kerosence
- Surfaces of Mg , Al, Zn pb are covered with a thin layer of oxide whish prevent them from further oxidation. Anodizing is a process of forming a tick oxide layer of aluminium.
- Iron does not burn on heating but iron filling burn vigorously.
- Copper does not burn but the hot metal is coated with a black coloured layer of copper (ii) oxide
- Silver and gold do not react with oxygen even at high temperatures.
Amphoteric oxide
Example ;
A
A
(SODIUM ALUMINATE )
Most metal oxides are insoluble in water but some of these dissolve in water to form alkalis. Sodium oxide and potassium oxide dissolved in water to produce alkali.
N
(ii) Reactions of metals with water:-
Metal+ water
Metal oxide + water
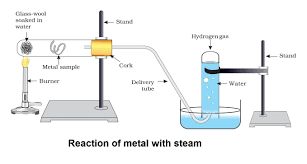
Metals like potassium and sodium react violenty with cold water.
Na + 2
The reaction of calcium of water is less violent
Ca + 2
Magnesium react with hot water to form magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen.
Mg + 2
Metals like aluminium iron and zinc do not react with cold or hot water. But they react with steam to form metal oxide and hydrogen.
2 Al + 3
3 Fe + 4
Metal such as lead ,copper, silver and gold do not react with water at all.
(ii) Reaction of metals with acids.
Metal + Dilute acid
Copper and silver do not react wit dil acids.
For example
Fe + 2HCl
Mg + 2HCl
Zn + 2HCl
(iii) Reaction of metals with solution of other Metal salts ;
Metal A+ Salts solution B
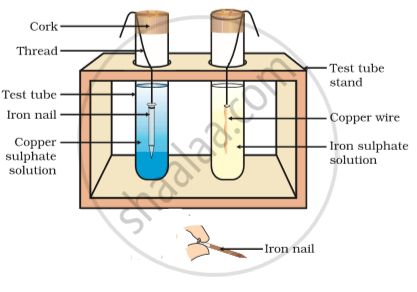
Reaction of metals with salt solutions.
More reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their compounds in solution form.
Fe + CuS
Fe displaces Cu because Fe is more reactive metals than Cu .
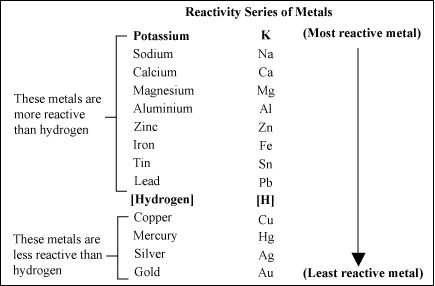
REACTIVITY SERIELS ;
The reactivity series is a list of metals arranged in the order of their decreasing activities.

 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
 PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
