- Books Name
- Chemistry Class 10 NCERT based
- Publication
- Grow Career Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
Chemical Reactions and Equations: Balanced and unbalanced chemical equations and balancing of chemical equations.Consider the following situations of daily life and think what happens when , In all the above situations, the nature and the identity of the initial substance have somewhat changed. We have already learnt about physical and chemical changes of matter in our previous classes. Whenever a chemical change occurs, we can say that a chemical reaction has taken place
- Milk is left at room temperature during summers.
- An iron tawa/pan/nail is left exposed to humid atmosphere.
- Grapes get fermented.
- Food is cooked.
- Food gets digested in our body.
- We respire.
Chemical Reaction: The transformation of chemical substance into another chemical substance is known as Chemical Reaction. For example: Rusting of iron, the setting of milk into curd, digestion of food, respiration, etc.
Example: The burning of magnesium in the air to form magnesium oxide is an example of a chemical reaction.
2Mg(s) + O2(g) △→ 2MgO(s)
Before burning in air, the magnesium ribbon is cleaned by rubbing with sandpaper . This is done to remove the protective layer of basic magnesium carbonate from the surface of the magnesium ribbon. Reactant: Substances which take part in a chemical reaction are called reactants. Example: Mg and O2.
Product: New substance formed after a chemical reaction is called a product.
Example: MgO.
Chemical Reaction's Characteristics
1. Change in temperature: The chemical reaction between quick lime water to form slaked lime is characterized by a change in temperature (which is a rise in temperature).
2. Change in state of substance: The combustion reaction of candle wax is characterised by a change in state from solid to liquid and gas (because the wax is a solid, water formed by the combustion of wax is a liquid at room temperature.
3. Formation of precipitate: The chemical reaction between sulphuric acid and barium chloride solution is characterised by the formation of a white precipitate of barium sulphate.
BaCl2(aq) + H2SO4(aq) ----→ BaSO4(s) (ppt) + 2HCl(aq)
4. Evolution of gas: The chemical reaction between zinc and dilute sulphuric acid is characterised by the evolution of hydrogen gas.
Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Chemical Equations - The chemical equation of the reaction is the representation of a chemical change in terms of symbols and formulae of the reactants and products.
Example: Potassium Hydrochloric Potassium Manganese Water Chlorine permanganate acid → chloride chloride
(a) Balanced Chemical Equation: A balanced chemical equation has the number of atoms of each element equal on both sides.
Example: Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
In this equation, numbers of zinc, hydrogen and sulphate are equal on both sides, so it is a Balanced Chemical Equation.
(b) Unbalanced Chemical Equation: If the number of atoms of each element in reactants is not equal to the number of atoms of each element present in the product, then the chemical equation is called Unbalanced Chemical Equation.
Example: Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
Balancing a Chemical Equation: To balance the given or any chemical equation, follow these steps:
Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
Table as shown here.
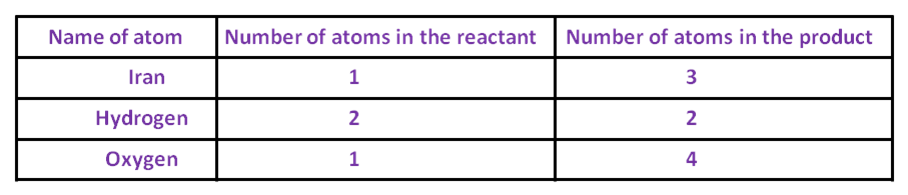
Fe + 4 × H2O → Fe3O4 + H2To balance the oxygen, one needs to multiply the oxygen on the LHS by 4, so that, the number of oxygen atoms becomes equal on both sides.
Now, the number of hydrogen atoms becomes 8 on the LHS, which is more than that on the RHS. To balance it, one needs to multiply the hydrogen on the RHS by 4.
Fe + 4 × H2O → Fe3O4 + 4 × H2
After that, the number of oxygen and hydrogen atoms becomes equal on both sides. The number of iron is one on the LHS, while it is three on the RHS. To balance it, multiply the iron on the LHS by 3.
3 × Fe + 4 × H2O → Fe3O4 + 4 × H2
Now the number of atoms of each element becomes equal on both sides. Thus, this equation becomes a balanced equation.
After balancing, the above equation can be written as follows:
3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2.
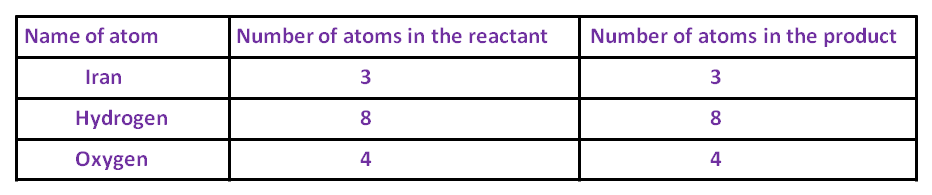

 PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
