- Books Name
- Chemistry Class 10 NCERT based
- Publication
- Grow Career Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
Metals: Physical properties of metals, chemical properties of metals and non-metal oxide.
Metals are the elements that conduct heat and electricity and are malleable and ductile. Examples are Iron (Fe), Aluminium (Al), Silver (Ag), Copper (Cu), Gold (Au), Platinum (Pt), Lead (Pb), Potassium (K), Sodium (Na), Calcium (Ca) and Magnesium (Mg) etc.
Metals are the elements which form positive ions by losing electrons. Thus, metals are known as Electropositive Elements.
How Do Metals and Nonmetals React
Metals lose valence electron(s) and form cations.
Non-metals gain those electrons in their valence shell and form anions.
The cation and the anion are attracted to each other by strong electrostatic force, thus forming an ionic bond.
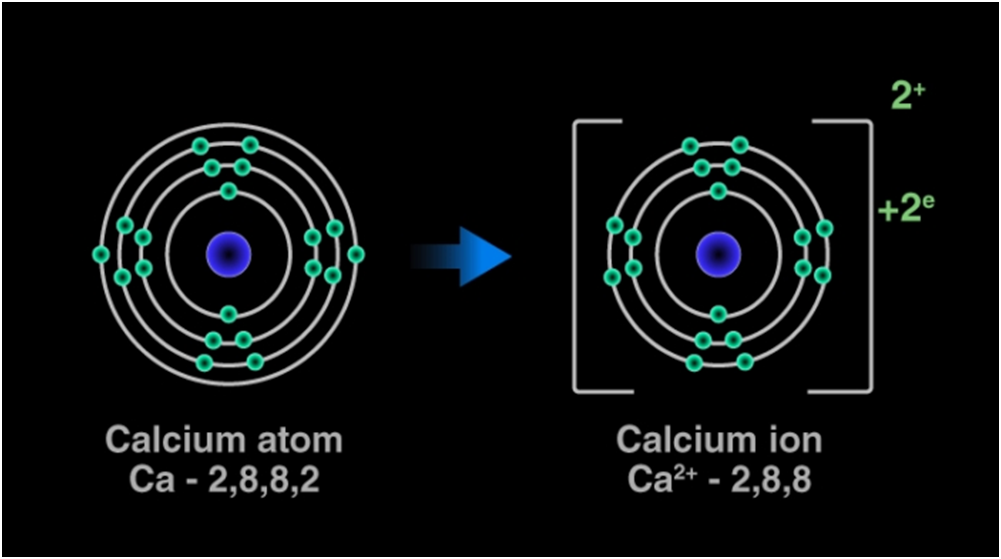
For example: In calcium chloride, the ionic bond is formed by opposite charged calcium and chloride ions.
Calcium atom loses 2 electrons and attains the electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas (Ar). By doing so, it gains a net charge of +2.
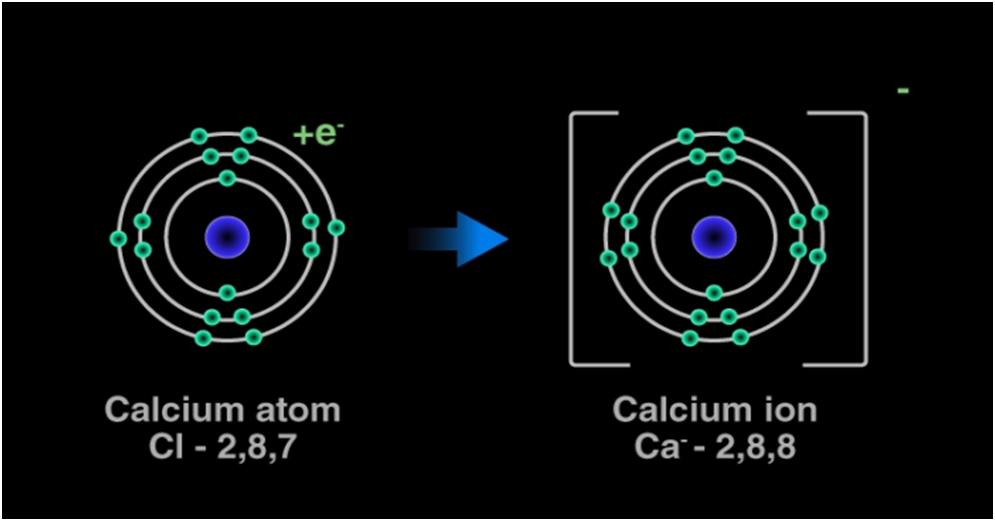
The two Chlorine atoms take one electron each, thus gaining a charge of -1 (each) and attain the electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas (Ar).
Physical Properties of Metals
- Hardness: Most of the metals are hard, except alkali metals, such as sodium, potassium, lithium, etc. are very soft metals. These can be cut by using a knife.
- Conduction: Metals are a good conductor of heat and electricity. This is the cause that electric wires are made of metals like copper and aluminium.
- Melting and Boiling Point: :Metals have generally high melting and boiling points. (Except sodium and potassium metals which have low melting and boiling point.)
- Strength: Most of the metals are strong and have high tensile strength. Because of this, big structures are made using metals, such as copper (Cu) and iron (Fe). (Except Sodium (Na) and potassium (K) which are soft metals).
- State: Metals are solid at room temperature except for mercury (Hg).
- Malleability: Metals are malleable. This means metals can be beaten into a thin sheet. Because of this property, iron is used in making big ships.
- Ductility: Metals are ductile. This means metals can be drawn into thin wire. Because of this property, a wire is made of metals.
- Density: Most of the metals have a high density.
- Colour: Most of the metals are grey in colour. But gold and copper are exceptions.
Non-Metals: Physical Properties of non-metals, chemical properties of non-metals, non¬metal oxides, Reaction of metal and Non-metal, Ionic bonds and formation of an ionic bond. Non-metals are the elements that do not conduct electricity and are neither malleable nor ductile.
Examples: Carbon (C), Sulphur (S), Phosphorous (P), Silicon (Si), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), Neon (Ne) and Argon (Ar) etc.
Non-metals are the elements which form negative ions by gaining an electron. Thus, non¬metals are also known as Electronegative Elements.
Physical properties of non-metals
- Hardness: Non-metals are not hard rather they are generally soft. But the diamond is an exception; it is the hardest naturally occurring substance.
- State: Non-metals may be solid, liquid or gas.
- Lustre: Non-metals have a dull appearance. Diamond and iodine are exceptions.
- Sonority: Non-metals are not sonorous, i.e., they do not produce a typical sound on being hit.
- Conduction: Non-metals are a bad conductor of heat and electricity. Graphite which is allotrope of carbon is a good conductor of electricity and is an exception.
- Malleability and ductility: Non-metals are brittle.
- Melting and boiling point: Non-metals have generally low melting and boiling points.
- Density: Most of the non-metals have low density.
- Colour: Non-metals are in many colours.
Carbon in the form of graphite is non-metal which conduct electricity.
Iodine is non-metal which is lustrous having a shining surface.
Carbon in the form of diamond is a non-metal which is extremely hard.
Diamond is a non-metal which has a very high melting point and boiling point.

 PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
